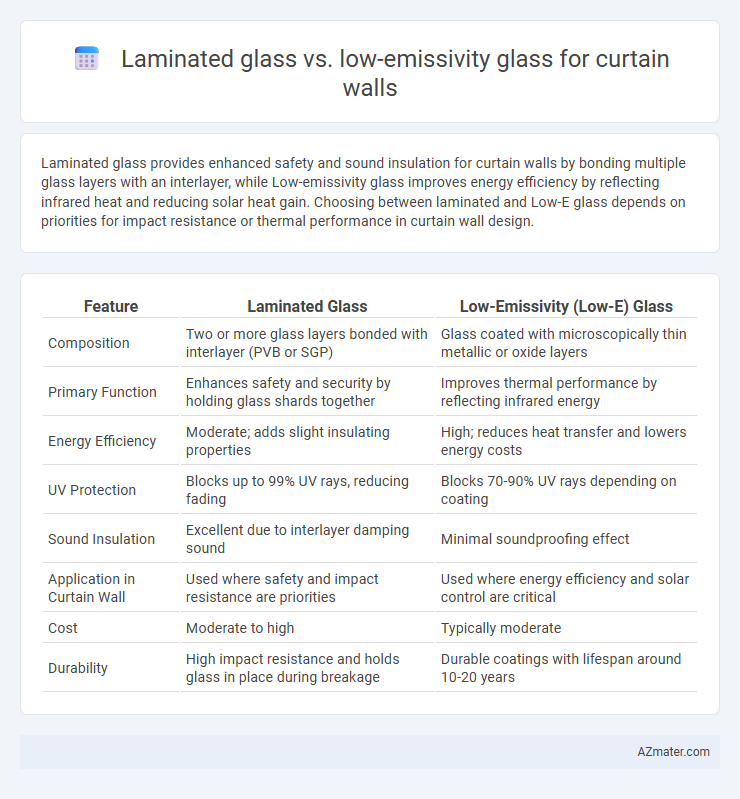
Laminated glass provides enhanced safety and sound insulation for curtain walls by bonding multiple glass layers with an interlayer, while Low-emissivity glass improves energy efficiency by reflecting infrared heat and reducing solar heat gain. Choosing between laminated and Low-E glass depends on priorities for impact resistance or thermal performance in curtain wall design.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Low-Emissivity (Low-E) Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Two or more glass layers bonded with interlayer (PVB or SGP) | Glass coated with microscopically thin metallic or oxide layers |
| Primary Function | Enhances safety and security by holding glass shards together | Improves thermal performance by reflecting infrared energy |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate; adds slight insulating properties | High; reduces heat transfer and lowers energy costs |
| UV Protection | Blocks up to 99% UV rays, reducing fading | Blocks 70-90% UV rays depending on coating |
| Sound Insulation | Excellent due to interlayer damping sound | Minimal soundproofing effect |
| Application in Curtain Wall | Used where safety and impact resistance are priorities | Used where energy efficiency and solar control are critical |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Typically moderate |
| Durability | High impact resistance and holds glass in place during breakage | Durable coatings with lifespan around 10-20 years |
Introduction to Curtain Wall Glazing Options
Curtain wall glazing options include laminated glass and low-emissivity (Low-E) glass, each offering distinct benefits for building envelopes. Laminated glass provides enhanced safety and noise reduction through its interlayer, making it ideal for impact resistance and security in curtain walls. Low-emissivity glass improves energy efficiency by reflecting infrared heat while allowing visible light to pass, significantly reducing heating and cooling costs in modern architectural designs.
Understanding Laminated Glass: Composition and Benefits
Laminated glass for curtain walls consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), enhancing safety by holding shards together upon breakage. This composition improves sound insulation, UV protection, and structural integrity, making it ideal for high-rise buildings exposed to wind loads and impact risks. Its ability to absorb energy and prevent glass shattering contributes to occupant safety and reduces maintenance costs in curtain wall applications.
