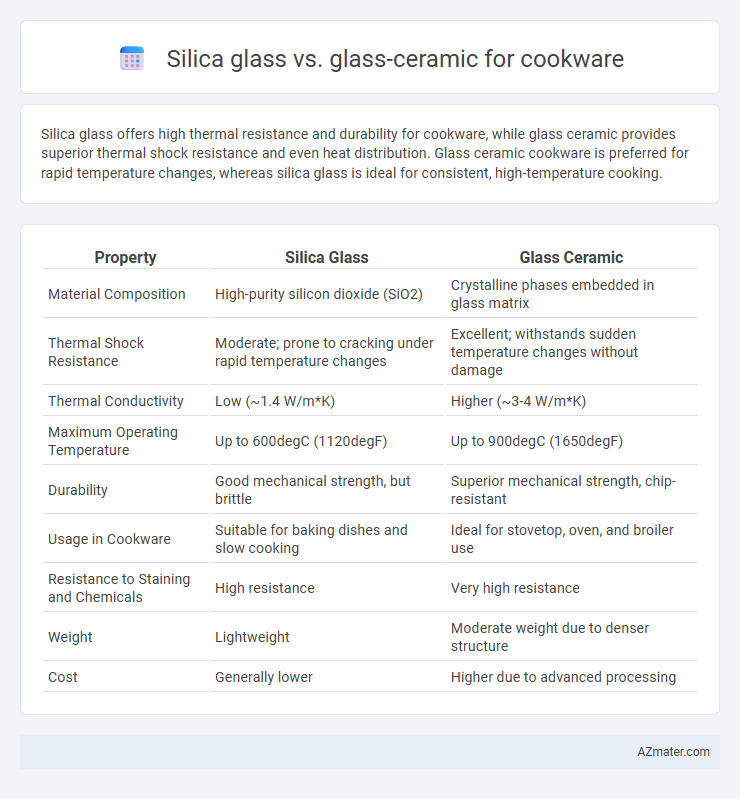
Silica glass offers high thermal resistance and durability for cookware, while glass ceramic provides superior thermal shock resistance and even heat distribution. Glass ceramic cookware is preferred for rapid temperature changes, whereas silica glass is ideal for consistent, high-temperature cooking.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silica Glass | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-purity silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Crystalline phases embedded in glass matrix |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate; prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes | Excellent; withstands sudden temperature changes without damage |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (~1.4 W/m*K) | Higher (~3-4 W/m*K) |
| Maximum Operating Temperature | Up to 600degC (1120degF) | Up to 900degC (1650degF) |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength, but brittle | Superior mechanical strength, chip-resistant |
| Usage in Cookware | Suitable for baking dishes and slow cooking | Ideal for stovetop, oven, and broiler use |
| Resistance to Staining and Chemicals | High resistance | Very high resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight | Moderate weight due to denser structure |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to advanced processing |
Introduction to Silica Glass and Glass Ceramic Cookware
Silica glass cookware is composed primarily of silicon dioxide, offering high thermal resistance and excellent chemical durability, making it ideal for transparent, non-porous cooking surfaces. Glass ceramic cookware, made from specially treated glass containing crystalline phases, exhibits superior thermal shock resistance and durability, enabling it to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. Both materials are non-reactive and provide safe, versatile options for stovetop and oven use, with glass ceramics generally favored for their mechanical strength and temperature stability.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Silica glass cookware is primarily composed of high-purity silicon dioxide (SiO2), produced through a melting process that creates a non-porous, transparent material with excellent thermal resistance. Glass ceramics are made by controlled crystallization of glass, involving nucleation and crystal growth phases that result in a material with fine-grained crystalline structures embedded in a glass matrix, offering superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength. The manufacturing differences lead to silica glass being more prone to thermal stress fractures, while glass ceramics combine glassy and crystalline properties for enhanced durability and performance in cookware applications.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Shock Performance
Silica glass, known for its high purity and low thermal expansion, offers exceptional heat resistance up to around 1300degC, making it highly durable under extreme temperatures. Glass ceramic cookware surpasses silica glass by combining crystallized phases that withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking, exhibiting superior thermal shock performance. This makes glass ceramics especially suitable for stovetop-to-oven transitions, where sudden temperature fluctuations commonly occur.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Silica glass offers high thermal stability and moderate scratch resistance but tends to be more brittle under impact compared to glass ceramic. Glass ceramic cookware, such as those made from cordierite or lithium aluminosilicate, exhibits exceptional durability and superior scratch resistance due to its crystallized microstructure. This makes glass ceramic a preferred choice for long-lasting cookware that withstands frequent use and abrasive cleaning.
Cooking Versatility and Suitable Applications
Silica glass offers excellent thermal stability and transparency, making it ideal for microwave and oven cookware that requires even heat distribution and visual monitoring of food. Glass ceramics exhibit superior resistance to thermal shock and mechanical strength, allowing them to withstand rapid temperature changes, which is beneficial for stovetop use and direct flame cooking. The choice between silica glass and glass ceramics depends on whether versatility in cooking methods or durability under extreme conditions is prioritized.
Aesthetic and Design Options
Silica glass cookware offers a sleek, transparent appearance that showcases the cooking process, enhancing kitchen aesthetics with its modern and minimalist design. Glass ceramic cookware features a matte or slightly frosted finish, available in various colors and patterns, providing versatile design options to complement diverse kitchen styles. The choice between the two depends on whether a clear, elegant look or a customizable, decorative surface better suits the user's aesthetic preferences.
Safety Considerations and Toxicity
Silica glass cookware offers high thermal shock resistance and is non-porous, minimizing chemical leaching and ensuring food safety. Glass ceramics provide superior durability and resistance to thermal stress, often containing fewer additives, which reduces potential toxicity risks. Both materials are generally non-toxic and safe for cooking, but glass ceramics typically exhibit enhanced resistance to cracks and chips, limiting contamination hazards.
Maintenance and Cleaning Ease
Silica glass cookware offers a smooth, non-porous surface that resists stains and is easy to clean with simple wiping or soaking methods, reducing maintenance time. Glass ceramic cookware, although more resistant to thermal shock, may develop surface scratches over time that require gentle cleaning with non-abrasive agents to preserve its appearance. Both materials benefit from avoiding harsh chemicals and metal scrubbers, but silica glass generally requires less specialized care for long-term maintenance.
Cost Comparison and Affordability
Silica glass cookware generally offers a more affordable option with lower production costs compared to glass ceramic, making it suitable for budget-conscious consumers. Glass ceramic cookware, while more expensive, provides superior thermal shock resistance and durability, justifying the higher price for long-term investment. Evaluating cost against performance, silica glass is ideal for everyday use, whereas glass ceramic suits those seeking enhanced cooking efficiency and longevity despite the premium cost.
Which Cookware Material is Right for You?
Silica glass offers excellent heat resistance and transparency, making it ideal for slow-cooking and baking where monitoring food is essential. Glass ceramics boast superior thermal shock resistance and durability, suitable for stovetop use and rapid temperature changes without cracking. Choosing between silica glass and glass ceramic depends on your cooking style: opt for silica glass for even heat distribution in the oven and glass ceramic for versatile, high-heat stovetop cooking.
Infographic: Silica glass vs Glass ceramic for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com