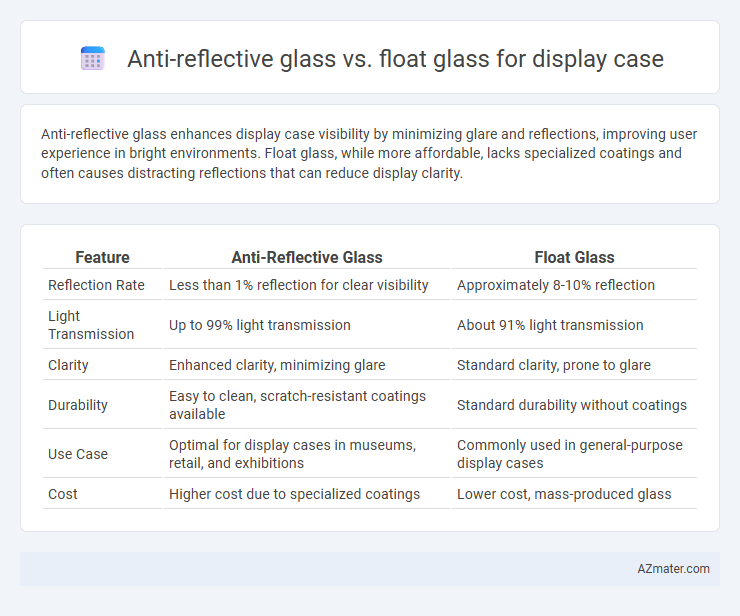
Anti-reflective glass enhances display case visibility by minimizing glare and reflections, improving user experience in bright environments. Float glass, while more affordable, lacks specialized coatings and often causes distracting reflections that can reduce display clarity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-Reflective Glass | Float Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Reflection Rate | Less than 1% reflection for clear visibility | Approximately 8-10% reflection |
| Light Transmission | Up to 99% light transmission | About 91% light transmission |
| Clarity | Enhanced clarity, minimizing glare | Standard clarity, prone to glare |
| Durability | Easy to clean, scratch-resistant coatings available | Standard durability without coatings |
| Use Case | Optimal for display cases in museums, retail, and exhibitions | Commonly used in general-purpose display cases |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized coatings | Lower cost, mass-produced glass |
Understanding Anti-Reflective Glass
Anti-reflective glass significantly reduces glare and reflections, enhancing visibility and clarity for display cases compared to standard float glass. Utilizing nanostructured coatings, anti-reflective glass minimizes light reflection to less than 1%, improving the viewer's experience by showcasing exhibits with true color accuracy and detail. Float glass, while cost-effective and commonly used, lacks these optical enhancements, often resulting in distracting reflections that compromise display quality.
What is Float Glass?
Float glass, also known as annealed glass, is produced by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal, typically tin, resulting in a smooth, uniform thickness ideal for display cases. It offers high clarity and strength but can cause significant reflections that hinder visibility of displayed items. Anti-reflective glass improves on float glass by incorporating special coatings that reduce glare and reflections, enhancing the viewing experience in display cases.
Key Differences Between Anti-Reflective and Float Glass
Anti-reflective glass significantly reduces glare and reflections by using a special coating, enhancing visibility and clarity in display cases, whereas float glass lacks this coating and often results in distracting reflections. Float glass is produced by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal, offering a smooth, uniform surface but without optical enhancement for viewing. The choice between anti-reflective and float glass impacts display quality, with anti-reflective glass providing superior light transmission and minimal distortion, ideal for high-end showcases.
Light Transmission and Clarity Comparison
Anti-reflective glass offers superior light transmission rates of up to 99%, significantly reducing surface reflections compared to standard float glass, which typically transmits around 85-90%. This enhanced clarity ensures clearer visibility and truer color representation in display cases, minimizing glare and visual distractions. Float glass, being more reflective, often results in reduced image sharpness and increased reflections, making anti-reflective glass the preferred choice for high-quality visual displays.
Reflection and Glare Reduction Benefits
Anti-reflective glass significantly reduces surface reflection, improving visibility and clarity in display cases by minimizing glare and light distortion compared to float glass. Its specialized coatings enhance contrast and color accuracy, providing a superior viewing experience even under strong lighting conditions. Float glass, lacking these coatings, can produce noticeable reflections and glare that detract from the displayed items' visibility.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Anti-reflective glass offers superior scratch resistance and durability compared to float glass, making it ideal for high-traffic display cases that require long-lasting clarity and protection. Its multi-layer coatings reduce glare while maintaining hardness levels that resist everyday abrasions and impacts. Float glass, although cost-effective and widely used, is more prone to scratches and surface wear, which can compromise visibility and durability in commercial display settings.
Cost Analysis: Anti-Reflective vs Float Glass
Anti-reflective glass typically costs 30-50% more than float glass due to additional coatings and manufacturing processes that reduce glare and improve display clarity. Float glass is more affordable but may lead to higher maintenance costs over time because of its susceptibility to reflections that can obscure product visibility. Choosing anti-reflective glass enhances customer experience and can increase sales, potentially offsetting the higher upfront investment compared to standard float glass in display cases.
Best Use Cases for Display Cases
Anti-reflective glass is ideal for display cases in museums or high-end retail stores where minimizing glare and enhancing visibility of exhibits is crucial. Float glass, being more affordable and durable, suits large-scale commercial displays or general-purpose showcases where cost-effectiveness and structural integrity are priorities. Selecting anti-reflective glass improves viewer experience by reducing reflections, while float glass offers robustness and ease of maintenance.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Anti-reflective glass for display cases requires less frequent cleaning due to its smudge-resistant coatings, reducing the buildup of fingerprints and dust compared to float glass. Float glass tends to accumulate more visible dirt and smudges, necessitating regular cleaning with specialized glass cleaners to maintain clarity. Maintenance of anti-reflective glass involves gentle cleaning methods with non-abrasive materials to preserve its coatings, while float glass can withstand more rigorous cleaning but shows more frequent visual degradation.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Display Case
Choosing anti-reflective glass for your display case enhances visibility by minimizing glare and reflections, making it ideal for showcasing artwork or collectibles under varied lighting conditions. Float glass, being more affordable and widely available, offers basic protection but may cause unwanted reflections that can obscure details in high-visibility settings. Prioritize anti-reflective glass when clarity and viewer experience are critical, while float glass suits budget-friendly or less display-sensitive applications.
Infographic: Anti-reflective glass vs Float glass for Display case
 azmater.com
azmater.com