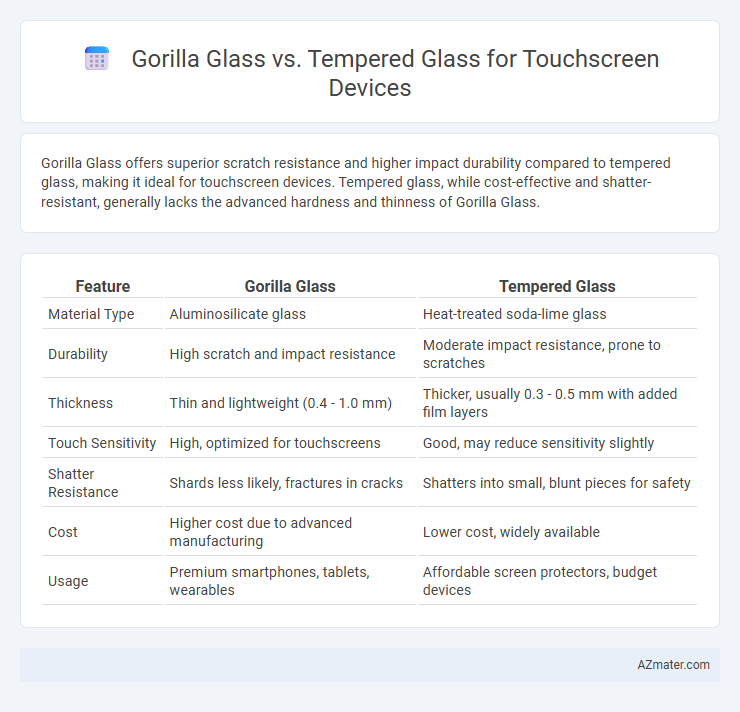
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and higher impact durability compared to tempered glass, making it ideal for touchscreen devices. Tempered glass, while cost-effective and shatter-resistant, generally lacks the advanced hardness and thinness of Gorilla Glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gorilla Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Aluminosilicate glass | Heat-treated soda-lime glass |
| Durability | High scratch and impact resistance | Moderate impact resistance, prone to scratches |
| Thickness | Thin and lightweight (0.4 - 1.0 mm) | Thicker, usually 0.3 - 0.5 mm with added film layers |
| Touch Sensitivity | High, optimized for touchscreens | Good, may reduce sensitivity slightly |
| Shatter Resistance | Shards less likely, fractures in cracks | Shatters into small, blunt pieces for safety |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced manufacturing | Lower cost, widely available |
| Usage | Premium smartphones, tablets, wearables | Affordable screen protectors, budget devices |
Introduction to Gorilla Glass and Tempered Glass
Gorilla Glass, engineered by Corning, is a chemically strengthened glass known for its high resistance to scratches and impact, making it ideal for touchscreen devices. Tempered glass, created through a thermal tempering process, offers enhanced strength and shatter resistance by compressing the surface layers, commonly used as a protective screen layer. Both materials balance durability and clarity, but Gorilla Glass integrates directly into device design while tempered glass typically serves as an external protective layer or screen protector.
Key Differences Between Gorilla Glass and Tempered Glass
Gorilla Glass is chemically strengthened aluminosilicate glass offering superior scratch resistance and higher durability compared to standard tempered glass, which is heat-treated to increase its strength but remains more prone to scratches. Gorilla Glass is thinner and lighter, enhancing touchscreen responsiveness and device aesthetics, while tempered glass is thicker and often used as an external protective layer or screen protector. The manufacturing process of Gorilla Glass involves ion exchange, resulting in a tougher surface that better withstands drops and impacts compared to the thermal tempering method used for tempered glass.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Gorilla Glass is an alkali-aluminosilicate sheet glass chemically strengthened through an ion-exchange process that replaces smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions, enhancing its surface compression and scratch resistance. Tempered glass undergoes a thermal or chemical treatment that creates balanced internal stresses by rapid cooling, increasing its strength and causing it to shatter into small granular chunks upon impact. The distinct manufacturing processes result in Gorilla Glass offering superior thinness and optical clarity, while tempered glass provides robust impact resistance but with increased thickness and potential optical distortion.
Scratch Resistance: Gorilla Glass vs Tempered Glass
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance compared to traditional tempered glass due to its chemically strengthened alkali-aluminosilicate composition, which enhances surface hardness and durability. Tempered glass, while providing impact resistance through thermal treatment, is more prone to surface scratches and abrasions in everyday use. The enhanced scratch resilience of Gorilla Glass makes it the preferred choice for touchscreen devices requiring long-lasting clarity and protection.
Impact and Shatter Resistance Comparison
Gorilla Glass, composed of chemically strengthened aluminosilicate, offers superior impact resistance by absorbing and dispersing energy effectively to minimize cracks upon drops. Tempered glass, created through a heat treatment process that compresses the surface, provides robust shatter resistance by breaking into small, blunt pieces instead of sharp shards when shattered. While Gorilla Glass excels in preventing deep cracks and scratches during impacts, tempered glass is often favored for its enhanced safety features in shattering scenarios.
Touch Sensitivity and Screen Clarity
Gorilla Glass offers superior touch sensitivity due to its advanced chemical composition and thin design, allowing for more accurate and responsive interactions on touchscreen devices. Tempered glass, while providing excellent durability and impact resistance, can slightly reduce screen clarity and touch responsiveness because of its thicker layers and coating materials. Users prioritizing optimal touch performance and visual clarity typically prefer Gorilla Glass for their devices.
Cost Analysis: Gorilla Glass vs Tempered Glass
Gorilla Glass typically incurs higher production costs due to its chemically strengthened aluminosilicate composition, resulting in superior scratch and impact resistance for touchscreen devices. Tempered glass, produced through thermal tempering of standard soda-lime glass, offers a more budget-friendly option with moderate durability but lower resistance to scratches and cracks. Cost analysis reveals Gorilla Glass as a premium investment for high-end devices, while tempered glass suits cost-sensitive applications requiring basic protection.
Durability and Long-term Performance
Gorilla Glass offers superior durability due to its chemically strengthened composition, making it highly resistant to scratches and impacts compared to traditional tempered glass. Tempered glass, while strong and shatter-resistant, tends to wear down faster and can develop micro-cracks over time, reducing long-term performance. Devices equipped with Gorilla Glass maintain touchscreen responsiveness and clarity longer, providing enhanced protection in everyday use and extreme conditions.
Common Applications in Touchscreen Devices
Gorilla Glass is widely used in smartphones and tablets due to its high scratch resistance and thin profile, making it ideal for sleek, durable touchscreen devices. Tempered glass is commonly found in budget smartphones, external screen protectors, and some industrial touchscreens for its impact resistance and lower manufacturing cost. Both materials are essential in consumer electronics, balancing durability and cost based on device requirements.
Conclusion: Which Glass is Better for Your Device?
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and durability due to its chemically strengthened properties, making it ideal for high-end touchscreen devices requiring long-lasting protection. Tempered glass provides excellent shatter resistance and impact protection but tends to be less scratch-resistant and can break into sharp shards. For optimal balance of toughness and safety, Gorilla Glass is often the better choice for touchscreen devices demanding premium resilience and clarity.
Infographic: Gorilla glass vs Tempered glass for Touchscreen device
 azmater.com
azmater.com