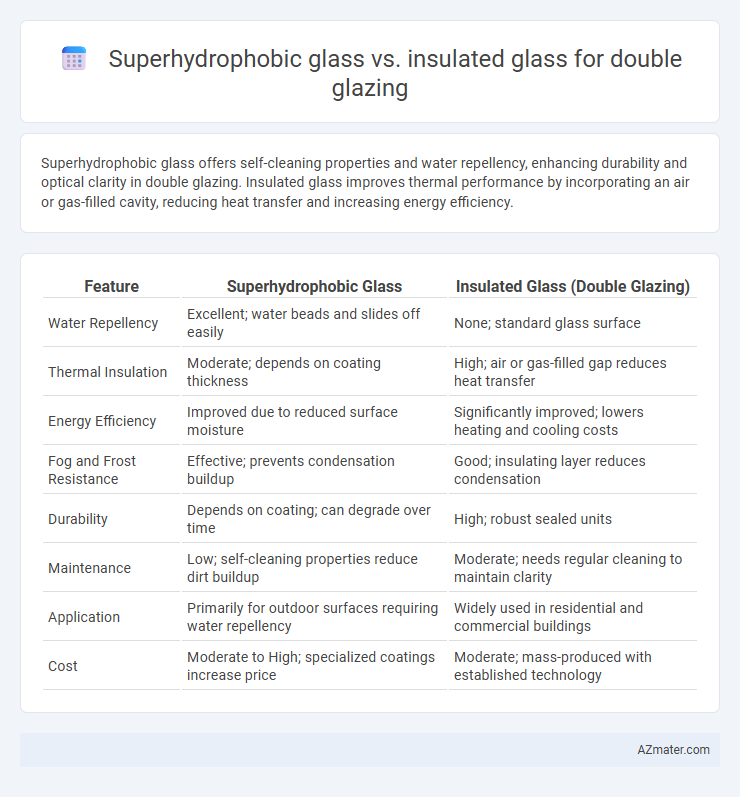
Superhydrophobic glass offers self-cleaning properties and water repellency, enhancing durability and optical clarity in double glazing. Insulated glass improves thermal performance by incorporating an air or gas-filled cavity, reducing heat transfer and increasing energy efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Superhydrophobic Glass | Insulated Glass (Double Glazing) |
|---|---|---|
| Water Repellency | Excellent; water beads and slides off easily | None; standard glass surface |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate; depends on coating thickness | High; air or gas-filled gap reduces heat transfer |
| Energy Efficiency | Improved due to reduced surface moisture | Significantly improved; lowers heating and cooling costs |
| Fog and Frost Resistance | Effective; prevents condensation buildup | Good; insulating layer reduces condensation |
| Durability | Depends on coating; can degrade over time | High; robust sealed units |
| Maintenance | Low; self-cleaning properties reduce dirt buildup | Moderate; needs regular cleaning to maintain clarity |
| Application | Primarily for outdoor surfaces requiring water repellency | Widely used in residential and commercial buildings |
| Cost | Moderate to High; specialized coatings increase price | Moderate; mass-produced with established technology |
Introduction to Double Glazing Technologies
Double glazing technologies enhance thermal insulation and reduce energy consumption in buildings by using two glass panes separated by a spacer filled with air or inert gas. Superhydrophobic glass incorporates a nanoscale coating that repels water and prevents dirt accumulation, improving clarity and reducing maintenance on exterior surfaces. Insulated glass units (IGUs) prioritize thermal performance with sealed gaps to minimize heat transfer, making them ideal for energy-efficient windows.
What is Superhydrophobic Glass?
Superhydrophobic glass features an ultra-water-repellent surface that prevents water droplets from adhering, ensuring clearer visibility and reduced maintenance in double glazing applications. Unlike insulated glass, which primarily focuses on thermal insulation by trapping air or gas between glass layers, superhydrophobic glass enhances durability and self-cleaning properties. This innovative coating significantly improves glass performance in humid or rainy environments while maintaining transparency and energy efficiency.
Understanding Insulated Glass Units (IGUs)
Insulated Glass Units (IGUs) consist of two or more glass panes separated by a spacer filled with air or inert gas, designed to improve thermal performance and reduce heat transfer. Superhydrophobic glass enhances IGUs by repelling water and dirt, maintaining clarity and reducing maintenance needs without compromising insulation properties. Comparing with traditional insulated glass, superhydrophobic coatings add functional durability while preserving the energy efficiency essential for double-glazing applications.
Key Performance Features of Superhydrophobic Glass
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water repellency and self-cleaning properties, reducing maintenance and preventing water stains, which enhances long-term transparency compared to traditional insulated glass. Its micro-nano textured surface minimizes adhesion of dirt and contaminants, improving durability and energy efficiency by maintaining clear solar heat gain control. Unlike insulated glass that primarily provides thermal insulation through air or gas layers, superhydrophobic glass combines hydrophobicity with energy savings, making it ideal for double glazing applications in humid or rainy climates.
Insulation Properties of Insulated Glass
Insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation due to its multiple glass panes separated by an air or gas-filled space, reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency in buildings. While superhydrophobic glass enhances water repellency and self-cleaning properties, it lacks the insulating air gap that significantly minimizes heat loss or gain. The insulating properties of double-glazed insulated glass make it an optimal choice for maintaining indoor temperature stability and reducing energy costs.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Superhydrophobic glass enhances energy efficiency by repelling water and dirt, maintaining clearer surfaces that optimize solar gain and reduce cooling loads. Insulated glass, typically composed of two or more glass panes separated by a gas-filled space, significantly improves thermal insulation by reducing heat transfer through conduction and convection. While insulated glass excels in minimizing heat loss and gain, superhydrophobic coatings primarily contribute to maintaining surface cleanliness, indirectly supporting energy efficiency by preserving the glass's transparency and solar control properties.
Maintenance and Cleaning Differences
Superhydrophobic glass significantly reduces maintenance by repelling water and dirt, minimizing the frequency and effort required for cleaning compared to insulated glass. Insulated glass requires regular cleaning of both panes and sealing edges to prevent condensation buildup and potential mold growth. The self-cleaning properties of superhydrophobic coatings enhance durability and clarity, making it more cost-effective for long-term maintenance in double-glazed windows.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Superhydrophobic glass exhibits exceptional durability due to its self-cleaning and anti-corrosive properties, significantly reducing maintenance and surface degradation over time compared to traditional insulated glass. Insulated glass, while effective in thermal insulation and noise reduction, may experience seal failure and moisture ingress that shorten its lifespan, typically lasting 10-20 years depending on environmental exposure. The enhanced resistance of superhydrophobic coatings to contaminants and weathering extends the functional lifespan of double glazing units by mitigating common durability issues found in insulated glass systems.
Cost Considerations and Return on Investment
Superhydrophobic glass typically incurs higher upfront costs compared to insulated glass due to advanced coatings that repel water and dirt, reducing maintenance expenses over time. Insulated glass offers energy efficiency benefits through thermal insulation, leading to significant savings on heating and cooling bills, which can result in a faster return on investment. Evaluating long-term performance and environmental conditions is crucial to maximizing cost-effectiveness in double glazing applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Double Glazing Needs
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water repellency and self-cleaning properties, making it ideal for exterior applications where maintenance and clarity are priorities. Insulated glass, consisting of multiple panes with a gas-filled gap, excels in thermal insulation and energy efficiency, reducing heating and cooling costs. Selecting the right glass depends on whether you prioritize moisture resistance and cleanliness or enhanced thermal performance for your double glazing needs.
Infographic: Superhydrophobic glass vs Insulated glass for Double glazing
 azmater.com
azmater.com