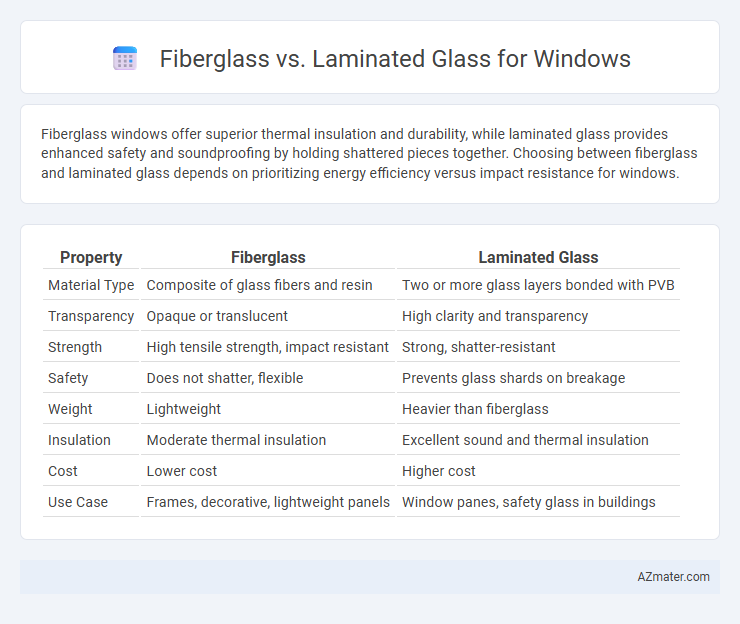
Fiberglass windows offer superior thermal insulation and durability, while laminated glass provides enhanced safety and soundproofing by holding shattered pieces together. Choosing between fiberglass and laminated glass depends on prioritizing energy efficiency versus impact resistance for windows.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fiberglass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Composite of glass fibers and resin | Two or more glass layers bonded with PVB |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | High clarity and transparency |
| Strength | High tensile strength, impact resistant | Strong, shatter-resistant |
| Safety | Does not shatter, flexible | Prevents glass shards on breakage |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than fiberglass |
| Insulation | Moderate thermal insulation | Excellent sound and thermal insulation |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Use Case | Frames, decorative, lightweight panels | Window panes, safety glass in buildings |
Introduction to Window Glass Options
Fibre glass window panes offer lightweight durability, impact resistance, and enhanced insulation properties, making them a versatile choice for modern construction. Laminated glass consists of multiple glass layers bonded with interlayers, providing superior safety, soundproofing, and UV protection. Both materials serve distinct functional and aesthetic purposes, influencing energy efficiency and security in residential and commercial window applications.
What is Fibreglass Glass?
Fibreglass glass refers to a composite material made from fine glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, offering exceptional strength and flexibility compared to standard laminated glass used in windows. This material provides superior impact resistance and thermal insulation, making it ideal for environments requiring durability and energy efficiency. Unlike laminated glass, which consists of multiple layers of glass with interlayers for safety and soundproofing, fibreglass glass combines lightweight properties with enhanced structural performance suitable for innovative architectural designs.
Understanding Laminated Glass
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which enhances safety by preventing shattering upon impact. This glass type offers superior sound insulation and UV protection compared to fiberglass, making it ideal for windows in residential and commercial buildings. Laminated glass also provides increased security and reduces energy loss, contributing to improved durability and thermal efficiency.
Differences in Structure and Composition
Fiberglass windows consist of a composite material made from woven glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, offering lightweight strength and flexibility. Laminated glass is composed of two or more glass layers bonded together with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), enhancing safety and sound insulation. The structural variation lies in fiberglass's fiber-reinforced polymer makeup compared to laminated glass's multi-layered glass and plastic assembly.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Fiberglass windows offer superior strength due to their high tensile strength and resistance to warping, making them highly durable under extreme weather conditions. Laminated glass provides enhanced durability through its multi-layered structure that holds shards together upon impact, offering excellent resistance to shattering and added security. When comparing tensile strength, fiberglass frames outperform laminated glass, but laminated glass excels in impact resistance, making each material optimal for different durability requirements in window applications.
Safety and Security Features
Fiberglass windows offer superior impact resistance and flexibility, reducing the risk of shattering upon impact, which enhances safety during extreme weather events. Laminated glass features a durable interlayer that holds shards together when broken, offering excellent protection against forced entry and reducing injury from glass fragments. Both materials improve security, but laminated glass provides a higher level of intrusion resistance due to its layered construction.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Fiberglass windows offer superior thermal insulation due to their low thermal conductivity, which reduces heat transfer and improves energy efficiency compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass provides enhanced acoustic insulation by incorporating a PVB interlayer that effectively dampens sound waves and minimizes noise penetration. Choosing fiberglass frames combined with laminated glass panels maximizes both thermal performance and soundproofing in window installations.
Cost Analysis: Fibre Glass vs. Laminated Glass
Fiber glass windows typically cost less upfront than laminated glass due to lower material and manufacturing expenses, making them a budget-friendly option for residential projects. Laminated glass commands a higher price because of its complex construction involving a plastic interlayer, enhancing safety and sound insulation which adds long-term value. Maintenance and replacement costs are generally higher for laminated glass, but its durability and enhanced security features can reduce overall lifecycle expenses compared to fiber glass.
Suitability for Different Window Applications
Fibre glass offers high impact resistance and durability, making it suitable for windows in areas prone to storms or physical damage, while laminated glass excels in security and sound insulation due to its interlayer that holds shards together upon breakage. Laminated glass is ideal for residential and commercial windows requiring enhanced safety and noise reduction, whereas fibre glass is preferred for lightweight, corrosion-resistant framing in industrial or coastal environments. Selecting between the two depends on the need for impact strength, safety features, and environmental exposure in specific window applications.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Fibre glass offers superior impact resistance and lightweight properties, making it ideal for locations requiring durability and ease of installation. Laminated glass excels in safety and sound insulation due to its bonded interlayer, providing enhanced protection against breakage and noise reduction. Choose fibre glass for strength and flexibility in design, while laminated glass is the preferred option for safety-conscious applications and enhanced acoustic performance.
Infographic: Fibre glass vs Laminated glass for Window
 azmater.com
azmater.com