What is Low-Emissivity (Low-E) Glass?
Low-Emissivity (Low-E) glass for curtain walls features a microscopically thin, transparent coating that reduces infrared and ultraviolet light transfer without compromising visible light transmission. This coating enhances energy efficiency by reflecting heat back to its source, maintaining interior temperature and reducing HVAC costs. Compared to laminated glass, which focuses on safety and sound insulation through interlayers, Low-E glass primarily improves thermal performance and solar control in building facades.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing improved impact resistance and some thermal insulation, but its thermal performance is generally less effective than Low-emissivity (Low-E) glass in curtain wall applications. Low-E glass features a microscopically thin, transparent coating that reflects infrared heat, significantly reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency by minimizing solar heat gain and heat loss. Curtain walls utilizing Low-E glass demonstrate superior thermal performance, achieving better U-values and reducing HVAC energy costs compared to laminated glass.
Safety and Security Features
Laminated glass offers superior safety and security for curtain walls by holding shattered pieces together upon impact, reducing the risk of injury and unauthorized entry. Low-emissivity (Low-E) glass primarily enhances energy efficiency by minimizing heat transfer but provides limited safety benefits compared to laminated glass. Combining laminated glass with Low-E coatings can optimize curtain wall performance, delivering both enhanced security and energy savings.
Acoustic Insulation Capabilities
Laminated glass offers superior acoustic insulation for curtain walls due to its interlayer that dampens sound vibrations, effectively reducing noise transmission from external environments. Low-emissivity (Low-E) glass primarily enhances thermal performance by reflecting infrared energy but provides limited acoustic insulation compared to laminated glass. Combining laminated glass with Low-E coatings can optimize curtain wall performance by balancing soundproofing with energy efficiency.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Laminated glass and low-emissivity (Low-E) glass both enhance curtain wall performance but differ in energy efficiency and sustainability impacts. Low-E glass maximizes energy efficiency by reflecting infrared radiation, reducing heat transfer significantly and lowering heating and cooling costs in buildings. Laminated glass offers improved safety and sound insulation with moderate thermal benefits, contributing to sustainability by enhancing building durability and occupant comfort while enabling the integration of Low-E coatings for optimized energy performance.
Cost Considerations: Laminated vs Low-E Glass
Laminated glass typically incurs higher initial costs due to its multi-layer construction involving a plastic interlayer that enhances safety and sound insulation, whereas low-emissivity (Low-E) glass often commands premium pricing because of its specialized coating that significantly improves thermal efficiency. Low-E glass reduces energy expenses by minimizing heat transfer, potentially offsetting its upfront price with long-term savings, while laminated glass's primary cost justification lies in enhanced durability and security rather than energy efficiency. Budgeting for curtain wall projects requires balancing the upfront investment in laminated or Low-E glass against their distinct performance benefits and lifecycle cost impacts.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Laminated glass offers superior design flexibility for curtain walls due to its ability to incorporate various interlayers that enhance color, texture, and light diffusion, enabling unique aesthetic effects. Low-emissivity (Low-E) glass excels in maintaining clear visibility and neutral color tones while improving energy efficiency, which preserves the architectural design intent without compromising exterior appearance. Both glass types support innovative curtain wall designs, but laminated glass is preferred when custom visual effects and layered depth are prioritized.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Curtain Wall Project
Choosing the right glass for your curtain wall project involves understanding the distinct benefits of laminated glass and low-emissivity (Low-E) glass. Laminated glass offers enhanced safety and sound insulation with its multiple layers bonded by interlayers, making it ideal for impact resistance and security. Low-E glass, coated with microscopically thin metallic layers, improves energy efficiency by minimizing heat transfer, thus reducing heating and cooling costs while allowing optimal natural light penetration.
Infographic: Laminated glass vs Low-emissivity glass for Curtain wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com