Photochromic glass dynamically adjusts its tint in response to UV light, enhancing privacy but offering limited impact resistance. Bulletproof glass, composed of laminated layers of polycarbonate and glass, provides robust protection against ballistic threats, making it ideal for high-security barriers.
Table of Comparison
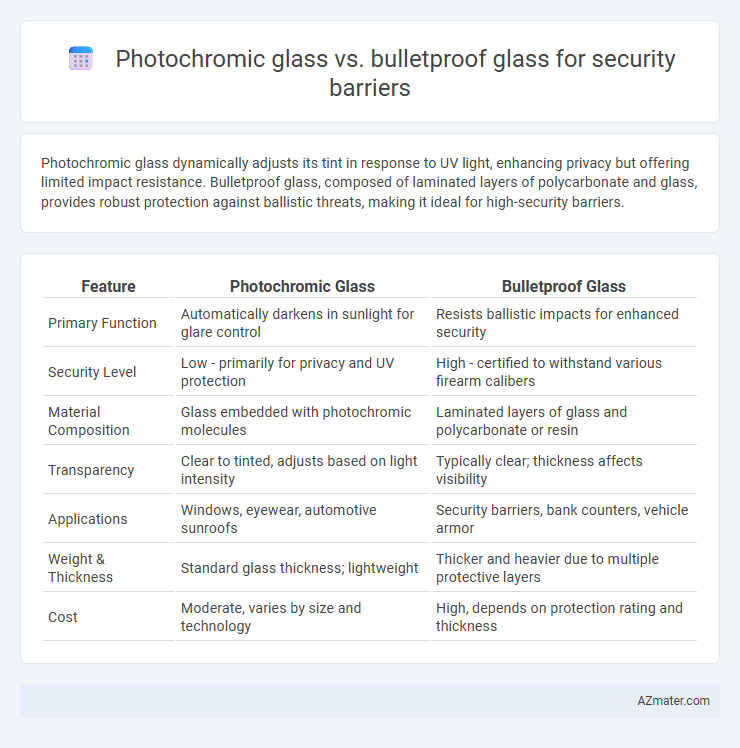
| Feature | Photochromic Glass | Bulletproof Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Automatically darkens in sunlight for glare control | Resists ballistic impacts for enhanced security |
| Security Level | Low - primarily for privacy and UV protection | High - certified to withstand various firearm calibers |
| Material Composition | Glass embedded with photochromic molecules | Laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate or resin |
| Transparency | Clear to tinted, adjusts based on light intensity | Typically clear; thickness affects visibility |
| Applications | Windows, eyewear, automotive sunroofs | Security barriers, bank counters, vehicle armor |
| Weight & Thickness | Standard glass thickness; lightweight | Thicker and heavier due to multiple protective layers |
| Cost | Moderate, varies by size and technology | High, depends on protection rating and thickness |
Introduction to Security Barrier Glass Technologies
Photochromic glass and bulletproof glass serve distinct roles in security barrier applications, with photochromic glass providing adaptive light control by darkening in response to sunlight to enhance privacy and reduce glare. Bulletproof glass, composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, offers high-impact resistance designed to prevent penetration from firearms and explosions, ensuring physical security. Advances in security barrier glass technologies focus on integrating these properties to balance visibility control with protective strength for enhanced safety in sensitive environments.
What is Photochromic Glass?
Photochromic glass dynamically adjusts its tint in response to sunlight, providing privacy and glare reduction while maintaining visibility. Unlike bulletproof glass, which is designed with layers of polycarbonate and glass to absorb and resist ballistic impacts, photochromic glass primarily enhances security by controlling light and visual access. Its adaptive properties make it suitable for environments needing both security and comfort through responsive shading.
What is Bulletproof Glass?
Bulletproof glass, also known as ballistic glass, is a laminated structure made of multiple layers of glass and polycarbonate materials designed to resist high-velocity projectiles and provide enhanced security against forced entry or gunfire. It is commonly used in security barriers for banks, armored vehicles, and secure facilities, offering both transparency and protection. Unlike photochromic glass, which changes tint based on light conditions, bulletproof glass focuses entirely on impact resistance and durability to safeguard lives and assets.
Key Features of Photochromic Glass in Security Applications
Photochromic glass offers dynamic light regulation by darkening in response to UV exposure, enhancing privacy and reducing glare in security barriers. Its automatic tinting properties improve visibility control without compromising transparency, making it ideal for environments requiring adaptable security measures. Unlike bulletproof glass, photochromic glass integrates smart optical changes rather than ballistic protection, serving as a supplementary security feature focused on environmental response.
Advantages of Bulletproof Glass for Security Barriers
Bulletproof glass provides superior protection for security barriers by offering high resistance to ballistic threats and forced entry attempts, making it ideal for safeguarding sensitive areas. Its multi-layered construction absorbs and disperses impact energy, preventing penetration and enhancing occupant safety. Unlike photochromic glass, bulletproof glass maintains consistent transparency and strength regardless of lighting conditions, ensuring reliable security at all times.
Performance Comparison: Photochromic vs Bulletproof Glass
Photochromic glass adjusts its tint in response to sunlight, enhancing privacy and reducing glare while maintaining visibility, but it lacks impact resistance. Bulletproof glass, composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, provides high-level protection against ballistic threats by absorbing and dispersing impact energy. For security barriers, bulletproof glass excels in durability and safety performance, whereas photochromic glass offers adaptive light control without substantial protective strength.
Cost Considerations and Maintenance Needs
Photochromic glass offers cost efficiency with lower initial investment compared to bulletproof glass, which tends to be significantly more expensive due to its multi-layered construction and impact resistance technology. Maintenance for photochromic glass is minimal, requiring only periodic cleaning to maintain its light-adjusting properties, while bulletproof glass demands regular inspections for cracks or delamination to ensure continued protection. Investing in bulletproof glass increases durability and security but incurs higher upkeep costs and potential replacement expenses over time.
Suitability for Various Security Environments
Photochromic glass adapts to changing light conditions, enhancing visibility and privacy for security barriers in environments requiring dynamic light control, such as office buildings or retail stores with varying daylight exposure. Bulletproof glass offers superior protection against ballistic threats, making it indispensable for high-risk security areas like bank teller windows, government facilities, and armored vehicles. Combining these technologies is uncommon due to the specialized nature of ballistic resistance versus light modulation, so selection depends heavily on threat level and environmental demands.
Future Trends in Security Glass Innovations
Photochromic glass is evolving with smart tinting capabilities that adapt to environmental lighting, enhancing privacy and energy efficiency in security barriers while maintaining visibility control. Bulletproof glass innovations emphasize multi-layered composites and nanotechnology for improved impact resistance and reduced weight, ensuring superior protection without compromising design flexibility. Future trends point to hybrid security glass combining photochromic properties with ballistic resistance, integrating IoT sensors for real-time threat detection and automated response systems.
Choosing the Right Glass for Optimal Security Barriers
Photochromic glass offers dynamic light modulation, enhancing visibility control and privacy in security barriers but lacks impact resistance required for high-threat areas. Bulletproof glass, composed of layered laminated materials such as polycarbonate and glass, provides superior resistance against ballistic and forced entry attacks, making it ideal for critical security installations. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing environmental adaptability with protection levels, prioritizing bulletproof glass for maximum threat mitigation and photochromic glass for environments where adjustable light filtration complements security needs.
Infographic: Photochromic glass vs Bulletproof glass for Security barrier
 azmater.com
azmater.com