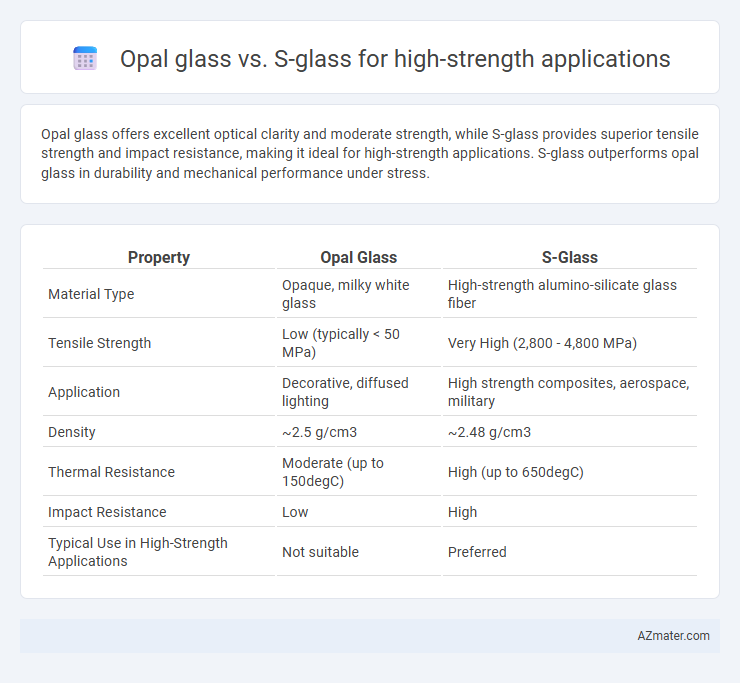
Opal glass offers excellent optical clarity and moderate strength, while S-glass provides superior tensile strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for high-strength applications. S-glass outperforms opal glass in durability and mechanical performance under stress.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Opal Glass | S-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Opaque, milky white glass | High-strength alumino-silicate glass fiber |
| Tensile Strength | Low (typically < 50 MPa) | Very High (2,800 - 4,800 MPa) |
| Application | Decorative, diffused lighting | High strength composites, aerospace, military |
| Density | ~2.5 g/cm3 | ~2.48 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate (up to 150degC) | High (up to 650degC) |
| Impact Resistance | Low | High |
| Typical Use in High-Strength Applications | Not suitable | Preferred |
Introduction to Opal Glass and S-Glass
Opal glass is a type of glass characterized by its milky white, translucent appearance, often used for aesthetic and insulating purposes but with moderate mechanical strength. S-glass, a high-performance fiber composed primarily of alumino-silicate, offers superior tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for high-strength structural applications such as aerospace and military components. The key difference lies in S-glass's exceptional mechanical properties and thermal resistance compared to the more decorative and less robust opal glass.
Chemical Composition Differences
Opal glass is primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2) with added alkali oxides and opacifying agents like titanium dioxide, resulting in lower chemical durability. S-glass exhibits a distinct chemical composition with approximately 65% SiO2, 25% Al2O3, and 10% MgO, enhancing its tensile strength and thermal stability for high-strength applications. The increased alumina and magnesia in S-glass contribute to superior mechanical properties and chemical resistance compared to the more silica-dominant opal glass.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Opal glass manufacturing involves melting silica with alkali oxides and adding opacifiers to create a translucent appearance, requiring precise temperature control for homogeneity. S-glass production utilizes a high-temperature melting process with specific alumina and magnesia compositions, followed by rapid cooling to enhance tensile strength and thermal resistance. Compared to opal glass, S-glass manufacturing demands advanced fiberizing techniques and stringent quality controls to ensure superior mechanical properties for high-strength applications.
Mechanical Strength and Performance
Opal glass exhibits moderate mechanical strength with improved impact resistance due to its microstructure, making it suitable for applications requiring enhanced durability. S-glass, renowned for its superior tensile strength and stiffness, outperforms Opal glass in high-strength applications with excellent resistance to fatigue and mechanical stress. The enhanced fiber composition in S-glass contributes to higher load-bearing capacity and better performance under dynamic mechanical conditions compared to Opal glass.
Thermal Resistance and Stability
Opal glass exhibits enhanced thermal resistance due to its high silica content, maintaining stability at temperatures up to 700degC, making it suitable for applications requiring moderate thermal endurance. S-glass, a high-strength fiberglass variant composed primarily of alumino-silicate fibers, offers superior thermal stability and maintains mechanical integrity at temperatures exceeding 1000degC, crucial for high-strength environments with extreme heat exposure. The choice between Opal glass and S-glass hinges on specific thermal resistance requirements and mechanical strength demands in high-performance industrial applications.
Weight and Density Considerations
Opal glass, with a density typically around 2.4 g/cm3, offers moderate weight and strength but falls short in high-strength applications compared to S-glass, which has a lower density of approximately 2.48 g/cm3 yet delivers superior tensile strength. The higher tensile strength of S-glass, often exceeding 4.9 GPa, makes it ideal for weight-sensitive structures requiring enhanced durability and impact resistance. Weight optimization in high-strength applications favors S-glass due to its combination of relatively low density and exceptional mechanical properties, outperforming opal glass in load-bearing and stress-critical components.
Optical Properties and Clarity
Opal glass offers diffused light transmission with a matte appearance, reducing glare but limiting optical clarity, making it less suitable for applications requiring high transparency. S-glass, known for superior tensile strength and excellent optical clarity, provides clear visibility and minimal light distortion crucial for high-strength optical applications. The choice between Opal glass and S-glass hinges on the balance between durability and the need for precise light transmission and clarity.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Opal glass offers moderate strength and is generally more cost-effective and widely available compared to S-glass, making it suitable for applications where budget constraints are critical. S-glass provides superior tensile strength and durability, ideal for high-strength applications but comes at a higher cost and limited availability. Choosing between Opal glass and S-glass depends on balancing performance requirements with project budget and supply chain considerations.
Application Suitability in High Strength Uses
Opal glass exhibits excellent chemical resistance and moderate mechanical strength, making it suitable for decorative and architectural applications but less ideal for high strength demands. S-glass, with its superior tensile strength and higher stiffness compared to E-glass, is specifically engineered for high strength applications like aerospace components, ballistic armor, and structural reinforcements. The enhanced mechanical properties of S-glass fibers provide optimal performance in environments requiring exceptional durability and load-bearing capacity, whereas Opal glass lacks the necessary toughness for such demanding uses.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Glass for Strength
Opal glass offers excellent aesthetic qualities and moderate strength, making it suitable for decorative applications but less ideal for high-strength requirements. S-glass, known for its superior tensile strength and thermal stability, is the preferred choice in high-strength applications such as aerospace and advanced composites. Selecting S-glass ensures maximum durability and performance where structural integrity is critical.
Infographic: Opal glass vs S-glass for High strength application
 azmater.com
azmater.com