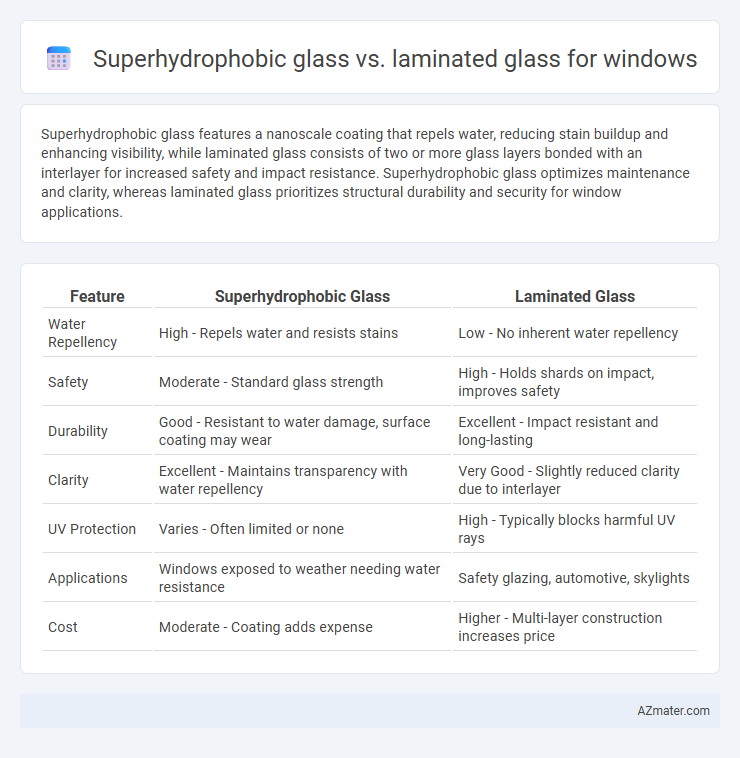
Superhydrophobic glass features a nanoscale coating that repels water, reducing stain buildup and enhancing visibility, while laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer for increased safety and impact resistance. Superhydrophobic glass optimizes maintenance and clarity, whereas laminated glass prioritizes structural durability and security for window applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Superhydrophobic Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Water Repellency | High - Repels water and resists stains | Low - No inherent water repellency |
| Safety | Moderate - Standard glass strength | High - Holds shards on impact, improves safety |
| Durability | Good - Resistant to water damage, surface coating may wear | Excellent - Impact resistant and long-lasting |
| Clarity | Excellent - Maintains transparency with water repellency | Very Good - Slightly reduced clarity due to interlayer |
| UV Protection | Varies - Often limited or none | High - Typically blocks harmful UV rays |
| Applications | Windows exposed to weather needing water resistance | Safety glazing, automotive, skylights |
| Cost | Moderate - Coating adds expense | Higher - Multi-layer construction increases price |
Introduction to Modern Window Technologies
Superhydrophobic glass features a nano-engineered coating that repels water and resists dirt accumulation, enhancing window clarity and reducing maintenance. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced safety, sound insulation, and UV protection. Modern window technologies increasingly combine these innovations to deliver durable, energy-efficient, and low-maintenance solutions for residential and commercial buildings.
What Is Superhydrophobic Glass?
Superhydrophobic glass features a nanostructured surface coating that repels water, preventing droplets from adhering and enhancing visibility during rain. This advanced technology reduces maintenance by minimizing water spots and dirt accumulation, making it ideal for environments with frequent precipitation. Unlike laminated glass, which provides structural safety by bonding multiple layers, superhydrophobic glass primarily improves water resistance and surface cleanliness.
What Is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, usually made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced strength and safety by preventing shattering upon impact. This type of glass is widely used in windows for its superior durability, sound insulation, and UV protection compared to regular glass. In contrast, superhydrophobic glass features a surface coating that repels water, reducing water spots and grime but does not inherently improve structural strength like laminated glass.
Durability Comparison: Superhydrophobic vs Laminated Glass
Superhydrophobic glass features a nanoscale coating that repels water and resists staining, maintaining clarity but offering moderate durability against physical impact and abrasion. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, providing superior impact resistance, enhanced safety, and sustained structural integrity under stress. While laminated glass excels in shatter resistance and long-term durability, superhydrophobic glass prioritizes surface protection and self-cleaning properties, making their durability benefits context-dependent.
Performance under Extreme Weather Conditions
Superhydrophobic glass exhibits exceptional water repellency and self-cleaning properties, enhancing visibility and reducing maintenance during heavy rain and snow. Laminated glass offers superior impact resistance and structural integrity, providing better protection against high winds, hail, and flying debris in extreme storms. Both materials improve window durability, but superhydrophobic glass excels in water management while laminated glass ensures enhanced safety and security.
Security and Safety Features
Superhydrophobic glass offers enhanced water-repellent properties that prevent water accumulation and reduce the risk of mold and bacteria growth, contributing to safer window environments. Laminated glass provides superior security features by incorporating a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, which holds shards together upon impact, minimizing injury from glass breakage and deterring forced entry. For optimal window safety, laminated glass excels in impact resistance and security, while superhydrophobic glass enhances durability and cleanliness through its water-repelling technology.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Superhydrophobic glass significantly reduces maintenance and cleaning efforts due to its water-repellent coating that prevents dirt, dust, and grime from adhering to the surface. Laminated glass, while offering enhanced safety and noise reduction, typically requires regular cleaning to maintain clarity because it lacks self-cleaning properties. In environments prone to pollution or moisture, superhydrophobic glass outperforms laminated glass by minimizing the frequency and intensity of cleaning needed.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation
Superhydrophobic glass offers enhanced energy efficiency by repelling water and reducing maintenance, maintaining clarity without compromising solar heat gain control, which contributes to better insulation performance. Laminated glass provides superior sound insulation and safety benefits by bonding multiple layers, but it may have slightly lower thermal resistance compared to advanced coated superhydrophobic options. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing long-term energy savings and minimal maintenance versus impact resistance and acoustic insulation.
Cost Effectiveness and Long-Term Value
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water repellency and self-cleaning properties, reducing maintenance costs over time compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass excels in impact resistance and safety, often providing better long-term value in security-sensitive installations despite higher initial costs. Evaluating cost effectiveness hinges on application needs, with superhydrophobic glass minimizing upkeep expenses, while laminated glass ensures durability and protection.
Choosing the Best Glass Type for Your Windows
Superhydrophobic glass offers exceptional water repellency and self-cleaning properties, making it ideal for windows exposed to heavy rainfall and moisture. Laminated glass provides superior safety and sound insulation by combining multiple layers with a plastic interlayer that holds shards in place upon breakage. Choosing the best glass type depends on whether the priority is low maintenance and water resistance or enhanced security and noise reduction for your windows.
Infographic: Superhydrophobic glass vs Laminated glass for Window
 azmater.com
azmater.com