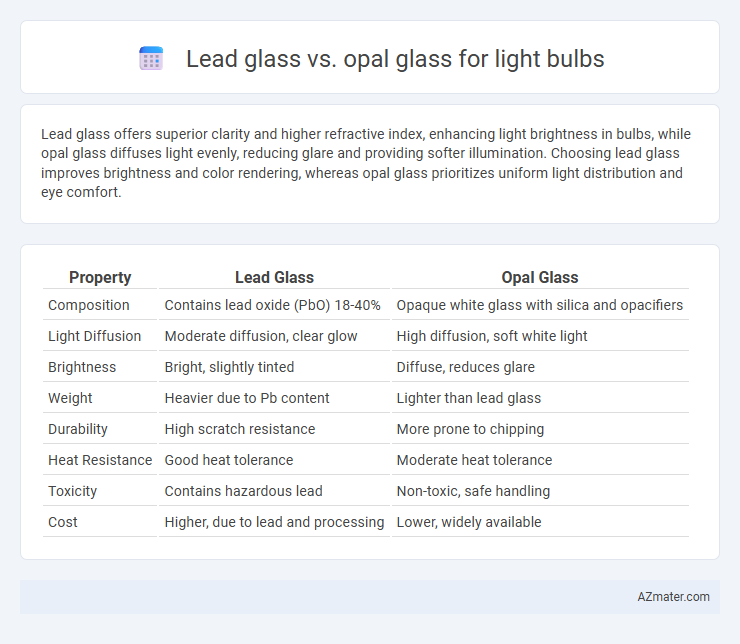
Lead glass offers superior clarity and higher refractive index, enhancing light brightness in bulbs, while opal glass diffuses light evenly, reducing glare and providing softer illumination. Choosing lead glass improves brightness and color rendering, whereas opal glass prioritizes uniform light distribution and eye comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lead Glass | Opal Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Contains lead oxide (PbO) 18-40% | Opaque white glass with silica and opacifiers |
| Light Diffusion | Moderate diffusion, clear glow | High diffusion, soft white light |
| Brightness | Bright, slightly tinted | Diffuse, reduces glare |
| Weight | Heavier due to Pb content | Lighter than lead glass |
| Durability | High scratch resistance | More prone to chipping |
| Heat Resistance | Good heat tolerance | Moderate heat tolerance |
| Toxicity | Contains hazardous lead | Non-toxic, safe handling |
| Cost | Higher, due to lead and processing | Lower, widely available |
Introduction to Lead Glass and Opal Glass
Lead glass, known for its high refractive index and density, enhances light diffusion and brilliance, making it ideal for decorative light bulbs. Opal glass features a smooth, milky-white appearance that provides uniform light distribution and reduces glare, commonly used in functional lighting applications. Both types of glass optimize light quality but serve distinct aesthetic and practical purposes in light bulb design.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Lead glass contains a high percentage of lead oxide, typically 18-40%, which increases its refractive index and density, resulting in superior clarity and brilliance compared to opal glass. Opal glass is primarily made from silica, soda, and lime with the addition of phosphates or fluorides to create its characteristic milky appearance by scattering light diffusely. Manufacturing lead glass requires careful melting and cooling to maintain its optical properties, while opal glass involves incorporating opacifying agents during production to achieve uniform translucency.
Light Transmission Qualities
Lead glass offers superior clarity and higher light transmission rates, typically around 90%, making it ideal for applications where maximum brightness is essential. Opal glass diffuses light more evenly, reducing glare but transmitting approximately 70-75% of light, which softens illumination and creates a warmer ambiance. The choice between lead and opal glass impacts the intensity and quality of light output in bulbs, balancing brightness against glare reduction.
Color and Aesthetic Appearance
Lead glass offers superior clarity and brilliance, enhancing the light bulb's luminosity with a crisp, sparkling appearance that accentuates color accuracy and vibrancy. Opal glass diffuses light softly, producing a warm, uniform glow with a milky white finish that reduces glare and creates a cozy ambiance. The choice between lead and opal glass significantly impacts the bulb's decorative appeal, with lead glass favoring elegance and sharp color contrasts, while opal glass prioritizes subtlety and smooth light distribution.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Lead glass offers higher density and resistance to thermal shock, resulting in greater durability when used in light bulbs compared to Opal glass. Opal glass, while providing excellent light diffusion, tends to be more prone to surface scratches and breakage under mechanical stress. The inherent strength of Lead glass due to lead oxide content strengthens its resilience, making it a preferred choice for long-lasting, robust lighting applications.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Management
Lead glass exhibits higher thermal resistance due to its dense composition, making it effective at withstanding elevated temperatures without deformation. Opal glass, characterized by its milky translucency, offers superior heat diffusion properties that enhance heat management by evenly dispersing heat away from the filament. This heat dispersion in opal glass reduces hot spots and extends bulb lifespan, while lead glass excels in environments requiring robust thermal stability.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Lead glass in light bulbs contains lead oxide, posing environmental risks during disposal due to lead's toxicity and potential groundwater contamination. Opal glass, free from heavy metals, offers a safer alternative with reduced health hazards and easier recycling processes. Choosing opal glass minimizes environmental impact and supports sustainable lighting solutions.
Cost and Market Availability
Lead glass light bulbs typically cost more due to the higher price of lead oxide and specialized manufacturing processes, whereas opal glass bulbs are more affordable and widely available in the market. Opal glass offers a diffuse light effect and is manufactured on a larger scale, making it the preferred choice for standard lighting applications. Lead glass, while less common and costlier, is used in niche markets requiring enhanced optical properties or decorative aesthetics.
Application Suitability in Lighting
Lead glass offers superior clarity and high refractive index, making it ideal for decorative and high-end lighting applications where brilliance and sparkle are desired. Opal glass provides uniform diffusion of light with soft, glare-free illumination, suitable for ambient and task lighting in residential and commercial environments. The choice depends on whether the application prioritizes aesthetic brilliance or comfortable, diffused light distribution.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Light Bulb
Lead glass offers superior clarity and brilliance, making it ideal for decorative light bulbs that emphasize aesthetic appeal and light refraction. Opal glass provides a diffused, soft light output, reducing glare and creating a uniform illumination perfect for ambient lighting applications. Choosing the right glass depends on the desired lighting effect, with lead glass enhancing sparkle and opal glass promoting gentle, even light distribution.
Infographic: Lead glass vs Opal glass for Light bulb
 azmater.com
azmater.com