Light-diffusing glass offers enhanced visibility and even heat distribution for cooktops, improving cooking precision. Glass ceramic provides superior thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking surfaces.
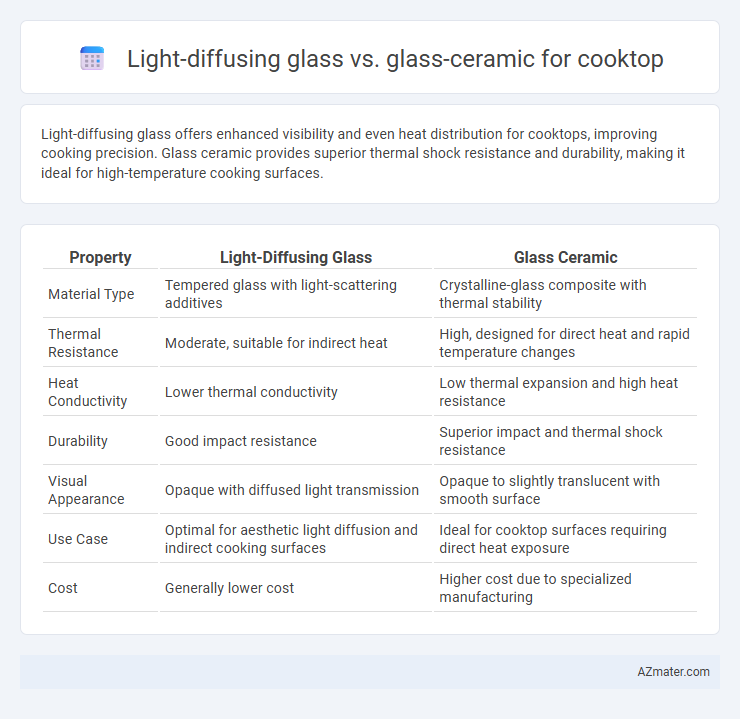
Table of Comparison
| Property | Light-Diffusing Glass | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Tempered glass with light-scattering additives | Crystalline-glass composite with thermal stability |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate, suitable for indirect heat | High, designed for direct heat and rapid temperature changes |
| Heat Conductivity | Lower thermal conductivity | Low thermal expansion and high heat resistance |
| Durability | Good impact resistance | Superior impact and thermal shock resistance |
| Visual Appearance | Opaque with diffused light transmission | Opaque to slightly translucent with smooth surface |
| Use Case | Optimal for aesthetic light diffusion and indirect cooking surfaces | Ideal for cooktop surfaces requiring direct heat exposure |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to specialized manufacturing |
Introduction to Modern Cooktop Materials
Light-diffusing glass improves visibility by evenly scattering light, enhancing cooktop aesthetics and user experience, while glass ceramic offers superior heat resistance and thermal shock durability essential for high-performance cooking surfaces. Modern cooktops increasingly favor glass ceramic due to its ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking, ensuring longevity and safety. Both materials contribute to sleek, efficient cooktop designs, but glass ceramic remains the industry standard for demanding cooking environments.
What is Light-Diffusing Glass?
Light-diffusing glass is engineered to scatter light evenly across its surface, reducing glare and enhancing visibility on cooktops. This type of glass offers a smooth, translucent finish that promotes uniform heat distribution while maintaining an aesthetically pleasing appearance. Compared to glass ceramic, which excels in thermal resistance and direct heat conduction, light-diffusing glass emphasizes improved user visibility and diffused illumination.
Understanding Glass Ceramic for Cooktops
Glass ceramic for cooktops offers superior thermal resistance and rapid heat distribution, making it more durable and efficient than light-diffusing glass. Its crystalline structure allows it to withstand high temperatures without cracking or warping, ensuring long-lasting performance under intense cooking conditions. This material also provides a smooth, easy-to-clean surface that resists stains and scratches better than traditional glass options.
Heat Resistance Comparison
Glass ceramic cooktops exhibit superior heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 1000degC, making them ideal for high-heat cooking environments. Light-diffusing glass typically has a lower heat tolerance, around 300degC to 500degC, risking thermal stress and cracking under intense heat. The enhanced thermal shock resistance of glass ceramic ensures durability and safety, outperforming conventional light-diffusing glass in demanding kitchen applications.
Thermal Efficiency and Conductivity
Light-diffusing glass offers moderate thermal conductivity and distributes heat evenly across the cooktop surface, enhancing thermal efficiency by preventing localized hotspots and reducing energy loss. Glass ceramic exhibits superior thermal resistance and low conductivity, allowing it to withstand rapid temperature changes while maintaining high energy retention and consistent heat transfer. Choosing glass ceramic for cooktops ensures better thermal stability and efficient energy use compared to light-diffusing glass.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Light-diffusing glass offers moderate durability and scratch resistance, making it suitable for cooktops with standard use but more prone to visible wear over time. Glass ceramic provides superior durability and exceptional scratch resistance due to its crystalline structure, ensuring long-lasting performance and minimal surface damage even under heavy use. Choosing glass ceramic enhances cooktop longevity and maintains a smooth, pristine surface compared to light-diffusing glass.
Visual Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Light-diffusing glass offers a smooth, uniform appearance that softens reflected light and enhances visual comfort, making it ideal for sleek, modern cooktop designs with minimal glare. Glass ceramic provides superior heat resistance and can incorporate intricate patterns or embedded elements without compromising translucency, allowing for greater design versatility in functional and decorative cooktops. Both materials support distinct aesthetic goals: light-diffusing glass excels in creating seamless, elegant surfaces, while glass ceramic enables customized visual effects and advanced durability under high temperatures.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Light-diffusing glass cooktops require gentle cleaning to preserve their optical properties, avoiding abrasive cleaners that can cause scratches or dullness. Glass ceramic cooktops feature a durable, non-porous surface resistant to stains and scratches, allowing for easier removal of spills and burnt residues with specialized cooktop cleaners or a soft cloth. Both materials benefit from regular wiping with a damp cloth, but glass ceramics generally demand less intensive maintenance due to their heat-resistant and smooth surface.
Cost and Availability
Light-diffusing glass cooktops generally have lower production costs and are widely available due to simpler manufacturing processes and abundant raw materials. Glass ceramic cooktops involve more complex, high-temperature treatments that increase their cost and limit availability to specialized suppliers. Prices for glass ceramic can be up to 30% higher than light-diffusing glass, impacting budget-conscious consumers and market accessibility.
Which Material Is Best for Your Cooktop?
Light-diffusing glass offers superior heat resistance and uniform light distribution, making it ideal for electric cooktops with integrated lighting. Glass ceramic provides excellent thermal shock resistance and high durability, suitable for induction and radiant cooktops due to its stability under rapid temperature changes. Choosing the best material depends on your cooktop type and cooking habits, with glass ceramic favored for durability and light-diffusing glass preferred for enhanced visual clarity.
Infographic: Light-diffusing glass vs Glass ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com