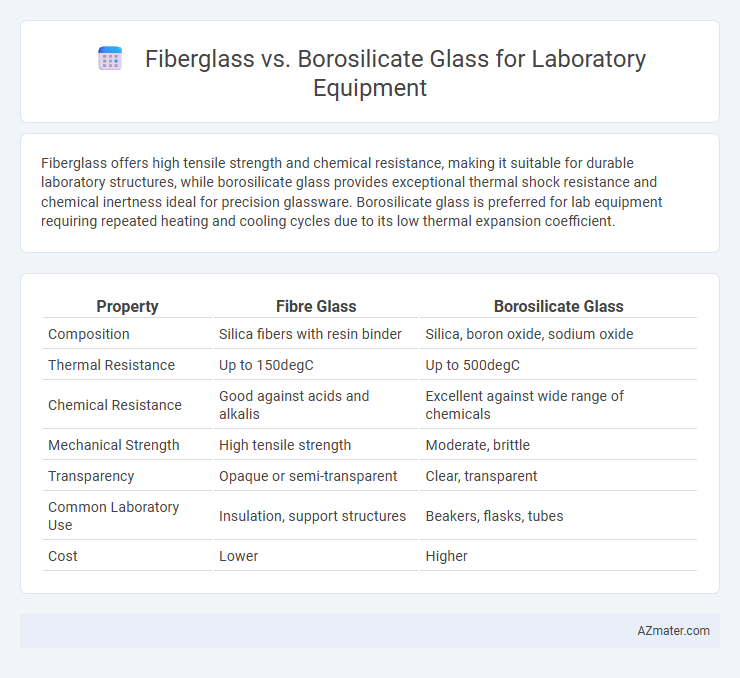
Fiberglass offers high tensile strength and chemical resistance, making it suitable for durable laboratory structures, while borosilicate glass provides exceptional thermal shock resistance and chemical inertness ideal for precision glassware. Borosilicate glass is preferred for lab equipment requiring repeated heating and cooling cycles due to its low thermal expansion coefficient.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fibre Glass | Borosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica fibers with resin binder | Silica, boron oxide, sodium oxide |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 150degC | Up to 500degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and alkalis | Excellent against wide range of chemicals |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate, brittle |
| Transparency | Opaque or semi-transparent | Clear, transparent |
| Common Laboratory Use | Insulation, support structures | Beakers, flasks, tubes |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Laboratory Glass Materials
Laboratory glass materials like fiberglass and borosilicate glass serve distinct roles based on their chemical and thermal properties. Borosilicate glass is renowned for its high resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making it ideal for precise laboratory applications requiring durability and clarity. Fiberglass, composed of fine glass fibers, offers excellent mechanical strength and insulation but lacks the chemical resistance and thermal stability necessary for most laboratory glassware.
What is Fibre Glass?
Fibre glass is a composite material made from fine fibers of glass woven into a fabric and reinforced with a resin matrix, offering excellent strength-to-weight ratio and chemical resistance for laboratory equipment. Unlike borosilicate glass, fibre glass is non-transparent and highly impact-resistant, making it suitable for protective gear and structural components rather than directly handling chemicals or high-temperature reactions. Its durability and resistance to thermal shock enhance the safety and longevity of lab infrastructure where mechanical strength is prioritized over optical clarity.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass composed primarily of silica and boron trioxide, known for its exceptional thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for laboratory equipment. Unlike fiberglass, which consists of fine glass fibers used mainly for insulation or reinforcement, borosilicate glass maintains structural integrity under rapid temperature changes and exposure to corrosive substances. This makes borosilicate glass the preferred choice for labware such as beakers, test tubes, and flasks, where precision and safety are critical.
Chemical Resistance: Fibre Glass vs Borosilicate Glass
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to fibre glass, with high durability against acids, bases, and solvents commonly used in laboratories. Fibre glass, while strong and lightweight, can degrade or leach fibers when exposed to harsh chemicals, limiting its use in certain lab environments. Therefore, borosilicate glass remains the preferred choice for laboratory equipment requiring reliable resistance to chemical corrosion and thermal shock.
Thermal Stability Comparison
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior thermal stability compared to fiberglass, with a low thermal expansion coefficient around 3.3 x 10^-6 /degC, enabling it to withstand rapid temperature changes up to 500degC without cracking. Fiberglass, primarily composed of silica and other minerals, has a higher thermal expansion and is prone to deformation or damage when exposed to extreme thermal fluctuations. Laboratory equipment made from borosilicate glass is preferred for precise thermal applications due to its resistance to thermal shock and chemical inertness.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Borosilicate glass exhibits higher mechanical strength and superior resistance to thermal shock compared to fiberglass, making it ideal for laboratory equipment subjected to rapid temperature changes. Fiberglass offers excellent flexibility and impact resistance but is more prone to degradation under prolonged chemical exposure and high temperatures. The durability of borosilicate glass ensures longevity in harsh laboratory environments, whereas fiberglass may require more frequent replacement due to wear and chemical damage.
Transparency and Optical Clarity
Borosilicate glass offers superior transparency and optical clarity compared to fiberglass, making it ideal for laboratory equipment requiring precise visual observation. The high-quality silica content in borosilicate glass ensures minimal distortion and excellent light transmission, essential for accurate measurements and reactions. Fiberglass, while durable and chemically resistant, has a fibrous structure that scatters light and reduces optical clarity, limiting its use in applications where clear visibility is critical.
Cost and Availability
Fiberglass laboratory equipment offers a cost-effective solution due to its lower production expenses and widespread availability, making it accessible for general laboratory use. Borosilicate glass, while more expensive, provides superior thermal and chemical resistance, often justifying its higher cost in precision and high-temperature applications. Availability of borosilicate glass tends to be more limited compared to fiberglass, which can be mass-produced and supplied at a larger scale with consistent quality.
Typical Applications in Laboratories
Fibre glass is commonly used in laboratory equipment requiring lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials such as fume hoods, protective enclosures, and chemical storage tanks. Borosilicate glass is preferred for laboratory glassware like beakers, test tubes, and condensers due to its excellent thermal resistance, chemical durability, and ability to withstand rapid temperature changes. While fibre glass is ideal for structural and protective applications, borosilicate glass excels in precise chemical reactions and heating processes.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Lab Needs
Fibre glass offers excellent thermal insulation and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for protective lab equipment and storage containers, while borosilicate glass provides superior chemical resistance and thermal shock durability, ideal for precision glassware like beakers and flasks. Borosilicate's low thermal expansion coefficient (approximately 3.3 x 10^-6 /degC) ensures minimal risk of cracking under rapid temperature changes, a critical factor in most laboratory procedures. Choosing between fibre glass and borosilicate glass hinges on the specific application requirements, balancing factors such as chemical compatibility, temperature tolerance, and mechanical strength for optimized lab performance.
Infographic: Fibre glass vs Borosilicate glass for Laboratory equipment
 azmater.com
azmater.com