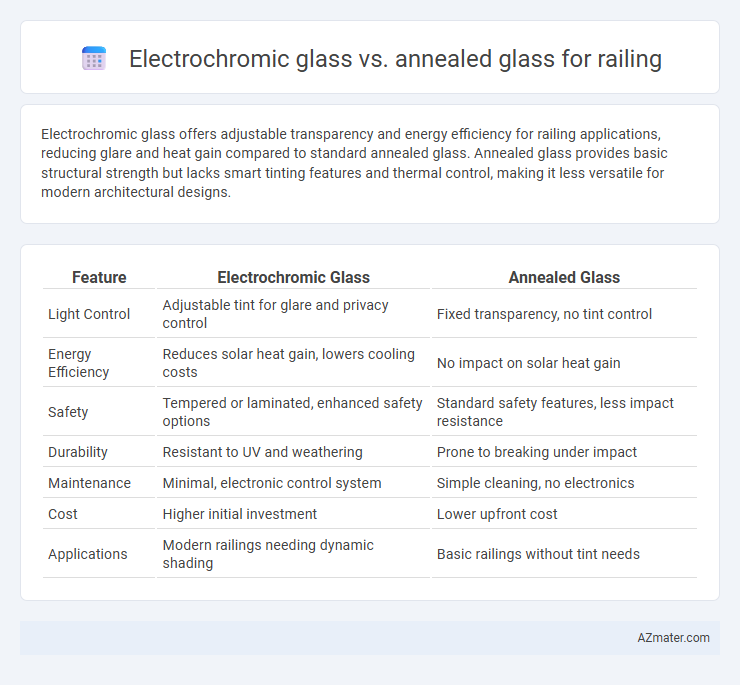
Electrochromic glass offers adjustable transparency and energy efficiency for railing applications, reducing glare and heat gain compared to standard annealed glass. Annealed glass provides basic structural strength but lacks smart tinting features and thermal control, making it less versatile for modern architectural designs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electrochromic Glass | Annealed Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Light Control | Adjustable tint for glare and privacy control | Fixed transparency, no tint control |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces solar heat gain, lowers cooling costs | No impact on solar heat gain |
| Safety | Tempered or laminated, enhanced safety options | Standard safety features, less impact resistance |
| Durability | Resistant to UV and weathering | Prone to breaking under impact |
| Maintenance | Minimal, electronic control system | Simple cleaning, no electronics |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Applications | Modern railings needing dynamic shading | Basic railings without tint needs |
Introduction to Glass Types for Railings
Electrochromic glass for railings offers dynamic tinting capabilities that enhance privacy and energy efficiency by adjusting transparency with electrical input. Annealed glass, commonly used for railings, provides a basic level of strength and clarity but lacks advanced functionality like light modulation. Selecting between electrochromic and annealed glass depends on the desired balance of aesthetic control, safety standards, and energy performance.
What is Electrochromic Glass?
Electrochromic glass is a smart glazing technology that changes its tint when an electrical voltage is applied, allowing dynamic control of light and heat passing through. This glass enhances privacy, reduces glare, and improves energy efficiency by adjusting transparency on demand. Unlike annealed glass, which is basic and static, electrochromic glass offers advanced functionality ideal for modern railing applications requiring adaptive shading and aesthetics.
Understanding Annealed Glass
Annealed glass is a type of glass that undergoes slow cooling to relieve internal stresses, creating a uniform and stable structure ideal for railing applications due to its strength and clarity. It offers excellent optical properties and cost-effectiveness but lacks the dynamic light control features present in electrochromic glass. While annealed glass provides safety and durability, electrochromic glass enhances privacy and energy efficiency by enabling adjustable tinting through electrical activation.
Key Properties Comparison
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic tinting capabilities that adjust transparency based on electrical input, enhancing privacy and solar control for railing applications, while annealed glass remains clear and static with no light modulation. Electrochromic glass typically has higher initial costs and requires electrical infrastructure, but provides superior energy efficiency by reducing heat gain and glare. Annealed glass is more affordable and easier to manufacture but lacks the advanced light control and thermal comfort benefits critical for modern railing designs.
Aesthetic Differences
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic transparency control, enabling customizable tint levels that enhance privacy and mood while maintaining sleek, modern aesthetics. Annealed glass, with its fixed clear or frosted appearance, provides a traditional and consistent visual style but lacks adaptability to changing light or privacy needs. The choice between the two significantly impacts the railing's design flexibility and visual appeal, with electrochromic glass delivering a cutting-edge, futuristic look compared to the classic simplicity of annealed glass.
Privacy and Light Control Capabilities
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic privacy and light control by adjusting its tint electronically, allowing users to switch between transparent and opaque states effortlessly. Annealed glass provides static transparency with no inherent ability to control light or privacy, making it less versatile for applications requiring variable shading or privacy. For railing installations, electrochromic glass enhances both aesthetic appeal and functional adaptability, ensuring privacy on demand while optimizing natural light.
Safety and Durability Factors
Electrochromic glass offers enhanced safety through its ability to switch between transparent and opaque states, providing privacy and glare reduction, which reduces accidents in railing applications. Its durability stems from robust multilayer coatings that resist UV radiation, scratches, and thermal stress, ensuring long-lasting performance compared to traditional annealed glass. Annealed glass, while cost-effective, is more susceptible to breakage and lacks the adaptive safety features of electrochromic glass, making it less ideal for high-traffic or safety-critical railing installations.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Electrochromic glass offers superior energy efficiency for railings by dynamically controlling solar heat gain and reducing reliance on HVAC systems, which lowers overall energy consumption. Annealed glass, while more affordable, lacks adaptive shading capabilities, resulting in higher heat transfer and increased energy use for temperature regulation. The sustainable benefits of electrochromic glass include reduced carbon emissions and enhanced occupant comfort through smart light modulation, making it a greener choice for environmentally conscious building designs.
Cost and Installation Considerations
Electrochromic glass for railing offers dynamic tint control, significantly reducing energy costs by managing solar heat gain, though its initial purchase price ranges from $150 to $300 per square foot, considerably higher than annealed glass, which typically costs $30 to $50 per square foot. Installation of electrochromic glass requires specialized labor familiar with electrical wiring and control systems, typically increasing labor costs by 20-30% compared to the straightforward installation of annealed glass, which requires standard mounting without electrical integration. Long-term, electrochromic glass can lower maintenance and energy expenses, while annealed glass remains a cost-effective option for simple, low-maintenance railing applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Railing
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic tinting capabilities that enhance privacy and energy efficiency for railing applications, making it ideal for modern architectural designs seeking adaptability and smart glass technology. Annealed glass, known for its cost-effectiveness and clarity, provides basic safety but lacks the responsive features of electrochromic options, making it suitable for traditional railing where budget constraints prevail. Selecting the right glass involves evaluating factors like sunlight control, safety standards, aesthetic preferences, and maintenance requirements to ensure optimal performance and durability in railings.
Infographic: Electrochromic glass vs Annealed glass for Railing
 azmater.com
azmater.com