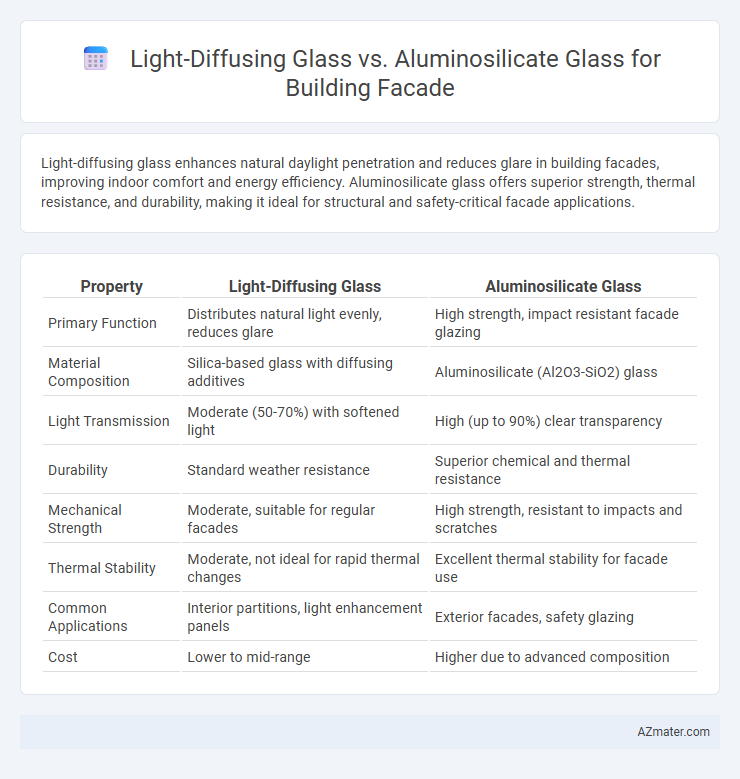
Light-diffusing glass enhances natural daylight penetration and reduces glare in building facades, improving indoor comfort and energy efficiency. Aluminosilicate glass offers superior strength, thermal resistance, and durability, making it ideal for structural and safety-critical facade applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Light-Diffusing Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Distributes natural light evenly, reduces glare | High strength, impact resistant facade glazing |
| Material Composition | Silica-based glass with diffusing additives | Aluminosilicate (Al2O3-SiO2) glass |
| Light Transmission | Moderate (50-70%) with softened light | High (up to 90%) clear transparency |
| Durability | Standard weather resistance | Superior chemical and thermal resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, suitable for regular facades | High strength, resistant to impacts and scratches |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate, not ideal for rapid thermal changes | Excellent thermal stability for facade use |
| Common Applications | Interior partitions, light enhancement panels | Exterior facades, safety glazing |
| Cost | Lower to mid-range | Higher due to advanced composition |
Introduction to Building Façade Glass Technologies
Light-diffusing glass enhances building facades by uniformly dispersing natural light, reducing glare and improving interior illumination, which boosts energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Aluminosilicate glass offers superior strength and thermal resistance compared to traditional glass, making it ideal for structural applications and enhancing building safety and durability. Both technologies represent advancements in facade glass solutions, balancing aesthetic appeal with functional performance in modern architectural design.
Overview of Light-Diffusing Glass
Light-diffusing glass enhances building facades by distributing natural light evenly, reducing glare and improving indoor illumination quality. This type of glass incorporates microscopic particles or surface treatments that scatter incoming light, creating a soft, uniform glow while maintaining transparency. Compared to aluminosilicate glass, primarily valued for its strength and thermal resistance, light-diffusing glass prioritizes visual comfort and aesthetic appeal in architectural applications.
Understanding Aluminosilicate Glass Properties
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance, high mechanical strength, and excellent chemical durability, making it ideal for building facades exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Unlike light-diffusing glass, which primarily enhances natural light distribution, aluminosilicate glass provides structural integrity while maintaining clarity and impact resistance. Its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and resist scratching ensures longevity and low maintenance in architectural applications.
Comparative Light Transmission and Diffusion
Light-diffusing glass typically offers superior light diffusion properties by scattering sunlight evenly across interior spaces, reducing glare and enhancing visual comfort, whereas aluminosilicate glass excels in maintaining higher light transmission with minimal diffusion, allowing more natural light penetration. The diffusion coefficient of light-diffusing glass ranges between 0.6 and 0.85, balancing brightness and privacy, while aluminosilicate glass transmits up to 90% of visible light with a diffusion level below 0.2, prioritizing clarity and transparency. Selecting between these materials depends on architectural goals: light-diffusing glass optimizes diffuse illumination for energy savings and occupant comfort, while aluminosilicate glass ensures structural strength and clearer daylight in facades.
Thermal Performance and Energy Efficiency
Light-diffusing glass enhances building facades by evenly distributing natural light, reducing glare and decreasing reliance on artificial lighting, which significantly improves energy efficiency. Aluminosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance with a high melting point and low thermal expansion, maintaining structural integrity under temperature fluctuations and improving insulation performance. Combining both materials can optimize daylight penetration while reducing heat transfer, leading to enhanced thermal performance and substantial energy savings in building facades.
Strength, Durability, and Safety Factors
Light-diffusing glass enhances building facades by distributing natural light evenly, reducing glare, and improving energy efficiency, but generally offers moderate strength compared to aluminosilicate glass. Aluminosilicate glass provides superior durability and impact resistance due to its chemical composition and treatment processes, making it highly suitable for safety-critical applications in facades. Both materials contribute to safety, yet aluminosilicate glass's enhanced fracture toughness and thermal stability make it a preferred choice for high-performance building exteriors.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Light-diffusing glass enhances building facades by softening natural light and creating dynamic visual effects that elevate aesthetic appeal. Aluminosilicate glass offers superior strength and thermal resistance, enabling innovative, slim-profile designs that maximize transparency and structural performance. Combining these materials provides architects with versatile options to achieve both striking visual textures and durable, contemporary facades.
Maintenance and Longevity in Façade Applications
Light-diffusing glass enhances natural light distribution while minimizing glare, reducing the need for frequent cleaning and maintenance in building facades due to its dirt-resistant surface properties. Aluminosilicate glass offers superior scratch and impact resistance, contributing to longer facade durability and lower replacement costs compared to conventional glass types. Both materials support extended facade lifespan, but aluminosilicate glass excels in structural integrity and toughness, making it ideal for high-traffic or harsh environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis: Short-term vs. Long-term Investment
Light-diffusing glass typically incurs higher upfront costs due to advanced manufacturing processes and specialized coatings, making it a significant short-term investment for building facades. Aluminosilicate glass offers lower initial expenses and robust durability, reducing maintenance and replacement costs over time, which enhances its appeal as a long-term investment. Evaluating lifecycle costs reveals that while light-diffusing glass improves indoor lighting efficiency and aesthetics, aluminosilicate glass provides superior structural strength and longevity, influencing overall return on investment in facade applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Sustainable Building Façades
Light-diffusing glass enhances natural light distribution within buildings, reducing reliance on artificial lighting and lowering energy consumption. Aluminosilicate glass offers superior strength, thermal resistance, and durability, ideal for structural and safety requirements in facades. Selecting between these glasses depends on balancing energy efficiency goals with mechanical performance for sustainable building design.
Infographic: Light-diffusing glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Building Façade
 azmater.com
azmater.com