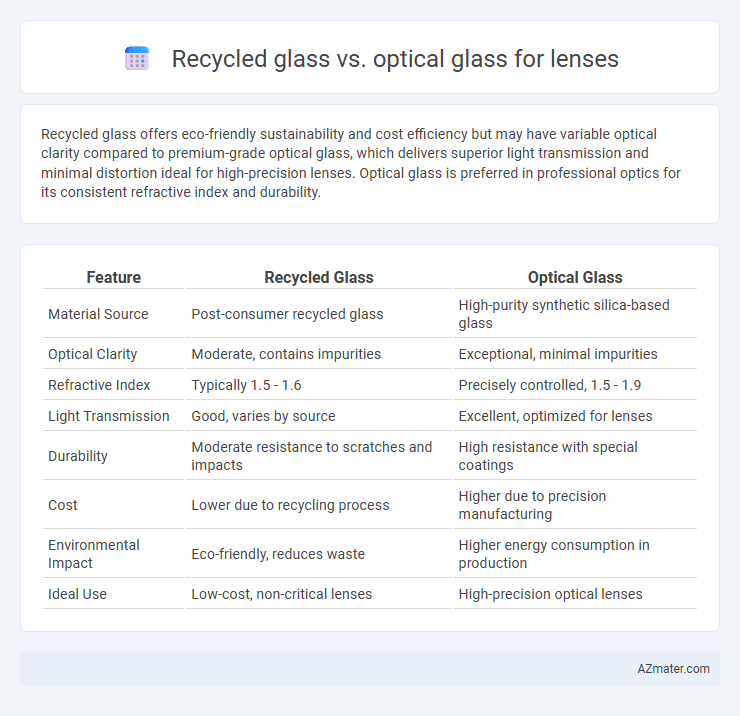
Recycled glass offers eco-friendly sustainability and cost efficiency but may have variable optical clarity compared to premium-grade optical glass, which delivers superior light transmission and minimal distortion ideal for high-precision lenses. Optical glass is preferred in professional optics for its consistent refractive index and durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Glass | Optical Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-consumer recycled glass | High-purity synthetic silica-based glass |
| Optical Clarity | Moderate, contains impurities | Exceptional, minimal impurities |
| Refractive Index | Typically 1.5 - 1.6 | Precisely controlled, 1.5 - 1.9 |
| Light Transmission | Good, varies by source | Excellent, optimized for lenses |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to scratches and impacts | High resistance with special coatings |
| Cost | Lower due to recycling process | Higher due to precision manufacturing |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, reduces waste | Higher energy consumption in production |
| Ideal Use | Low-cost, non-critical lenses | High-precision optical lenses |
Introduction to Glass Types in Lens Manufacturing
Recycled glass offers an eco-friendly alternative in lens manufacturing by reducing raw material consumption and energy use, while optical glass provides superior clarity and precise refractive properties essential for high-performance lenses. The fundamental difference lies in the chemical composition and purity, with optical glass engineered for consistent light transmission and minimal distortion. Selecting between recycled and optical glass depends on balancing environmental impact with optical precision required for specific lens applications.
What is Recycled Glass?
Recycled glass is made from post-consumer or industrial glass waste that is melted down and reformed to create new glass products, including lenses. This environmentally friendly material conserves natural resources and reduces energy consumption compared to producing optical glass from raw silica. While recycled glass offers sustainability benefits, optical glass is specifically engineered for high precision, clarity, and refractive properties essential in premium lens manufacturing.
What is Optical Glass?
Optical glass is a high-purity material specifically engineered for superior light transmission, minimal distortion, and precise refractive properties essential in lens manufacturing. Unlike recycled glass, which may contain impurities affecting clarity and consistency, optical glass offers controlled chemical composition and properties tailored for critical applications in photography, microscopy, and optics. Its specialized formulations enhance image resolution, color fidelity, and durability, making it the preferred choice in high-performance optical lenses.
Raw Material Sources and Sustainability
Recycled glass for lenses is sourced from post-consumer and industrial glass waste, reducing landfill impact and lowering energy consumption during reprocessing, which enhances sustainability compared to optical glass made from virgin raw materials like high-purity silica sand and specialty additives. Optical glass production requires extensive mining and refining processes, contributing to higher carbon emissions and resource depletion. Using recycled glass supports circular economy principles by minimizing raw material extraction and promoting eco-friendly lens manufacturing.
Clarity and Optical Performance Comparison
Recycled glass lenses often exhibit lower optical clarity and increased impurities compared to optical glass, which is engineered for high precision and minimal distortion. Optical glass offers superior refractive index consistency and enhanced light transmission, resulting in sharper focus and reduced chromatic aberration. Studies show that while recycled glass provides cost-effective sustainability benefits, it falls short in delivering the precise optical performance demanded in advanced lens applications.
Durability and Lifespan of Lenses
Recycled glass lenses offer decent durability but generally have lower resistance to scratches and impact compared to optical glass, which is specifically engineered for superior hardness and longevity in lens applications. Optical glass, composed of high-purity materials with precise refractive indices, ensures prolonged lifespan by maintaining clarity and structural integrity under constant use. The enhanced durability of optical glass translates into better performance stability for cameras, microscopes, and eyeglasses, making it the preferred choice for high-quality lens manufacturing.
Environmental Impact: Recycled vs Optical Glass
Recycled glass lenses significantly reduce environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to optical glass, which requires intensive mining and refining processes. Utilizing recycled glass decreases landfill waste and conserves raw materials, promoting sustainable production within the optics industry. Optical glass manufacturing relies heavily on high-purity raw materials, resulting in higher carbon footprints and resource depletion relative to recycled alternatives.
Cost Factors and Production Efficiency
Recycled glass for lenses significantly reduces raw material costs compared to optical-grade glass, making it a cost-effective alternative in large-scale production. Optical glass requires precise formulation and refining processes to achieve high purity and consistent refractive indices, which increase manufacturing expenses and reduce production efficiency. Using recycled glass improves sustainability and lowers energy consumption during melting, accelerating production cycles without compromising basic optical quality in non-critical applications.
Applications: When to Use Recycled or Optical Glass
Recycled glass lenses are ideal for eco-friendly and cost-effective optical components in applications such as decorative eyewear, low-precision lenses, and light diffusers, where sustainability outweighs the need for high optical clarity. Optical glass, known for its superior refractive index and minimal impurities, is essential in high-precision instruments like microscopes, cameras, and binoculars, ensuring accurate light transmission and image quality. Choosing between recycled and optical glass depends primarily on the required optical performance, budget constraints, and environmental considerations.
Future Trends in Glass Lens Technology
Recycled glass offers an eco-friendly alternative for lens production, reducing raw material consumption and carbon footprint, while optical glass continues to provide superior clarity and precise refractive properties essential for advanced lens applications. Future trends focus on hybrid materials combining recycled and optical glass to enhance sustainability without compromising optical performance, supported by innovations in nano-coatings and smart lens technology. Research in lightweight, durable composites and environmentally conscious manufacturing processes is driving the evolution of glass lens technology toward greener, high-efficiency solutions.
Infographic: Recycled glass vs Optical glass for Lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com