Recycled glass used in safety glass reduces environmental impact and energy consumption, while laminated glass offers superior strength and shatter resistance by bonding multiple glass layers with an interlayer. Laminated glass is preferred for automotive and architectural safety applications due to its ability to hold shards in place upon impact.
Table of Comparison
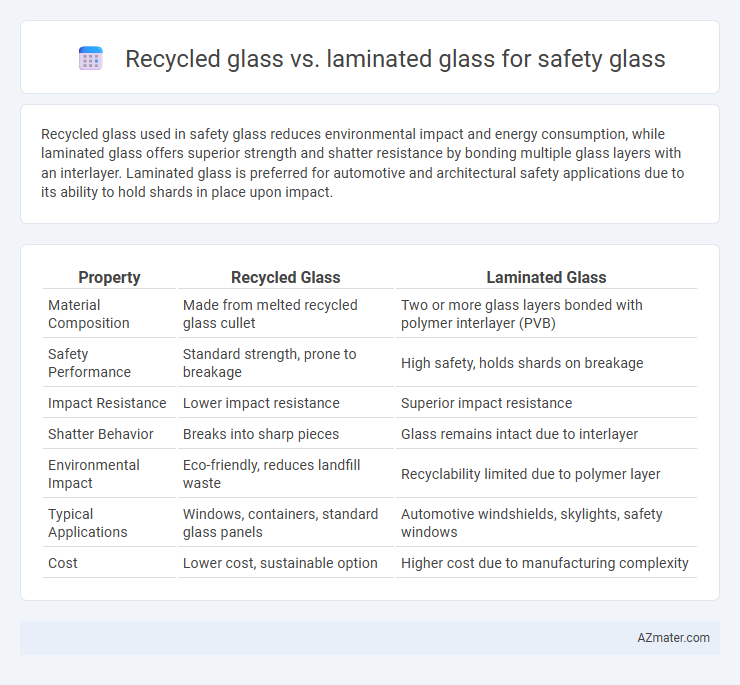
| Property | Recycled Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Made from melted recycled glass cullet | Two or more glass layers bonded with polymer interlayer (PVB) |
| Safety Performance | Standard strength, prone to breakage | High safety, holds shards on breakage |
| Impact Resistance | Lower impact resistance | Superior impact resistance |
| Shatter Behavior | Breaks into sharp pieces | Glass remains intact due to interlayer |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, reduces landfill waste | Recyclability limited due to polymer layer |
| Typical Applications | Windows, containers, standard glass panels | Automotive windshields, skylights, safety windows |
| Cost | Lower cost, sustainable option | Higher cost due to manufacturing complexity |
Introduction to Safety Glass: Recycled vs Laminated
Safety glass incorporates materials designed to prevent injury upon impact, with recycled glass and laminated glass serving distinct roles in this domain. Recycled glass enhances environmental sustainability by reducing energy consumption and raw material use, while laminated glass provides superior safety through multiple layers bonded with a plastic interlayer that holds shards together. Both types meet stringent safety standards, but laminated glass offers enhanced impact resistance and clarity, making it preferable for automotive and architectural applications.
What is Recycled Glass? Key Properties and Uses
Recycled glass is made from post-consumer or industrial glass waste that is melted and remolded into new glass products, retaining high durability and environmental benefits such as reduced energy consumption and lower carbon emissions. Key properties of recycled glass include excellent clarity, resistance to chemicals, and the ability to be tempered or laminated for enhanced safety applications. Common uses of recycled glass in safety glass involve windows, doors, and facades in buildings, where it offers sustainable strength and impact resistance comparable to traditional laminated glass.
Understanding Laminated Glass: Structure and Benefits
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together by an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced safety by holding shards in place upon impact. This structure offers superior resistance to penetration, noise reduction, and UV protection compared to recycled glass. The combination of durability and safety makes laminated glass an ideal choice for automotive windshields, building facades, and safety glazing applications.
Strength and Impact Resistance: Comparing Both Types
Recycled glass used in safety glass often involves incorporating post-consumer glass cullet, which can be engineered to maintain high strength and durability, though its performance depends on the specific composition and manufacturing process. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing superior impact resistance by holding shattered shards together and enhancing overall strength. While laminated glass generally outperforms recycled glass in impact resistance and fracture control, advancements in recycled glass processing have improved its strength, making it a viable eco-friendly option for certain safety glass applications.
Safety Performance in Real-World Applications
Recycled glass safety glass demonstrates comparable impact resistance and shatterproof qualities to laminated glass, making it a sustainable yet reliable option for real-world applications. Laminated glass, composed of multiple glass layers bonded by interlayers like PVB, excels in preventing glass shards from dispersing upon impact, enhancing occupant safety in automotive and architectural settings. Both materials meet stringent safety standards such as ANSI Z97.1 and EN 12600, with laminated glass providing superior post-impact integrity due to its layered structure, while recycled glass offers strong environmental benefits without compromising fundamental safety requirements.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Recycling
Recycled glass safety glass significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and raw material use compared to laminated glass, which relies heavily on virgin materials and complex manufacturing processes. The recycling process for recycled glass safety glass enables the material to be reused multiple times without compromising structural integrity, promoting sustainability. Laminated glass, while offering superior safety features, poses challenges in recycling due to its multi-layer composition, often resulting in landfill waste and higher carbon footprints.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Long-Term Value
Recycled glass offers a cost-effective solution for safety glass with lower initial installation expenses due to its availability and manufacturing efficiency. Laminated glass, while higher in upfront cost, provides enhanced durability and impact resistance, translating into lower maintenance and replacement costs over time. The long-term value of laminated glass is amplified by its superior safety performance, making it a preferred investment for critical applications despite higher installation costs.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Recycled glass offers a unique, eco-friendly aesthetic with its subtle color variations and textures, enhancing the visual appeal of safety glass in sustainable design projects. Laminated glass provides superior design flexibility, allowing incorporation of interlayers in various hues, patterns, and opacities to achieve customized visual effects while maintaining structural integrity. The combination of recycled glass's distinct appearance and laminated glass's versatile layering options supports innovative and stylish safety glass solutions for modern architecture.
Common Applications in Construction and Architecture
Recycled glass safety glass is commonly used in sustainable construction projects and eco-friendly architectural designs due to its environmental benefits and aesthetic versatility. Laminated glass predominates in structural applications requiring high impact resistance and enhanced security, such as storefronts, skylights, and balustrades. Both materials meet safety standards but differ in energy efficiency and recyclability, influencing their selection in green building initiatives versus high-performance safety requirements.
Choosing the Right Safety Glass: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right safety glass involves evaluating factors such as impact resistance, environmental impact, and clarity. Recycled glass offers eco-friendly benefits with good strength but may have slight variations in clarity compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass provides superior impact resistance and retention of glass shards upon breakage, making it a reliable choice for enhanced safety in automotive and architectural applications.
Infographic: Recycled glass vs Laminated glass for Safety glass
 azmater.com
azmater.com