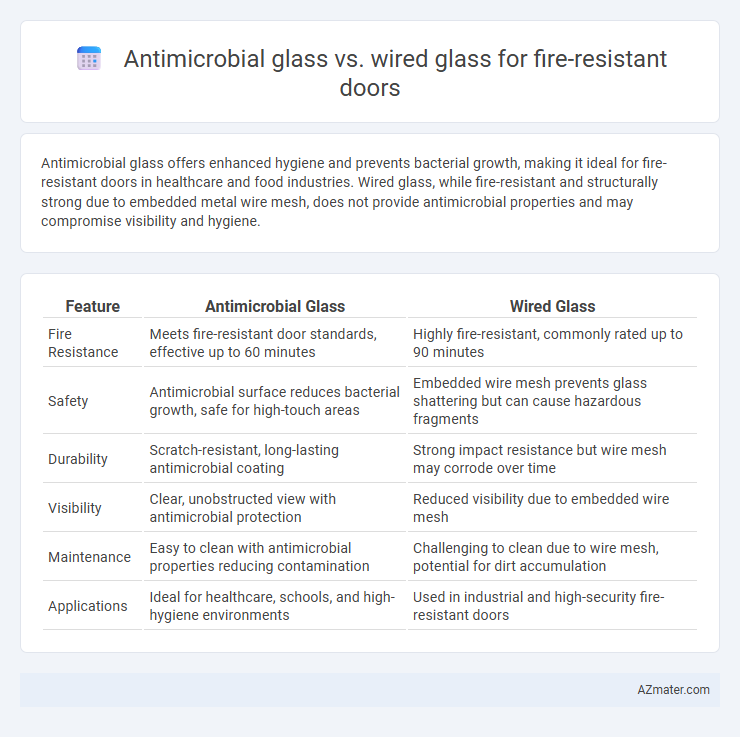
Antimicrobial glass offers enhanced hygiene and prevents bacterial growth, making it ideal for fire-resistant doors in healthcare and food industries. Wired glass, while fire-resistant and structurally strong due to embedded metal wire mesh, does not provide antimicrobial properties and may compromise visibility and hygiene.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Antimicrobial Glass | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Meets fire-resistant door standards, effective up to 60 minutes | Highly fire-resistant, commonly rated up to 90 minutes |
| Safety | Antimicrobial surface reduces bacterial growth, safe for high-touch areas | Embedded wire mesh prevents glass shattering but can cause hazardous fragments |
| Durability | Scratch-resistant, long-lasting antimicrobial coating | Strong impact resistance but wire mesh may corrode over time |
| Visibility | Clear, unobstructed view with antimicrobial protection | Reduced visibility due to embedded wire mesh |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean with antimicrobial properties reducing contamination | Challenging to clean due to wire mesh, potential for dirt accumulation |
| Applications | Ideal for healthcare, schools, and high-hygiene environments | Used in industrial and high-security fire-resistant doors |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant Door Glazing Options
Fire-resistant door glazing options include antimicrobial glass and wired glass, each offering distinct advantages for safety and hygiene. Antimicrobial glass incorporates surface treatments that inhibit microbial growth, enhancing cleanliness in healthcare and food service environments. Wired glass contains embedded metal mesh to prevent shattering during fire exposure, providing reliable heat and flame resistance in commercial and industrial settings.
Understanding Antimicrobial Glass: Key Features
Antimicrobial glass for fire-resistant doors integrates silver ion technology or copper coatings that inhibit mold, bacteria, and viruses, enhancing hygiene without compromising fire safety. This glass type maintains high heat resistance and complies with fire rating standards, ensuring structural integrity during fire incidents. Unlike wired glass, which relies on embedded mesh for fire protection but lacks antimicrobial properties, antimicrobial glass offers dual functionality in environments demanding cleanliness and fire resistance.
