Laminated glass offers enhanced safety and sound insulation by fusing multiple layers with a plastic interlayer, making it ideal for impact resistance in curtain walls. Insulated glass improves thermal performance through dual or triple panes separated by gas-filled spaces, significantly reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency in curtain wall systems.
Table of Comparison
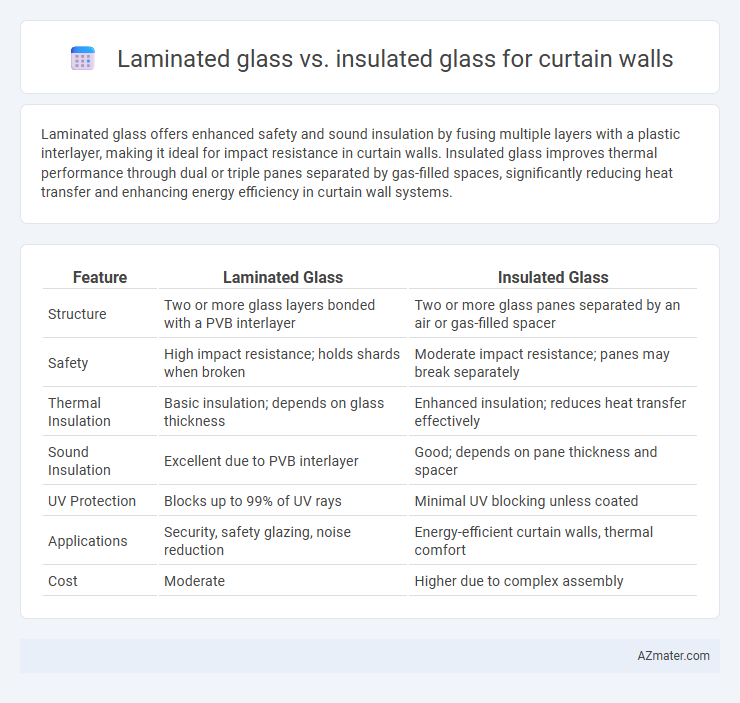
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Insulated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Two or more glass layers bonded with a PVB interlayer | Two or more glass panes separated by an air or gas-filled spacer |
| Safety | High impact resistance; holds shards when broken | Moderate impact resistance; panes may break separately |
| Thermal Insulation | Basic insulation; depends on glass thickness | Enhanced insulation; reduces heat transfer effectively |
| Sound Insulation | Excellent due to PVB interlayer | Good; depends on pane thickness and spacer |
| UV Protection | Blocks up to 99% of UV rays | Minimal UV blocking unless coated |
| Applications | Security, safety glazing, noise reduction | Energy-efficient curtain walls, thermal comfort |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to complex assembly |
Introduction to Curtain Wall Glazing Options
Laminated glass and insulated glass are key glazing options for curtain walls, each offering distinct performance benefits. Laminated glass provides enhanced safety and security by holding shards in place upon breakage, making it ideal for high-impact resistance applications. Insulated glass improves thermal efficiency through multiple panes separated by a gas-filled space, reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy savings in building facade systems.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass for curtain walls consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), enhancing safety by preventing shattering upon impact. It offers superior sound insulation, UV protection, and increased resistance to forced entry compared to standard glass. This makes laminated glass ideal for curtain wall applications demanding high security, durability, and noise reduction.
What is Insulated Glass?
Insulated glass (IG) consists of two or more glass panes separated by a spacer and sealed to create a hermetically sealed airspace, enhancing thermal insulation in curtain wall systems. This construction reduces heat transfer, improves energy efficiency, and minimizes condensation compared to single-pane laminated glass. IG units are preferred in curtain walls for superior climate control and sound reduction, contributing to a building's overall sustainability and occupant comfort.
Structural Performance Comparison
Laminated glass in curtain walls offers enhanced safety and impact resistance due to its interlayer bonding, effectively holding shards together under stress, whereas insulated glass units (IGUs) primarily focus on thermal performance with two or more panes separated by a spacer. Structurally, laminated glass provides superior durability against wind loads and potential impact-related damages, making it ideal for areas prone to storms or vandalism. Insulated glass, while offering improved energy efficiency and condensation resistance, generally exhibits lower impact resistance and may require additional reinforcement to meet the same structural performance as laminated glass in high-stress curtain wall applications.
Acoustic Insulation: Laminated vs Insulated Glass
Laminated glass offers superior acoustic insulation for curtain walls by using a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that effectively dampens sound vibrations and reduces noise transmission. Insulated glass, consisting of two or more glass panes separated by an air or gas-filled gap, improves sound insulation primarily through the air space that disrupts sound waves but typically provides less noise reduction compared to laminated glass. For environments requiring maximum noise control, laminated glass excels in minimizing impact and airborne sound transmission in curtain wall applications.
Thermal Efficiency and Energy Savings
Laminated glass in curtain walls enhances thermal efficiency by providing improved sound insulation and reducing heat transfer through its interlayer, but insulated glass units (IGUs) offer superior energy savings by using multiple panes with air or gas-filled cavities to significantly minimize heat loss and gain. Insulated glass typically achieves higher U-values and better thermal performance, making it more effective in maintaining indoor temperature stability and reducing HVAC energy consumption. Choosing insulated glass over laminated glass optimizes curtain wall systems for energy-efficient building designs and long-term operational cost savings.
Safety and Security Features
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer that holds fragments in place upon impact, offering superior safety by reducing the risk of injury from shattered glass in curtain wall applications. Insulated glass comprises two or more panes separated by a spacer filled with air or gas, primarily enhancing thermal performance but providing less resistance to forced entry and impact compared to laminated glass. For curtain walls requiring enhanced safety and security features, laminated glass is preferred due to its impact resistance and ability to maintain barrier integrity against breakage or intrusion.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Laminated glass in curtain walls offers enhanced design flexibility with its ability to incorporate various interlayer colors, patterns, and textures, enabling architects to achieve custom aesthetic effects while providing safety and sound insulation. Insulated glass units (IGUs) improve thermal performance and reduce condensation, supporting sleek, modern designs with slimmer profiles and larger spans that maintain energy efficiency without sacrificing visual clarity. Both glass types enable creative facade solutions, but laminated glass excels in decorative customization, whereas insulated glass prioritizes performance-driven aesthetics for sustainable curtain wall applications.
Cost Considerations and Maintenance
Laminated glass for curtain walls generally incurs lower initial costs compared to insulated glass, but may require more frequent maintenance due to potential delamination or surface damage. Insulated glass units (IGUs) offer superior thermal performance and durability, reducing long-term energy costs and maintenance needs despite higher upfront investment. Selecting between laminated and insulated glass depends on balancing budget constraints with expected lifecycle efficiency and upkeep demands.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Curtain Wall
Selecting the appropriate glass for curtain walls requires understanding the distinct advantages of laminated and insulated glass. Laminated glass offers superior safety and noise reduction by holding shattered pieces together, making it ideal for high-traffic or impact-prone areas. Insulated glass enhances thermal performance and energy efficiency through its dual-pane construction filled with inert gas, significantly reducing heat transfer in building envelopes.
Infographic: Laminated glass vs Insulated glass for Curtain wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com