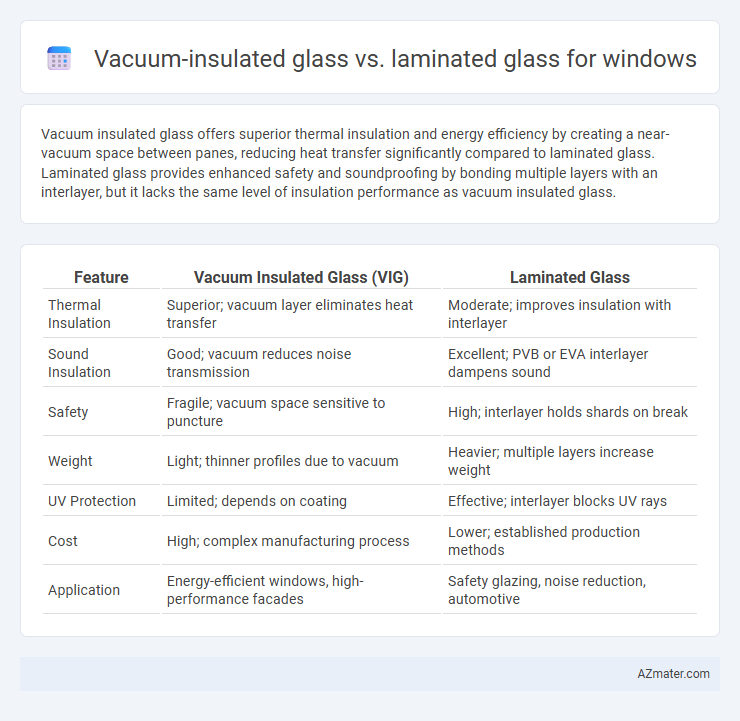
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency by creating a near-vacuum space between panes, reducing heat transfer significantly compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass provides enhanced safety and soundproofing by bonding multiple layers with an interlayer, but it lacks the same level of insulation performance as vacuum insulated glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Superior; vacuum layer eliminates heat transfer | Moderate; improves insulation with interlayer |
| Sound Insulation | Good; vacuum reduces noise transmission | Excellent; PVB or EVA interlayer dampens sound |
| Safety | Fragile; vacuum space sensitive to puncture | High; interlayer holds shards on break |
| Weight | Light; thinner profiles due to vacuum | Heavier; multiple layers increase weight |
| UV Protection | Limited; depends on coating | Effective; interlayer blocks UV rays |
| Cost | High; complex manufacturing process | Lower; established production methods |
| Application | Energy-efficient windows, high-performance facades | Safety glazing, noise reduction, automotive |
Introduction to Vacuum Insulated Glass and Laminated Glass
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum layer, providing superior thermal insulation and reducing heat transfer through windows. Laminated glass is made by bonding two or more glass layers with an interlayer, enhancing safety, sound insulation, and UV protection while maintaining structural integrity. Both materials offer distinct benefits, with VIG excelling in energy efficiency and laminated glass prioritizing impact resistance and security.
How Vacuum Insulated Glass Works
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum that eliminates conductive and convective heat transfer, significantly enhancing thermal insulation compared to laminated glass. The vacuum space prevents heat loss, while ultra-thin spacers maintain the gap without compromising clarity or strength. Unlike laminated glass, which primarily offers impact resistance and sound insulation through interlayers, VIG targets superior energy efficiency by minimizing heat flow in windows.
Understanding Laminated Glass Technology
Laminated glass technology involves bonding two or more layers of glass with a durable interlayer, usually polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which provides enhanced safety, sound insulation, and UV protection. Unlike vacuum insulated glass, which focuses on thermal insulation through a vacuum layer, laminated glass excels in impact resistance and prevents glass shards from scattering upon breakage. This technology is widely used in automotive, architectural, and security applications for its combination of strength and safety.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal insulation by creating a near-vacuum space between glass panes, significantly reducing heat transfer compared to laminated glass, which relies on layers of glass and polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayers primarily for safety and soundproofing. VIG achieves U-values as low as 0.5 W/m2K, outperforming laminated glass typical U-values around 2.7 W/m2K, indicating better thermal resistance and energy efficiency. This enhanced thermal performance makes vacuum insulated glass ideal for climates requiring stringent heat retention or cooling efficiency in windows.
Acoustic Insulation: Which Glass Performs Better?
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) provides superior acoustic insulation compared to laminated glass due to its vacuum layer, which eliminates airborne sound transmission effectively. Laminated glass, while effective at reducing impact noise through its interlayer, cannot match the near-soundproof barrier created by the vacuum space in VIG. For environments requiring maximum noise reduction, VIG offers a more advanced solution by minimizing sound wave passage through the window assembly.
Safety and Security Features
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior impact resistance and shatterproof qualities, enhancing window safety by minimizing breakage risks during accidents or intrusions. Laminated glass incorporates a durable interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, preventing injury and deterring forced entry effectively. Both technologies improve security, but laminated glass excels in stopping penetration attempts, while vacuum insulated glass focuses more on thermal insulation with added structural integrity.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior energy efficiency by creating an insulating vacuum between glass panes, significantly reducing heat transfer and lowering heating and cooling costs compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass provides moderate energy savings through its soundproofing and UV filtering properties but lacks the thermal insulation capacity of vacuum insulated glass. Although vacuum insulated glass has higher upfront costs, its enhanced energy efficiency results in greater long-term cost savings on energy bills.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior durability due to its airtight seal preventing moisture ingress and gas leakage, significantly reducing the risk of fogging and thermal degradation over time. Laminated glass, composed of multiple glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, provides excellent impact resistance and safety but may delaminate or discolor under prolonged UV exposure if not properly maintained. Maintenance for vacuum insulated glass involves ensuring the integrity of the vacuum seal, while laminated glass requires regular inspection for interlayer damage and edge seal deterioration to maintain long-term performance.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers a sleek, minimalist appearance with ultra-thin profiles that enhance modern architectural aesthetics, providing superior transparency and light transmission compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass allows for extensive design flexibility by incorporating decorative interlayers such as colored films, patterns, or textures to create customized visual effects while maintaining structural safety. Both options support contemporary window designs, but VIG excels in delivering unobstructed views with a slim frame, whereas laminated glass provides more versatility in aesthetic customization and privacy features.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Windows
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation by utilizing a vacuum space between glass panes, effectively reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency in windows. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers bonded with an interlayer, enhances safety and sound insulation while providing UV protection and resistance to impact. Selecting the right glass depends on prioritizing energy savings with vacuum insulated glass or emphasizing safety and noise reduction with laminated glass for your windows.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Laminated glass for Window
 azmater.com
azmater.com