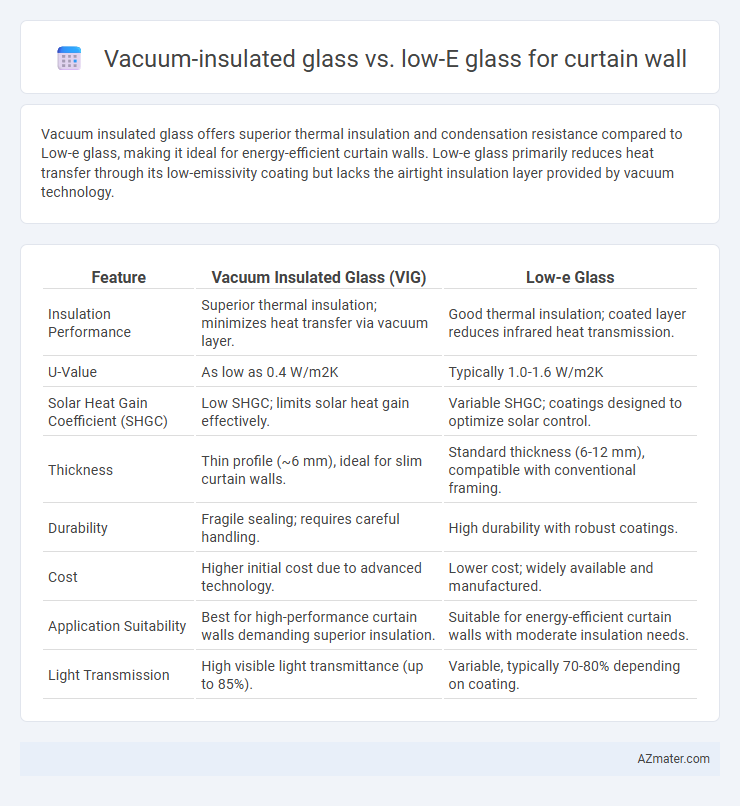
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and condensation resistance compared to Low-e glass, making it ideal for energy-efficient curtain walls. Low-e glass primarily reduces heat transfer through its low-emissivity coating but lacks the airtight insulation layer provided by vacuum technology.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) | Low-e Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation Performance | Superior thermal insulation; minimizes heat transfer via vacuum layer. | Good thermal insulation; coated layer reduces infrared heat transmission. |
| U-Value | As low as 0.4 W/m2K | Typically 1.0-1.6 W/m2K |
| Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) | Low SHGC; limits solar heat gain effectively. | Variable SHGC; coatings designed to optimize solar control. |
| Thickness | Thin profile (~6 mm), ideal for slim curtain walls. | Standard thickness (6-12 mm), compatible with conventional framing. |
| Durability | Fragile sealing; requires careful handling. | High durability with robust coatings. |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced technology. | Lower cost; widely available and manufactured. |
| Application Suitability | Best for high-performance curtain walls demanding superior insulation. | Suitable for energy-efficient curtain walls with moderate insulation needs. |
| Light Transmission | High visible light transmittance (up to 85%). | Variable, typically 70-80% depending on coating. |
Introduction to Curtain Wall Glazing Options
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) and Low-e glass are prominent glazing options for curtain walls, each offering distinct thermal performance benefits. VIG provides superior insulation through a vacuum layer that minimizes heat transfer, ideal for energy-efficient building envelopes. Low-e glass enhances solar control by reflecting infrared radiation while allowing visible light, reducing heating and cooling loads in commercial facades.
What is Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG)?
Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a narrow vacuum space, minimizing heat transfer and enhancing thermal insulation in curtain walls. Unlike Low-e glass, which uses a microscopically thin metal oxide coating to reflect infrared energy, VIG eliminates conduction and convection by creating a near-vacuum, significantly reducing U-values to as low as 0.5 W/m2K. This superior thermal performance makes VIG ideal for energy-efficient building facades requiring slim profiles without compromising daylight or transparency.
Understanding Low-E Glass Technology
Low-E glass technology for curtain walls utilizes a microscopically thin, transparent coating that reflects infrared energy while allowing visible light to pass through, enhancing energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer. Compared to vacuum insulated glass, Low-E glass achieves improved thermal performance through selective wavelength reflection rather than physical insulation, making it effective in managing solar heat gain and minimizing heat loss. Implementing Low-E coatings in curtain wall systems optimizes indoor comfort and reduces building energy consumption without significantly increasing glass thickness or weight.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal insulation for curtain walls by minimizing heat transfer through a near-vacuum space between glass layers, achieving U-values as low as 0.3 W/m2K. Low-e glass enhances thermal performance by reflecting infrared radiation with a thin metallic coating, typically reaching U-values around 1.1 W/m2K, which is less effective compared to VIG. The sealed vacuum in VIG significantly reduces conduction and convection, making it the preferred choice for maximizing energy efficiency in high-performance curtain wall systems.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal performance for curtain walls by minimizing heat transfer through its vacuum layer, resulting in significant energy efficiency and reduced HVAC costs compared to low-e glass. Low-e glass, coated with a microscopically thin metallic layer, reflects infrared heat while allowing visible light, providing moderate energy savings at a lower initial cost. While VIG entails higher upfront investment, its enhanced insulation capability delivers greater long-term cost savings through improved temperature regulation and reduced energy consumption.
Acoustic Performance: VIG vs Low-E Glass
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior acoustic performance compared to Low-E glass by creating a nearly airless space between panes that significantly reduces sound transmission. Low-E glass primarily enhances thermal insulation with selective coatings but provides moderate soundproofing, relying on air or gas-filled cavities that can still allow noise penetration. For curtain wall applications demanding high sound attenuation, VIG is the optimal choice due to its exceptional ability to dampen external noise pollution.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal insulation and durability due to its hermetically sealed vacuum cavity, minimizing condensation and reducing the risk of seal failure over time in curtain wall applications. Low-e glass, coated with microscopically thin metallic layers, improves energy efficiency by reflecting infrared heat while maintaining visible light transmission but may require more frequent cleaning and careful maintenance to preserve its coating integrity. Both glass types demand attention to installation quality, with VIG generally exhibiting lower maintenance needs, whereas Low-e glass coatings can degrade with improper handling or harsh environmental exposure.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thinness and sleek profile, enabling minimalist curtain wall designs with larger uninterrupted glass surfaces, enhancing aesthetic appeal. Low-e glass provides versatile coating options that control solar heat gain and light transmission without compromising exterior appearance, allowing diverse architectural styles. Both technologies support design flexibility, but vacuum insulated glass excels in creating slim, modern facades ideal for high-end commercial buildings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal insulation by minimizing heat transfer through a near-vacuum layer, significantly reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling in curtain wall applications. Low-e glass enhances sustainability by reflecting infrared radiation while allowing visible light, which lowers greenhouse gas emissions by improving building energy efficiency. Choosing VIG or Low-e glass depends on specific environmental goals, as VIG excels in energy savings with minimal material use, whereas Low-e glass provides cost-effective solar control and durability for sustainable building design.
Choosing the Best Glass Solution for Curtain Walls
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal insulation by minimizing heat transfer through a near-vacuum space, significantly improving energy efficiency and reducing HVAC costs in curtain wall applications. Low-e glass incorporates a thin, transparent coating that reflects infrared heat while allowing natural light, balancing solar control and daylighting but with less insulation performance compared to VIG. Selecting the best glass solution for curtain walls depends on project priorities such as energy savings, daylight management, condensation resistance, and overall building envelope performance.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Low-e glass for Curtain wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com