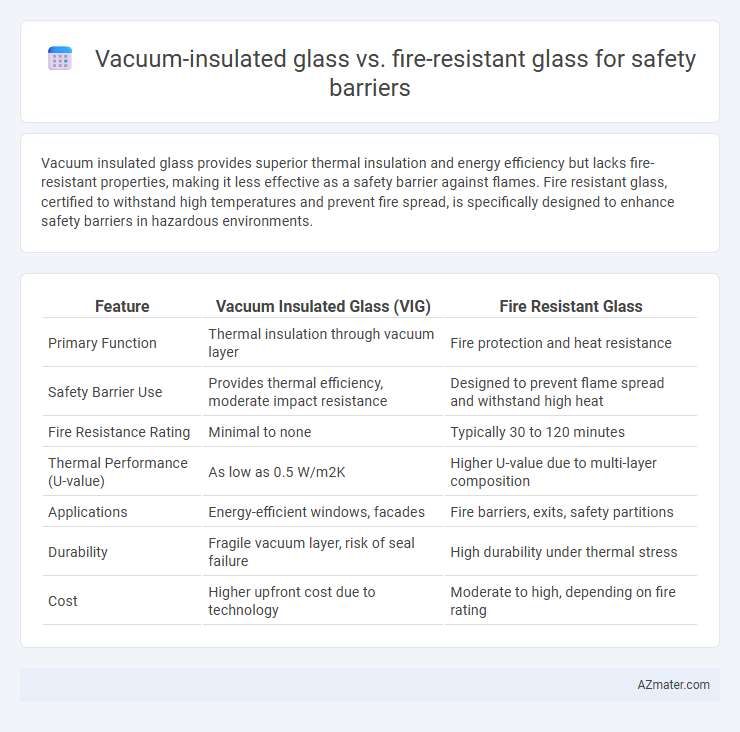
Vacuum insulated glass provides superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency but lacks fire-resistant properties, making it less effective as a safety barrier against flames. Fire resistant glass, certified to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread, is specifically designed to enhance safety barriers in hazardous environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) | Fire Resistant Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Thermal insulation through vacuum layer | Fire protection and heat resistance |
| Safety Barrier Use | Provides thermal efficiency, moderate impact resistance | Designed to prevent flame spread and withstand high heat |
| Fire Resistance Rating | Minimal to none | Typically 30 to 120 minutes |
| Thermal Performance (U-value) | As low as 0.5 W/m2K | Higher U-value due to multi-layer composition |
| Applications | Energy-efficient windows, facades | Fire barriers, exits, safety partitions |
| Durability | Fragile vacuum layer, risk of seal failure | High durability under thermal stress |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost due to technology | Moderate to high, depending on fire rating |
Introduction to Safety Barrier Glass Types
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation by eliminating heat transfer through a vacuum space, making it ideal for energy-efficient safety barriers. Fire resistant glass is engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames and smoke, enhancing safety in fire-prone environments. Selecting the appropriate safety barrier glass depends on specific performance requirements such as thermal efficiency or fire resistance in building design.
What is Vacuum Insulated Glass?
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum space, significantly reducing thermal transfer and enhancing insulation properties. This technology offers superior energy efficiency and sound insulation compared to conventional glass types, making it ideal for safety barriers requiring both visibility and minimal heat loss. While VIG provides excellent thermal performance, fire resistant glass is specifically engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent flame spread, prioritizing fire safety over insulation.
What is Fire Resistant Glass?
Fire resistant glass is specially engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames and smoke, making it essential for safety barriers in fire-prone areas. Unlike vacuum insulated glass, which prioritizes thermal insulation and energy efficiency, fire resistant glass maintains its integrity during fire exposure, providing critical time for evacuation and minimizing structural damage. This type of glass often incorporates multiple layers with intumescent interlayers or ceramic elements to achieve fire ratings ranging from 20 minutes to several hours.
Key Differences Between Vacuum Insulated and Fire Resistant Glass
Vacuum insulated glass consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum, providing exceptional thermal insulation but limited fire resistance, primarily used for energy efficiency and noise reduction. Fire resistant glass is specially designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames and smoke, making it suitable for safety barriers in fire-prone areas with specific fire rating standards such as UL 9, BS 476, or EN 13501. Key differences include vacuum insulated glass's focus on thermal performance and airtightness, while fire resistant glass prioritizes structural integrity and visibility during fire events.
Safety Performance: Vacuum Insulated Glass
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal insulation while maintaining robust structural integrity, making it an effective safety barrier in environments requiring energy efficiency and impact resistance. Its unique vacuum layer minimizes heat transfer, reducing the risk of thermal stress and glass breakage under rapid temperature changes compared to conventional fire-resistant glass. Although fire-resistant glass excels in fire containment, VIG provides enhanced safety performance in scenarios demanding durability against mechanical forces and extreme thermal variations.
Safety Performance: Fire Resistant Glass
Fire resistant glass offers superior safety performance for barriers by effectively preventing the spread of flames, smoke, and heat during fire incidents. Its specialized construction includes intumescent layers that expand when exposed to high temperatures, maintaining the barrier's integrity for extended periods and enabling safe evacuation routes. Vacuum insulated glass, while excellent for thermal insulation, lacks the fire-resistant properties necessary for active fire protection in safety barriers.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities Comparison
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation by minimizing heat transfer through the evacuated space between glass panes, significantly reducing energy loss compared to traditional fire resistant glass. Fire resistant glass, while designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread, typically has higher thermal conductivity, leading to less effective insulation under normal conditions. For safety barriers requiring both fire resistance and energy efficiency, vacuum insulated glass provides enhanced thermal performance but may need to be combined with fire resistant treatments to meet fire safety standards.
Fire Protection and Resistance Analysis
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation but lacks inherent fire resistance, making it less effective as a safety barrier against high-temperature exposure. Fire resistant glass is specifically engineered to withstand extreme heat and prevent fire spread by maintaining structural integrity and offering up to 120 minutes of fire resistance, depending on its rating. For safety barriers requiring fire protection, fire resistant glass provides significantly better performance in containment and prevention of heat transfer during fire incidents.
Applications in Safety Barriers
Vacuum insulated glass enhances safety barriers by offering superior thermal insulation and reducing heat transfer, making it ideal for environments requiring temperature control and energy efficiency. Fire resistant glass in safety barriers provides critical protection by withstanding high temperatures and preventing the spread of flames and smoke, essential in fire-prone areas such as stairwells and emergency exits. Both types of glass improve occupant safety but serve distinct roles: vacuum insulated glass excels in thermal management, while fire resistant glass focuses on fire containment and structural integrity.
Choosing the Right Glass for Enhanced Safety
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and soundproofing, making it ideal for safety barriers where energy efficiency and noise reduction are priorities. Fire resistant glass is engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent flame penetration, ensuring enhanced protection in fire-prone environments. Selecting the appropriate glass depends on specific safety requirements, such as thermal insulation needs versus fire resistance standards mandated by building codes.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Fire resistant glass for Safety barrier
 azmater.com
azmater.com