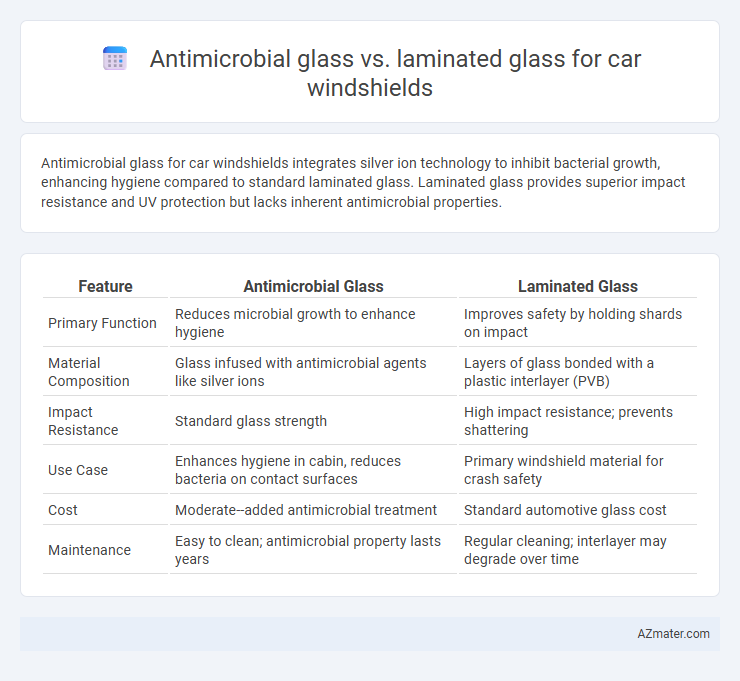
Antimicrobial glass for car windshields integrates silver ion technology to inhibit bacterial growth, enhancing hygiene compared to standard laminated glass. Laminated glass provides superior impact resistance and UV protection but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Antimicrobial Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Reduces microbial growth to enhance hygiene | Improves safety by holding shards on impact |
| Material Composition | Glass infused with antimicrobial agents like silver ions | Layers of glass bonded with a plastic interlayer (PVB) |
| Impact Resistance | Standard glass strength | High impact resistance; prevents shattering |
| Use Case | Enhances hygiene in cabin, reduces bacteria on contact surfaces | Primary windshield material for crash safety |
| Cost | Moderate--added antimicrobial treatment | Standard automotive glass cost |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean; antimicrobial property lasts years | Regular cleaning; interlayer may degrade over time |
Introduction to Car Windshield Technologies
Car windshield technologies have evolved to enhance safety, durability, and hygiene, with antimicrobial glass and laminated glass representing two advanced options. Antimicrobial glass incorporates agents that inhibit bacterial and viral growth, making it ideal for reducing pathogen transmission inside vehicles. Laminated glass consists of multiple layers bonded with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) for impact resistance and shatter prevention, ensuring structural integrity during accidents.
What is Antimicrobial Glass?
Antimicrobial glass for car windshields incorporates a special coating or embedded agents that inhibit the growth of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, enhancing hygiene and safety inside the vehicle. Unlike laminated glass, which primarily provides impact resistance and shatterproof properties through layered construction with an interlayer, antimicrobial glass adds functional protection against microbial contamination. This advanced glass technology is particularly beneficial in reducing surface-borne pathogens, making it ideal for vehicles requiring higher standards of cleanliness.
Understanding Laminated Glass
Laminated glass for car windshields consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced safety by preventing shattering upon impact. This structure improves resistance to penetration and noise reduction, making it a standard choice in automotive applications. Unlike antimicrobial glass, which is treated to inhibit microbial growth, laminated glass primarily focuses on structural integrity and occupant protection during collisions.
Key Differences: Antimicrobial vs Laminated Glass
Antimicrobial glass integrates a specially treated surface designed to inhibit the growth of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, enhancing hygiene and reducing the risk of cross-contamination in car windshields. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, offering superior impact resistance, shatter protection, and UV filtering capabilities essential for vehicle safety. While laminated glass prioritizes structural durability and passenger protection during collisions, antimicrobial glass emphasizes maintaining a cleaner, germ-free surface for improved health and safety.
Safety Features and Crash Protection
Antimicrobial glass for car windshields integrates a surface coating that inhibits bacterial growth, enhancing hygiene but offering similar impact resistance as standard laminated glass. Laminated glass consists of two glass layers bonded by a flexible interlayer, providing superior crash protection by preventing shattering and reducing injury risks during collisions. While antimicrobial glass improves cabin safety from microbial exposure, laminated glass remains essential for structural integrity and occupant protection in accidents.
Health Benefits of Antimicrobial Glass
Antimicrobial glass used in car windshields inhibits the growth of bacteria, viruses, and fungi on the glass surface, significantly reducing the risk of pathogen transmission inside the vehicle. This glass type maintains a cleaner and safer environment by preventing microbial contamination, which is especially crucial for individuals with allergies or weakened immune systems. Unlike traditional laminated glass, antimicrobial glass enhances hygiene without compromising visibility or durability, promoting overall health and well-being for passengers.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Antimicrobial glass for car windshields incorporates copper or silver ions that inhibit microbial growth, enhancing hygiene without compromising structural integrity, typically offering durability comparable to standard laminated glass. Laminated glass consists of two glass layers bonded with a PVB interlayer, providing superior impact resistance, crack prevention, and longer lifespan under harsh conditions. While antimicrobial glass adds health benefits, laminated glass remains the industry standard for durability and extended lifespan due to its enhanced resistance to shattering and environmental stress.
Cost Analysis: Which Is More Affordable?
Antimicrobial glass for car windshields typically costs 20-30% more than laminated glass due to the incorporation of silver ions or other antimicrobial agents in the manufacturing process. Laminated glass, a standard industry choice, combines two layers of glass with a plastic interlayer, offering durability and safety at a lower price point, usually ranging between $100 to $400 per replacement. For budget-conscious consumers, laminated glass remains the more affordable option, while antimicrobial glass caters to those prioritizing hygiene and protection against microbial growth despite the higher cost.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Antimicrobial glass for car windshields integrates nanosilver or copper ions, reducing the need for chemical cleaning agents, which lowers environmental pollution and enhances sustainability. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers including polyvinyl butyral (PVB), offers durability and recyclability but involves more energy-intensive manufacturing and disposal processes. Selecting antimicrobial glass minimizes chemical waste and energy consumption, promoting eco-friendly automotive solutions.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Car Windshield
Antimicrobial glass for car windshields offers enhanced hygiene by inhibiting bacterial growth on the surface, making it ideal for vehicles frequently used by multiple passengers or in public transportation. Laminated glass provides superior safety by combining layers of glass and plastic, preventing shards from scattering during impact and improving structural integrity. Choosing the right glass depends on prioritizing either health benefits or crash safety, with laminated glass being the standard for most vehicles while antimicrobial coating serves as an excellent supplementary feature.
Infographic: Antimicrobial glass vs Laminated glass for Car windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com