Wired Glass Explained: Structure and Function
Wired glass features a mesh of embedded steel wires within the glass pane, enhancing fire resistance by preventing the glass from shattering under heat stress. This structure maintains the integrity of fire-resistant doors, ensuring containment of smoke and flames while allowing visibility. Wired glass is favored in safety applications where fire protection and durability are critical, contrasting with antimicrobial glass, which prioritizes hygiene but lacks the high-temperature resilience key for fire doors.
Fire Resistance: How Each Glass Type Performs
Antimicrobial glass and wired glass both provide fire resistance suitable for fire-resistant doors, but wired glass offers superior protection due to its embedded wire mesh that prevents shattering under high temperatures. Antimicrobial glass primarily enhances hygiene by inhibiting microbial growth, with fire resistance properties comparable to standard tempered glass but generally less robust than wired glass. Fire-resistant doors utilizing wired glass meet stringent fire safety standards, maintaining structural integrity and visibility during fire exposure more effectively than antimicrobial glass options.
Safety Considerations: Antimicrobial vs Wired Glass
Antimicrobial glass for fire-resistant doors enhances hygiene by inhibiting bacterial growth, making it ideal for healthcare and food industry settings where sanitation is critical. Wired glass offers superior fire safety by preventing glass breakage and maintaining structural integrity under extreme heat, ensuring effective fire containment. Selecting between antimicrobial and wired glass hinges on balancing infection control needs against robust fire resistance and physical durability requirements.
Durability and Maintenance Comparison
Antimicrobial glass offers enhanced durability with its resistance to microbial growth, reducing the risk of surface degradation over time, making it ideal for high-traffic fire-resistant doors. Wired glass, while traditionally robust due to embedded wire mesh providing structural integrity during fires, tends to be more susceptible to cracking and requires frequent inspections and maintenance to ensure safety compliance. Maintenance needs of antimicrobial glass are minimal since its surface inhibits bacteria and dirt accumulation, whereas wired glass may demand repairs or replacements more often due to chipping or wire mesh exposure.
Hygiene Benefits: The Role of Antimicrobial Properties
Antimicrobial glass enhances fire-resistant doors by actively inhibiting the growth of bacteria and viruses on the surface, significantly reducing the risk of contamination in high-touch areas. Wired glass, while providing structural fire resistance, lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, making it less effective for hygiene-critical environments such as hospitals and food processing facilities. Incorporating antimicrobial glass in fire-resistant doors ensures both safety compliance and improved sanitary conditions, supporting infection control protocols.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Antimicrobial glass offers sleek, modern aesthetics with smooth surfaces and crystal-clear transparency, enhancing visual appeal and hygiene in fire-resistant doors. Wired glass, characterized by its embedded metal mesh, provides a traditional, industrial look but limits design flexibility due to heavier weight and reduced clarity. The smooth, customizable nature of antimicrobial glass allows for versatile design options, making it ideal for contemporary architectural applications seeking both safety and style.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Lifecycle Costs
Antimicrobial glass for fire-resistant doors typically carries a higher upfront cost compared to wired glass due to advanced materials and coatings that inhibit microbial growth. Installation costs are often similar, but antimicrobial glass may require specialized handling and certification for fire resistance, influencing labor expenses. Over the lifecycle, antimicrobial glass can reduce maintenance and replacement costs thanks to its durability and hygiene benefits, whereas wired glass might incur higher long-term costs due to potential damage and cleaning requirements.
Choosing the Right Glass for Fire-Resistant Doors
Selecting the right glass for fire-resistant doors requires comparing antimicrobial glass and wired glass based on safety and functionality. Antimicrobial glass offers enhanced hygiene by inhibiting bacterial growth, ideal for healthcare and public spaces, while wired glass provides superior fire resistance and structural integrity during exposure to high temperatures. Prioritizing certifications like UL 752 or BS 476 ensures compliance with fire safety standards, making wired glass a preferred choice for robust fire containment.
Infographic: Antimicrobial glass vs Wired glass for Fire-resistant door
 azmater.com
azmater.com