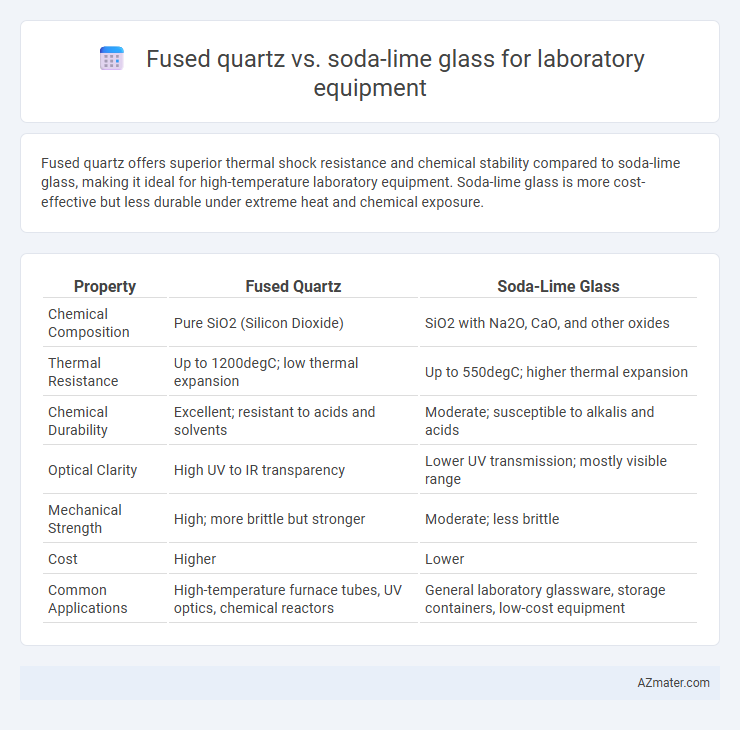
Fused quartz offers superior thermal shock resistance and chemical stability compared to soda-lime glass, making it ideal for high-temperature laboratory equipment. Soda-lime glass is more cost-effective but less durable under extreme heat and chemical exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fused Quartz | Soda-Lime Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Pure SiO2 (Silicon Dioxide) | SiO2 with Na2O, CaO, and other oxides |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 1200degC; low thermal expansion | Up to 550degC; higher thermal expansion |
| Chemical Durability | Excellent; resistant to acids and solvents | Moderate; susceptible to alkalis and acids |
| Optical Clarity | High UV to IR transparency | Lower UV transmission; mostly visible range |
| Mechanical Strength | High; more brittle but stronger | Moderate; less brittle |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Applications | High-temperature furnace tubes, UV optics, chemical reactors | General laboratory glassware, storage containers, low-cost equipment |
Introduction to Laboratory Glassware Materials
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal shock resistance and chemical inertness, making it ideal for high-temperature and corrosive laboratory applications. Soda-lime glass is more affordable and widely used for general-purpose lab equipment but lacks the durability and purity of fused quartz. Choosing between these materials depends on the specific laboratory requirements for temperature tolerance, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness.
Composition of Fused Quartz and Soda-Lime Glass
Fused quartz consists primarily of pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) with minimal impurities, offering excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance ideal for laboratory equipment. Soda-lime glass is composed mainly of silicon dioxide (about 70-75%), sodium oxide (Na2O), and calcium oxide (CaO), providing lower cost but reduced thermal and chemical durability compared to fused quartz. The high purity and unique molecular structure of fused quartz result in superior performance for high-precision and high-temperature applications in labs.
Thermal Resistance and Stability Comparison
Fused quartz exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to soda-lime glass, withstanding temperatures up to 1200degC without deformation, while soda-lime glass typically tolerates only around 600degC. The thermal stability of fused quartz minimizes expansion and contraction during rapid temperature changes, reducing the risk of cracking and ensuring precise measurements in laboratory settings. In contrast, soda-lime glass has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion, making it more susceptible to thermal shock and less reliable for high-temperature applications.
Chemical Durability and Reactivity
Fused quartz exhibits exceptional chemical durability due to its high purity and resistance to most acids, alkalis, and solvents, making it ideal for laboratory equipment exposed to aggressive chemicals. Soda-lime glass, while cost-effective, is more susceptible to chemical attack, especially from alkaline solutions, leading to potential surface degradation and contamination. The superior inertness of fused quartz enhances the longevity and reliability of laboratory apparatus, ensuring minimal reactivity and high resistance in demanding chemical environments.
Optical Properties: Transparency and Clarity
Fused quartz exhibits superior optical properties compared to soda-lime glass, offering higher transparency and exceptional clarity across a broad wavelength range from ultraviolet to infrared. Its low birefringence and minimal light scattering make it ideal for precise optical measurements and applications requiring high purity light transmission. Soda-lime glass, while cost-effective and widely used, has limited UV transparency and greater light distortion, reducing its suitability for advanced laboratory optical equipment.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Fused quartz exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to soda-lime glass, with higher resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress, making it ideal for high-precision laboratory equipment. Its durability extends to chemical inertness and sustained performance under extreme temperature variations, unlike soda-lime glass which often suffers from brittleness and lower thermal tolerance. Laboratories requiring long-term reliability and robustness frequently select fused quartz for critical applications where both strength and resistance to environmental factors are paramount.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Fused quartz offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability for laboratory equipment but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to soda-lime glass, which is more affordable and widely available. Soda-lime glass dominates the market due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing, making it a common choice for standard labware. Availability of fused quartz is limited and often requires specialized suppliers, whereas soda-lime glass is readily stocked by most laboratory glassware distributors.
Applications in Laboratory Settings
Fused quartz offers superior thermal shock resistance and high chemical purity, making it ideal for high-temperature applications and precise chemical analyses in laboratory equipment. Soda-lime glass, while more cost-effective and widely used, is suitable for general-purpose containers and apparatus where extreme heat resistance and chemical inertness are not critical. Laboratories requiring durability under rapid temperature changes and minimal contamination prefer fused quartz for specialized tasks like spectroscopy and high-temperature reactions.
Safety and Handling Considerations
Fused quartz offers superior thermal shock resistance and higher chemical inertness compared to soda-lime glass, reducing the risk of breakage and contamination during laboratory procedures. Its enhanced durability ensures safer handling under extreme temperature changes, whereas soda-lime glass is more prone to cracking and weaker against corrosive chemicals. Choosing fused quartz can significantly improve laboratory safety by minimizing hazards related to glass failure and chemical interactions.
Choosing the Right Material for Specific Laboratory Needs
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal resistance up to 1200degC and superior chemical durability, making it ideal for high-temperature reactions and corrosive environments in laboratory settings. Soda-lime glass, while more affordable and easier to fabricate, has limited thermal stability and can withstand temperatures only up to approximately 500degC, suitable for routine laboratory procedures and less aggressive chemical exposure. Selecting between fused quartz and soda-lime glass depends on the specific requirements of temperature tolerance, chemical resistance, and budget constraints in laboratory applications.
Infographic: Fused quartz vs Soda-lime glass for Laboratory equipment
 azmater.com
azmater.com