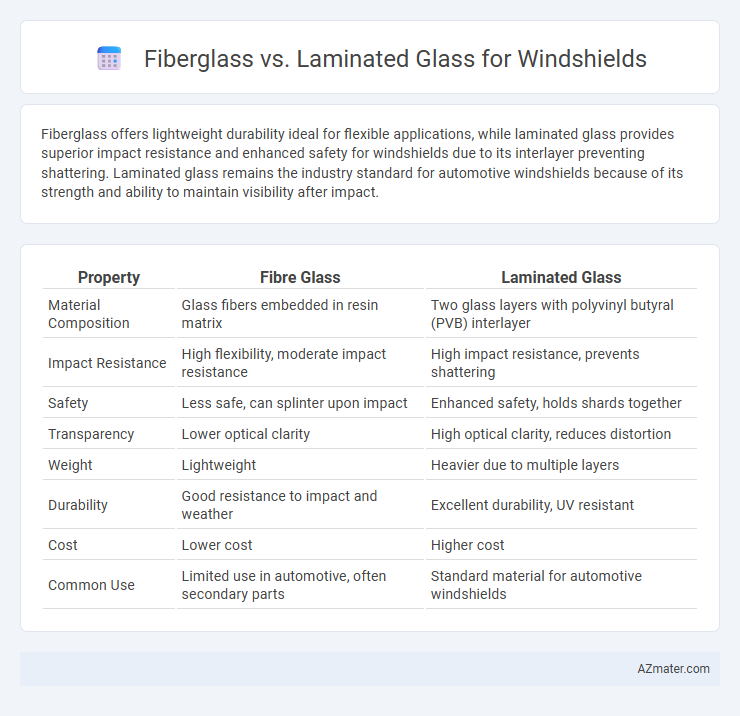
Fiberglass offers lightweight durability ideal for flexible applications, while laminated glass provides superior impact resistance and enhanced safety for windshields due to its interlayer preventing shattering. Laminated glass remains the industry standard for automotive windshields because of its strength and ability to maintain visibility after impact.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fibre Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Glass fibers embedded in resin matrix | Two glass layers with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer |
| Impact Resistance | High flexibility, moderate impact resistance | High impact resistance, prevents shattering |
| Safety | Less safe, can splinter upon impact | Enhanced safety, holds shards together |
| Transparency | Lower optical clarity | High optical clarity, reduces distortion |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to multiple layers |
| Durability | Good resistance to impact and weather | Excellent durability, UV resistant |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Common Use | Limited use in automotive, often secondary parts | Standard material for automotive windshields |
Introduction to Windshield Materials
Windshields utilize advanced materials like fiberglass and laminated glass to ensure durability and safety. Fiberglass offers high tensile strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for lightweight and flexible applications. Laminated glass, consisting of two glass layers bonded by a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, provides superior shatter resistance and UV protection essential for automotive windshields.
What is Fiberglass Glass?
Fiberglass glass is a composite material made from fine glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, offering high tensile strength and lightweight properties. Unlike laminated glass, which consists of two or more glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer for impact resistance, fiberglass provides enhanced flexibility and resistance to cracking under stress. Its unique structure makes fiberglass suitable for applications requiring durability and shock absorption, but it lacks the optical clarity and direct impact protection that laminated glass windshield offers.
Understanding Laminated Glass
Laminated glass, consisting of two layers of glass bonded by an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), offers superior safety and durability compared to fiberglass. It effectively absorbs impact, preventing shattering and maintaining windshield integrity in accidents. This enhances occupant protection and reduces the risk of injury from flying glass fragments.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Fiberglass windshields are composed of woven glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, offering a lightweight yet durable structure through a curing process that solidifies the composite material. Laminated glass consists of two layers of glass with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, manufactured using heat and pressure to bond the layers, enhancing safety by preventing shattering upon impact. The manufacturing of fiberglass involves mold shaping and resin infusion, while laminated glass production emphasizes controlled lamination and tempering techniques for clarity and strength.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Fiberglass windshields offer enhanced impact resistance due to their composite material structure, making them less prone to shattering under stress, while laminated glass provides superior durability through its multi-layered construction, which holds shards together upon impact, greatly improving safety. Laminated glass typically exceeds fiberglass in long-term weather resistance and UV protection, maintaining optical clarity and structural integrity over time. Strength tests reveal laminated glass withstands higher force thresholds without penetration, making it the preferred choice for automotive windshields where durability and occupant protection are critical.
Safety Features of Each Material
Fiberglass windshields offer enhanced impact resistance and flexibility, absorbing shocks effectively to reduce the risk of shattering during collisions. Laminated glass consists of two glass layers bonded by a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, providing superior safety by preventing glass shards from dispersing upon impact. The PVB layer in laminated glass also enhances UV protection and maintains structural integrity, making it the preferred choice for automotive windshields in terms of occupant safety.
Cost Analysis: Fiberglass vs Laminated Glass
Fiberglass windshields typically have a lower upfront cost compared to laminated glass, making them a budget-friendly option for vehicle repairs. Laminated glass, while more expensive initially, offers better durability and enhanced safety features, potentially reducing long-term replacement and repair expenses. Cost analysis shows that laminated glass provides greater value over time due to its resistance to shattering and improved impact absorption.
UV and Weather Resistance
Fiberglass windshields offer excellent UV resistance due to their resin matrix, preventing degradation from prolonged sun exposure, while laminated glass provides superior weather resistance with its interlayer preventing moisture penetration and enhancing durability in harsh conditions. Laminated glass also reduces UV radiation transmission by up to 99%, protecting vehicle interiors and occupants from harmful rays. Fiberglass's flexibility allows it to withstand temperature fluctuations without cracking, whereas laminated glass maintains structural integrity under extreme weather variations.
Repair and Replacement Considerations
Fiberglass windshields offer easier repair options due to their flexible resin composition, allowing minor cracks and chips to be fixed without full replacement. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers with a plastic interlayer, provides enhanced safety but typically requires complete replacement when damaged, as repairs are often ineffective. Repair costs for laminated glass are higher, and delays in addressing damage can compromise structural integrity and occupant protection.
Best Choice for Automotive Windshields
Laminated glass is the best choice for automotive windshields due to its superior safety features, consisting of two glass layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that prevents shattering upon impact. Fiberglass, while strong and lightweight, lacks the transparency and shatter-resistant qualities essential for clear visibility and passenger protection in vehicles. The automotive industry favors laminated glass for windshields because it combines durability, safety, and compliance with safety regulations.
Infographic: Fibre glass vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com