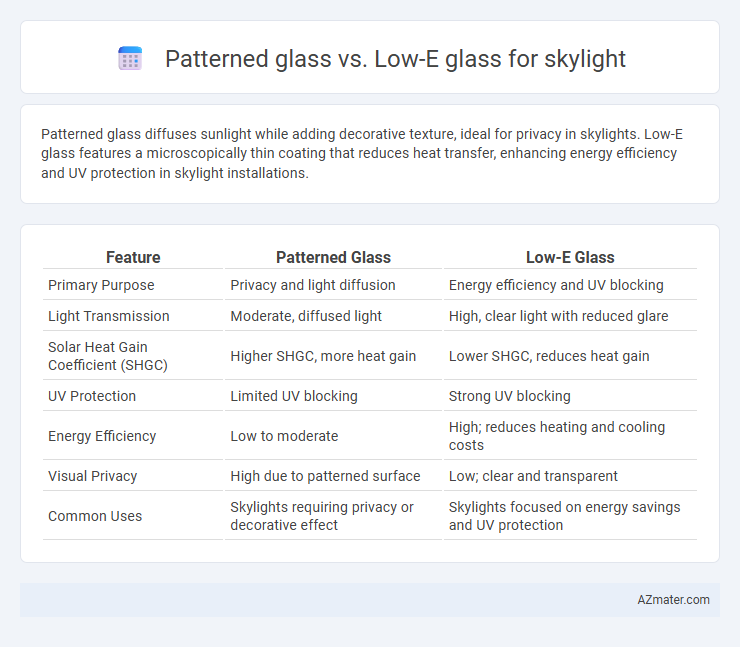
Patterned glass diffuses sunlight while adding decorative texture, ideal for privacy in skylights. Low-E glass features a microscopically thin coating that reduces heat transfer, enhancing energy efficiency and UV protection in skylight installations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Patterned Glass | Low-E Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Privacy and light diffusion | Energy efficiency and UV blocking |
| Light Transmission | Moderate, diffused light | High, clear light with reduced glare |
| Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) | Higher SHGC, more heat gain | Lower SHGC, reduces heat gain |
| UV Protection | Limited UV blocking | Strong UV blocking |
| Energy Efficiency | Low to moderate | High; reduces heating and cooling costs |
| Visual Privacy | High due to patterned surface | Low; clear and transparent |
| Common Uses | Skylights requiring privacy or decorative effect | Skylights focused on energy savings and UV protection |
Introduction: The Importance of Skylight Glass Selection
Skylight glass selection significantly impacts energy efficiency, natural light diffusion, and interior comfort. Patterned glass provides unique textures that enhance privacy and reduce glare, while Low-E glass offers superior thermal insulation by reflecting infrared heat and minimizing UV radiation. Choosing the right skylight glass balances aesthetics with performance, ensuring optimal daylighting and energy savings.
What is Patterned Glass?
Patterned glass for skylights features textured surfaces that diffuse natural light, reducing glare while maintaining privacy and obscuring visibility from outside. Unlike Low-E glass, which has a special coating to minimize heat transfer and improve energy efficiency, patterned glass primarily enhances aesthetics and light distribution. It is ideal for spaces requiring both illumination and visual screening without compromising on style or natural brightness.
Understanding Low-E Glass Technology
Low-E glass for skylights features a microscopically thin coating that reflects infrared heat while allowing visible light to pass through, significantly improving energy efficiency by reducing heat gain in summer and heat loss in winter. Patterned glass, while offering privacy and decorative appeal, lacks the advanced thermal control provided by Low-E coatings. Understanding Low-E glass technology reveals its capacity to maintain indoor comfort, lower energy bills, and protect furnishings from UV damage, making it an optimal choice for energy-conscious skylight installations.
Light Transmission: Patterned Glass vs Low-E Glass
Patterned glass for skylights offers moderate light transmission with a textured surface that diffuses sunlight, reducing glare and enhancing privacy. Low-E glass features a specialized coating that maximizes visible light transmission while minimizing infrared and ultraviolet rays, improving energy efficiency without compromising natural daylight. Choosing between patterned glass and Low-E glass depends on the balance between aesthetics, light diffusion, and thermal performance desired for the skylight.
Energy Efficiency and Thermal Performance
Patterned glass in skylights diffuses sunlight, reducing glare while offering moderate insulation, but it generally has lower thermal performance compared to Low-E glass. Low-E (low-emissivity) glass features a microscopically thin metallic coating that reflects infrared heat, significantly enhancing energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. This superior thermal regulation reduces HVAC costs and improves indoor comfort, making Low-E glass the preferred choice for energy-efficient skylight installations.
Privacy and Aesthetic Considerations
Patterned glass offers enhanced privacy for skylights by obscuring visibility while diffusing natural light, making it ideal for spaces requiring discretion. Low-E glass optimizes energy efficiency and clarity, maintaining clear views with minimal heat transfer but provides limited privacy without additional treatments. Choosing between patterned and Low-E glass depends on the balance desired between privacy needs and aesthetic preferences for daylight diffusion or transparency.
UV Protection and Fading Resistance
Patterned glass offers moderate UV protection by diffusing sunlight but allows some UV rays to penetrate, potentially contributing to fading of interior furnishings. Low-E glass contains a microscopically thin metallic coating that significantly blocks UV radiation, reducing fading and protecting interior materials from sun damage. For skylights, Low-E glass provides superior UV protection and enhanced fading resistance, making it a more effective choice for preserving indoor aesthetics.
Cost Comparison: Initial Investment and Long-term Savings
Patterned glass skylights typically have a lower initial cost due to simpler manufacturing processes, making them more budget-friendly upfront compared to Low-E glass. Low-E glass, while more expensive initially, offers superior energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer, resulting in significant long-term savings on heating and cooling expenses. Over time, the investment in Low-E glass often pays off through reduced utility bills and enhanced thermal comfort, outweighing the higher upfront cost.
Maintenance and Durability of Both Glass Types
Patterned glass for skylights offers enhanced privacy and can mask dirt or streaks, reducing visible maintenance but may require regular cleaning to prevent buildup in textured surfaces. Low-E glass features a durable coating that resists fading and damage from UV rays, minimizing wear and maintaining thermal efficiency over time with low maintenance. Both glass types provide durability, but Low-E glass generally outperforms patterned glass in longevity due to its specialized energy-saving coating and resistance to environmental stressors.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Skylight Needs
Patterned glass offers enhanced privacy and diffuses natural light, reducing glare and adding decorative appeal to skylights, making it ideal for spaces requiring both aesthetics and light control. Low-E glass features a special coating that reflects infrared and ultraviolet rays, improving energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss and reducing solar heat gain, perfect for maintaining consistent indoor temperatures. Selecting between patterned and Low-E glass depends on your priorities: opt for patterned glass to balance light diffusion with privacy or choose Low-E glass to optimize thermal performance and energy savings in your skylight.
Infographic: Patterned glass vs Low-E glass for Skylight
 azmater.com
azmater.com