Superhydrophobic glass repels water, enhancing visibility and safety in automotive windshields by preventing water accumulation. Laminated glass combines layers of glass and plastic for increased impact resistance and passenger protection during collisions.
Table of Comparison
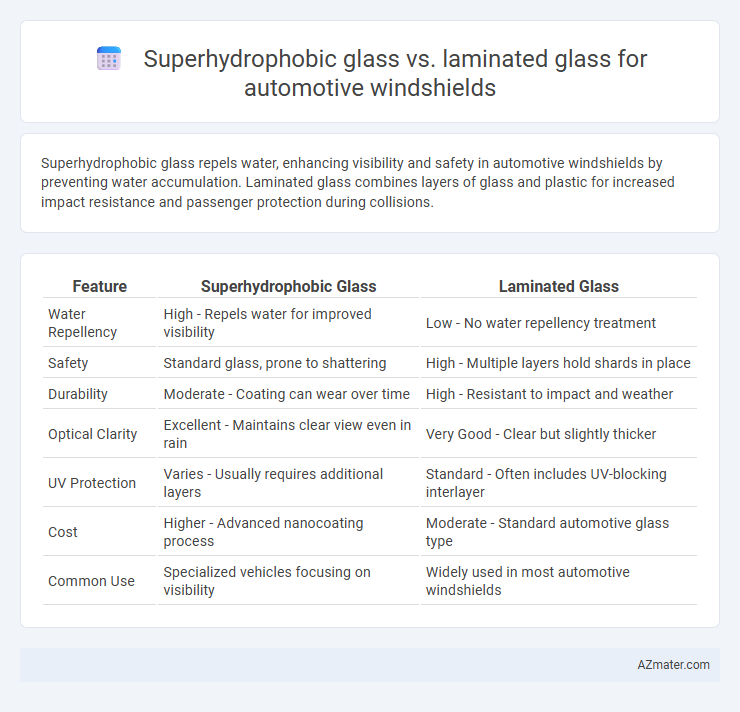
| Feature | Superhydrophobic Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Water Repellency | High - Repels water for improved visibility | Low - No water repellency treatment |
| Safety | Standard glass, prone to shattering | High - Multiple layers hold shards in place |
| Durability | Moderate - Coating can wear over time | High - Resistant to impact and weather |
| Optical Clarity | Excellent - Maintains clear view even in rain | Very Good - Clear but slightly thicker |
| UV Protection | Varies - Usually requires additional layers | Standard - Often includes UV-blocking interlayer |
| Cost | Higher - Advanced nanocoating process | Moderate - Standard automotive glass type |
| Common Use | Specialized vehicles focusing on visibility | Widely used in most automotive windshields |
Overview of Automotive Windshield Technologies
Superhydrophobic glass offers advanced water-repellent properties that enhance visibility during rain by causing water droplets to bead and roll off quickly, reducing the need for windshield wipers. Laminated glass, a traditional automotive windshield technology, consists of two glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing structural integrity, impact resistance, and passenger safety by preventing shattering. Both technologies optimize driving safety, with superhydrophobic coatings improving visibility and laminated glass ensuring durability and protection against collisions.
What is Superhydrophobic Glass?
Superhydrophobic glass is engineered with a nanoscale textured coating that repels water, creating a surface with water contact angles exceeding 150 degrees, which results in self-cleaning and enhanced visibility during rain. In contrast to laminated glass, which primarily offers impact resistance and shatter protection through a plastic interlayer, superhydrophobic glass focuses on water repellency and minimizes the need for wiper use. Automotive windshields treated with superhydrophobic coatings improve driver safety by reducing glare and water accumulation without compromising the structural integrity provided by laminated glass.
Key Features of Laminated Glass
Laminated glass for automotive windshields consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced impact resistance and safety by preventing shattering upon impact. Its key features include high durability, UV protection, sound insulation, and structural integrity that helps maintain the windshield's shape during collisions. Laminated glass also offers superior resistance to penetration, contributing to passenger protection and vehicle security compared to superhydrophobic glass, which primarily improves water repellency but lacks the robust safety benefits inherent to laminated structures.
Durability Comparison between Superhydrophobic and Laminated Glass
Superhydrophobic glass features a nano-coating that repels water and reduces dirt adhesion but may degrade over time due to exposure to UV rays, abrasion, and environmental factors, impacting its long-term durability on automotive windshields. Laminated glass consists of two glass layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, offering superior structural integrity, impact resistance, and durability against cracks and shattering in automotive applications. While superhydrophobic glass provides enhanced water repellency, laminated glass remains the more durable choice for windshield safety and longevity under harsh driving conditions.
Safety Benefits: Superhydrophobic vs Laminated Windshields
Superhydrophobic glass enhances automotive safety by repelling water and reducing glare, improving driver visibility during wet conditions and minimizing accident risks. Laminated glass offers superior impact resistance and prevents shattering by holding broken glass fragments together, providing critical protection in collisions. Combining superhydrophobic coatings with laminated glass can optimize windshield safety by merging enhanced visibility with structural integrity.
Visibility and Performance in Adverse Weather
Superhydrophobic glass for automotive windshields enhances visibility by repelling water droplets, reducing the need for wipers during rain and improving driver safety in adverse weather. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers with a plastic interlayer, offers superior impact resistance and prevents shattering but does not inherently improve water repellency or visibility in wet conditions. Performance-wise, superhydrophobic coatings optimize water runoff and reduce fogging, while laminated glass excels in structural durability and occupant protection during collisions.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Superhydrophobic glass significantly reduces water and dirt accumulation on automotive windshields, minimizing the need for frequent cleaning and enhancing visibility over time. Laminated glass offers superior durability and impact resistance, preventing shattering and extending windshield lifespan under harsh driving conditions. Maintenance costs for superhydrophobic coatings may increase due to their gradual wear, whereas laminated glass typically requires less frequent replacement, contributing to overall longevity.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Superhydrophobic glass typically incurs higher initial costs due to advanced coating technologies designed to repel water and improve visibility, increasing manufacturing expenses compared to standard laminated glass used in automotive windshields. Laminated glass offers a more affordable solution with effective safety features like impact resistance and shatterproof properties, making it the predominant choice for cost-sensitive automotive markets. While superhydrophobic glass enhances functional performance, laminated glass balances affordability with essential protection, providing a cost-efficient windshield option.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Superhydrophobic glass significantly reduces water adhesion, leading to less frequent windshield cleaning and decreased water and chemical detergent usage, thereby lowering environmental pollution. Laminated glass, while offering enhanced safety by preventing shattering, involves multilayer materials such as polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which are more challenging to recycle and contribute to higher environmental impact during disposal. Choosing superhydrophobic glass promotes sustainability through extended durability and reduced maintenance resources, whereas laminated glass prioritizes occupant safety but at a potential cost to end-of-life environmental efficiency.
Which Glass Is Best for Automotive Windshields?
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water repellency and improved visibility during rain by creating a self-cleaning surface that reduces water droplet adhesion, enhancing driver safety. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers bonded with a polymer interlayer, provides exceptional impact resistance and shatterproof protection, essential for occupant safety in collisions. For automotive windshields, laminated glass remains the industry standard due to its structural integrity and safety benefits, while superhydrophobic coatings can be applied to laminated glass to combine durability with enhanced water resistance.
Infographic: Superhydrophobic glass vs Laminated glass for Automotive windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com