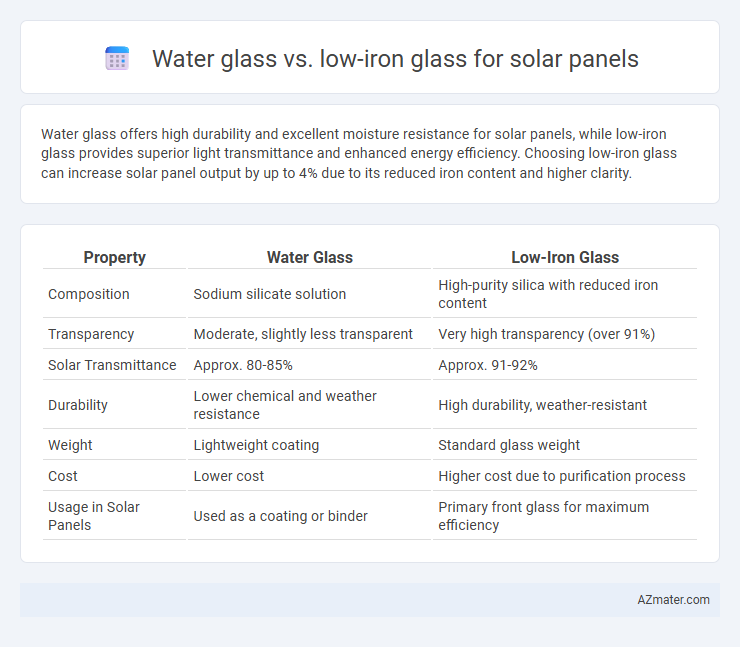
Water glass offers high durability and excellent moisture resistance for solar panels, while low-iron glass provides superior light transmittance and enhanced energy efficiency. Choosing low-iron glass can increase solar panel output by up to 4% due to its reduced iron content and higher clarity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Water Glass | Low-Iron Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Sodium silicate solution | High-purity silica with reduced iron content |
| Transparency | Moderate, slightly less transparent | Very high transparency (over 91%) |
| Solar Transmittance | Approx. 80-85% | Approx. 91-92% |
| Durability | Lower chemical and weather resistance | High durability, weather-resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight coating | Standard glass weight |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to purification process |
| Usage in Solar Panels | Used as a coating or binder | Primary front glass for maximum efficiency |
Introduction to Solar Panel Glass Types
Solar panel glass primarily includes water glass and low-iron glass, each offering distinct characteristics impacting solar efficiency. Water glass, known for its protective qualities and affordability, provides moderate light transmission suitable for standard panels. Low-iron glass enhances solar energy absorption through higher transparency and reduced iron content, making it optimal for high-performance photovoltaic systems.
Defining Water Glass and Low-Iron Glass
Water glass, also known as sodium silicate, is a liquid, glass-like substance used in sealing and protective coatings for solar panels, enhancing durability and resistance to environmental factors. Low-iron glass contains minimal iron oxide content, typically less than 0.1%, resulting in higher clarity and better light transmittance, which improves solar panel efficiency. The choice between water glass coatings and low-iron glass substrates impacts the overall performance and longevity of solar energy systems.
Key Material Differences
Water glass, primarily composed of sodium silicate, differs significantly from low-iron glass used in solar panels, which features reduced iron oxide content to enhance light transmittance. Low-iron glass offers superior transparency, allowing up to 92% solar energy transmission, essential for maximizing photovoltaic efficiency. In contrast, water glass lacks this clarity and durability under prolonged UV exposure, making it less suitable for solar panel applications where minimal light absorption and high strength are critical.
Light Transmission Comparison
Water glass, commonly used in solar panel manufacturing, typically achieves a light transmission rate of around 90%, while low-iron glass can exceed 92% due to its reduced iron content, minimizing greenish tint and light absorption. The higher light transmission of low-iron glass enhances solar panel efficiency by allowing more sunlight to reach the photovoltaic cells, resulting in increased energy output. Consequently, low-iron glass is preferred in high-performance solar modules where maximizing light penetration is critical.
Impact on Solar Panel Efficiency
Water glass, known for its high transparency and anti-reflective properties, enhances solar panel efficiency by allowing more sunlight to penetrate the cells, resulting in increased energy output. Low-iron glass contains reduced iron content, significantly minimizing greenish tint and improving light transmission, which also boosts solar panel performance. Choosing low-iron glass typically leads to higher solar energy yield compared to standard water glass due to its superior clarity and light transmittance.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Water glass offers strong weather resistance due to its enhanced hydrophobic properties, reducing moisture ingress and promoting longevity in solar panels. Low-iron glass provides superior durability with higher hardness and abrasion resistance, ensuring better performance under harsh environmental conditions. Both materials excel in extending solar panel lifespan, but low-iron glass slightly surpasses water glass in withstanding physical impacts and prolonged UV exposure.
Cost Analysis of Both Glasses
Water glass offers a cost-effective option for solar panel manufacturing due to its lower raw material and processing expenses compared to low-iron glass. Low-iron glass, while providing superior light transmittance and energy efficiency, commands a higher price because of its specialized refining process to reduce iron content. Evaluating total life-cycle costs, low-iron glass may justify its initial investment through enhanced energy yield, but water glass remains attractive for budget-conscious projects prioritizing upfront cost savings.
Environmental Considerations
Water glass, also known as liquid glass, offers sustainable environmental benefits due to its non-toxic composition and recyclability, minimizing ecological impact during production and disposal. Low-iron glass enhances solar panel efficiency with higher light transmittance, reducing energy loss and supporting lower carbon emissions over the panel's lifecycle. Both materials contribute to eco-friendly solar solutions, but low-iron glass's superior clarity improves energy yield, while water glass provides an environmentally safe alternative for panel encapsulation and protection.
Applications in the Solar Industry
Water glass, known for its high durability and anti-reflective properties, is commonly used as a protective coating on solar panels to enhance light transmission and prevent corrosion. Low-iron glass, featuring superior transparency and reduced iron content, significantly increases solar panel efficiency by allowing more sunlight to penetrate the photovoltaic cells. In the solar industry, low-iron glass is preferred for premium modules requiring maximum energy output, while water glass coatings are applied to improve weather resistance and maintain long-term performance.
Choosing the Right Glass for Solar Panels
Choosing the right glass for solar panels involves evaluating water glass and low-iron glass based on durability, light transmittance, and cost-effectiveness. Low-iron glass offers higher transparency with up to 91% light transmittance, enhancing solar panel efficiency compared to standard water glass, which typically transmits around 88%. Prioritizing low-iron glass improves solar energy capture and long-term performance, making it the optimal choice for maximizing photovoltaic output in solar installations.
Infographic: Water glass vs Low-iron glass for Solar panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com