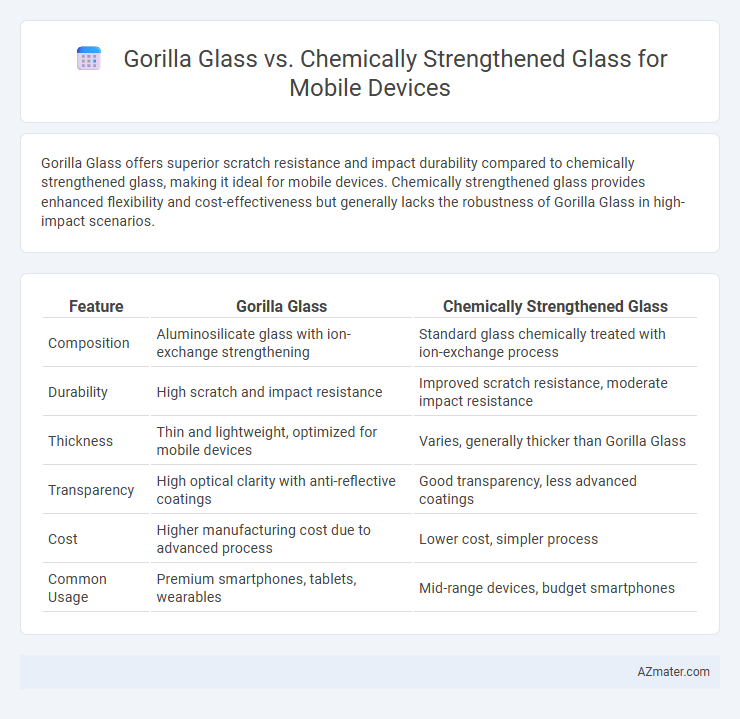
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and impact durability compared to chemically strengthened glass, making it ideal for mobile devices. Chemically strengthened glass provides enhanced flexibility and cost-effectiveness but generally lacks the robustness of Gorilla Glass in high-impact scenarios.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gorilla Glass | Chemically Strengthened Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminosilicate glass with ion-exchange strengthening | Standard glass chemically treated with ion-exchange process |
| Durability | High scratch and impact resistance | Improved scratch resistance, moderate impact resistance |
| Thickness | Thin and lightweight, optimized for mobile devices | Varies, generally thicker than Gorilla Glass |
| Transparency | High optical clarity with anti-reflective coatings | Good transparency, less advanced coatings |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost due to advanced process | Lower cost, simpler process |
| Common Usage | Premium smartphones, tablets, wearables | Mid-range devices, budget smartphones |
Introduction to Mobile Device Glass Technologies
Mobile device glass technologies primarily include Gorilla Glass and chemically strengthened glass, each engineered to enhance durability and scratch resistance. Gorilla Glass, produced through an ion-exchange process, offers exceptional toughness and clarity, making it a preferred choice for flagship smartphones and tablets. Chemically strengthened glass undergoes similar ion-exchange treatment but varies in thickness and chemical composition, providing a balance between strength and flexibility for various mobile device applications.
What is Gorilla Glass?
Gorilla Glass is a brand of chemically strengthened glass developed by Corning, designed specifically for mobile devices to provide high scratch resistance and durability. It undergoes an ion-exchange process that replaces smaller ions in the glass with larger ones, creating a compressive layer that enhances its strength against drops and impacts. Widely used in smartphones and tablets, Gorilla Glass offers superior clarity and toughness compared to standard chemically strengthened glass alternatives.
Overview of Chemically Strengthened Glass
Chemically strengthened glass undergoes an ion-exchange process that enhances its surface compressive stress, significantly improving scratch resistance and impact durability for mobile devices. Unlike Gorilla Glass, which is an alkali-aluminosilicate type glass known for its thinness and light weight, chemically strengthened glass offers superior toughness by replacing smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions. This treatment results in a harder, more damage-resistant surface, making it a preferred choice for high-performance smartphone displays and touchscreens.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Gorilla Glass is an aluminosilicate glass composed primarily of silicon dioxide with added aluminum oxide, manufactured through an ion-exchange process that replaces smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions to increase surface compression and improve scratch resistance. Chemically strengthened glass also undergoes ion exchange but may use different base compositions, such as soda-lime glass, and involves varying ion exchange parameters tailored to effect toughness and flexibility. The key manufacturing difference lies in Gorilla Glass's proprietary low-temperature fusion process, enabling thin, lightweight glass with enhanced durability compared to the broader range of chemically strengthened glasses that may sacrifice thinness for strength.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Gorilla Glass and chemically strengthened glass both offer enhanced scratch resistance and impact protection for mobile devices, but Gorilla Glass typically provides superior toughness due to its aluminosilicate composition and specialized ion-exchange process. Chemically strengthened glass undergoes potassium ion exchange to increase surface compression, improving scratch resistance but often making it more brittle under extreme stress compared to Gorilla Glass. In terms of durability, Gorilla Glass is engineered to balance hardness with flexibility, reducing the risk of cracking from drops, whereas chemically strengthened glass emphasizes surface hardness at the potential cost of increased fragility.
Scratch Resistance: Gorilla Glass vs Chemically Strengthened Glass
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance due to its chemically strengthened aluminosilicate composition, which enhances surface compression and toughness. Chemically strengthened glass provides good scratch resistance but generally exhibits lower hardness levels compared to Gorilla Glass, making it more susceptible to surface abrasion. The advanced ion-exchange process used in Gorilla Glass creates a denser, more resilient surface that better withstands daily wear and tear on mobile devices.
Impact Resistance and Drop Performance
Gorilla Glass, developed by Corning, features a chemically strengthened aluminosilicate composition that offers superior impact resistance and drop performance compared to standard chemically strengthened glass made from soda-lime or alkali-aluminosilicate materials. The ion-exchange process in Gorilla Glass creates a compressive layer that significantly improves toughness and reduces the likelihood of cracks or shattering upon impact. In drop tests, devices with Gorilla Glass consistently demonstrate higher survival rates and enhanced durability under repeated impacts, making it a preferred choice for rugged mobile displays.
Cost and Manufacturing Scalability
Gorilla Glass, produced by Corning, offers cost-efficient mass production due to its well-established manufacturing processes and widespread supplier network, making it highly scalable for mobile device manufacturers. Chemically strengthened glass, while providing comparable hardness and scratch resistance, often incurs higher production costs and presents challenges in scaling due to specialized ion-exchange treatment requirements. Mobile device manufacturers prioritize Gorilla Glass for its balance of durability, cost-effectiveness, and streamlined supply chain availability in high-volume production settings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gorilla Glass utilizes an alkaline-aluminosilicate composition enhanced through ion-exchange processes, offering durability with relatively lower environmental input than traditional glass manufacturing. Chemically strengthened glass typically requires similar ion-exchange techniques but may involve different raw material sourcing and energy consumption profiles, impacting its overall sustainability footprint. Life cycle assessments highlight that Gorilla Glass often benefits from optimized production efficiency and recyclability, contributing to reduced carbon emissions and material waste in mobile device applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Glass for Mobile Devices
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and shatter protection through its aluminosilicate composition, making it ideal for high-impact scenarios in mobile devices. Chemically strengthened glass utilizes ion exchange processes to enhance surface compression, providing excellent durability with a smoother finish but generally less impact resistance compared to Gorilla Glass. Selecting the best glass depends on device usage priorities, with Gorilla Glass favored for rugged protection and chemically strengthened glass chosen for sleek design and moderate durability.
Infographic: Gorilla glass vs Chemically strengthened glass for Mobile device
 azmater.com
azmater.com