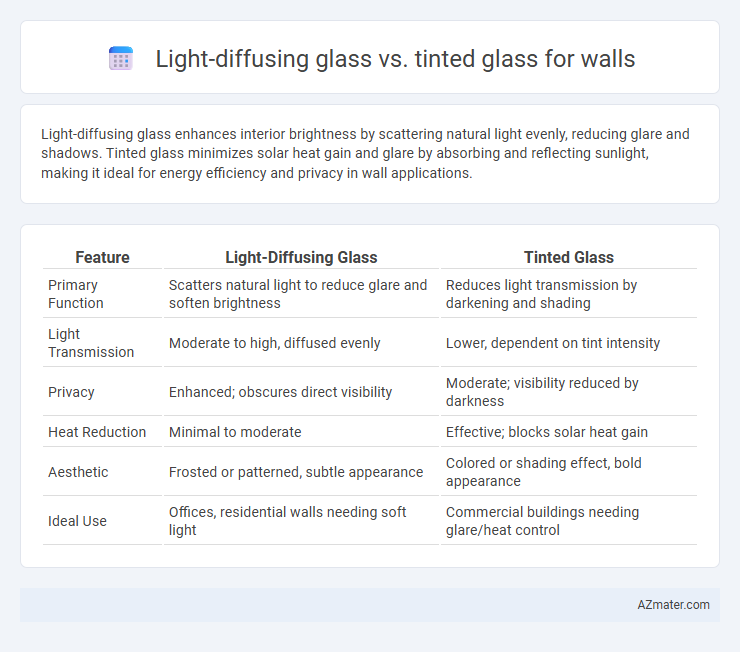
Light-diffusing glass enhances interior brightness by scattering natural light evenly, reducing glare and shadows. Tinted glass minimizes solar heat gain and glare by absorbing and reflecting sunlight, making it ideal for energy efficiency and privacy in wall applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Light-Diffusing Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Scatters natural light to reduce glare and soften brightness | Reduces light transmission by darkening and shading |
| Light Transmission | Moderate to high, diffused evenly | Lower, dependent on tint intensity |
| Privacy | Enhanced; obscures direct visibility | Moderate; visibility reduced by darkness |
| Heat Reduction | Minimal to moderate | Effective; blocks solar heat gain |
| Aesthetic | Frosted or patterned, subtle appearance | Colored or shading effect, bold appearance |
| Ideal Use | Offices, residential walls needing soft light | Commercial buildings needing glare/heat control |
Introduction to Light-Diffusing and Tinted Glass
Light-diffusing glass evenly disperses natural and artificial light, reducing glare and enhancing ambiance without compromising privacy, making it ideal for interior walls and partitions. Tinted glass contains colored pigments that reduce solar heat gain and control light transmission, providing energy efficiency and privacy while maintaining some level of exterior visibility. Both materials serve distinct architectural and design purposes, optimizing light management and environmental comfort in building interiors.
Key Differences Between Light-Diffusing and Tinted Glass
Light-diffusing glass scatters incoming light to create a soft, uniform illumination that enhances privacy without significantly reducing brightness, making it ideal for interior wall applications where natural light is desired without glare. Tinted glass reduces light transmission by absorbing a portion of sunlight, effectively minimizing heat and UV exposure while offering greater privacy and glare control, often used in exterior walls or facades. The key difference lies in light control: light-diffusing glass maintains interior brightness and privacy through diffusion, whereas tinted glass decreases light intensity and heat by filtering sunlight.
Light Transmission and Privacy Comparison
Light-diffusing glass enhances natural light transmission by scattering incoming sunlight to create uniform illumination while maintaining a high level of privacy by obscuring visibility through the panel. Tinted glass reduces light transmission by absorbing and reflecting sunlight, lowering glare and heat gain but offering limited privacy since it remains somewhat transparent from both sides. For walls, light-diffusing glass is ideal where bright, evenly distributed light and strong privacy are priorities, whereas tinted glass suits applications needing moderate light reduction with less emphasis on complete privacy.
Energy Efficiency: Which Glass Performs Better?
Light-diffusing glass enhances energy efficiency by evenly dispersing natural light, reducing the need for artificial lighting and minimizing heat gain through its translucent properties. Tinted glass primarily reduces solar heat by absorbing and reflecting infrared radiation, thereby lowering cooling costs but potentially decreasing natural daylight transmission. For optimal energy performance in wall applications, light-diffusing glass balances daylight utilization with thermal insulation, while tinted glass excels in heat rejection but may require supplemental lighting.
Impact on Indoor Comfort and Ambiance
Light-diffusing glass enhances indoor comfort by evenly dispersing natural light, reducing glare and creating a soft, ambient glow that minimizes eye strain and boosts mood. Tinted glass controls solar heat gain by absorbing and reflecting sunlight, significantly reducing indoor temperature and glare but can darken the space, affecting natural color perception. Choosing between the two influences ambiance: light-diffusing glass fosters a bright, balanced environment, while tinted glass offers a cooler, shaded atmosphere ideal for heat control.
Aesthetic Appeal: Design Options and Versatility
Light-diffusing glass enhances aesthetic appeal by evenly scattering incoming light to create a soft, ambient glow, offering versatile design options for modern interiors and ensuring privacy without sacrificing brightness. Tinted glass provides a range of color tones that reduce glare and heat while adding a sleek, sophisticated look ideal for both residential and commercial walls. Both types cater to different design preferences, with light-diffusing glass emphasizing softness and versatility, and tinted glass focusing on boldness and solar control.
Installation Considerations and Costs
Light-diffusing glass enhances natural light distribution while reducing glare, making it ideal for interior walls in commercial and residential spaces, though installation requires precise alignment to maintain aesthetic consistency, often increasing labor costs. Tinted glass, commonly used for privacy and solar heat control on exterior walls, typically involves straightforward installation similar to standard glass panels but may incur higher initial costs due to specialized coatings. Budget planning should consider that light-diffusing glass often demands custom fabrication and skilled installers, whereas tinted glass offers more cost-effective options with quicker installation times.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Light-diffusing glass enhances wall aesthetics by evenly scattering light, reducing glare while maintaining privacy, and typically has a durable surface resistant to scratches and discoloration. Tinted glass offers superior UV protection and heat reduction but may require more maintenance to prevent streaks and smudges that affect clarity. Both types demand regular cleaning, yet light-diffusing glass often demonstrates greater longevity in retaining its visual quality under varying environmental conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Light-diffusing glass enhances natural daylight penetration, reducing the need for artificial lighting and lowering energy consumption, which contributes to sustainability by decreasing carbon emissions. Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain, improving energy efficiency in cooling systems and minimizing HVAC-related environmental impact. Both options support eco-friendly building designs, but diffusing glass optimizes daylight harvesting while tinted glass primarily manages heat control.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Wall: Expert Recommendations
Light-diffusing glass enhances natural light distribution while maintaining privacy, making it ideal for interior walls needing soft, uniform illumination. Tinted glass reduces glare and solar heat gain, perfect for exterior walls exposed to strong sunlight and aiming for energy efficiency. Experts recommend selecting light-diffusing glass for areas requiring visual comfort indoors and tinted glass for exterior walls to balance aesthetics and thermal performance.
Infographic: Light-diffusing glass vs Tinted glass for Wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com