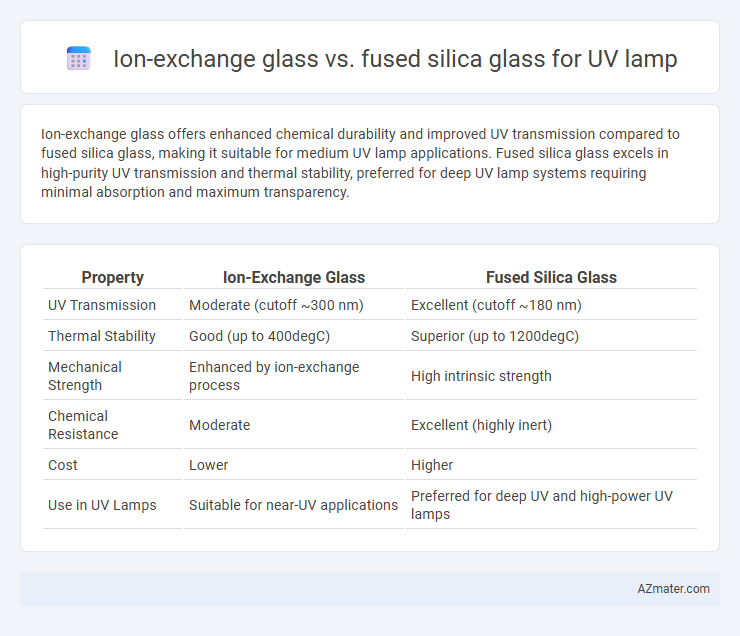
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced chemical durability and improved UV transmission compared to fused silica glass, making it suitable for medium UV lamp applications. Fused silica glass excels in high-purity UV transmission and thermal stability, preferred for deep UV lamp systems requiring minimal absorption and maximum transparency.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ion-Exchange Glass | Fused Silica Glass |
|---|---|---|
| UV Transmission | Moderate (cutoff ~300 nm) | Excellent (cutoff ~180 nm) |
| Thermal Stability | Good (up to 400degC) | Superior (up to 1200degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | Enhanced by ion-exchange process | High intrinsic strength |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | Excellent (highly inert) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Use in UV Lamps | Suitable for near-UV applications | Preferred for deep UV and high-power UV lamps |
Introduction to UV Lamp Glass Materials
Ion-exchange glass and fused silica glass are key materials used in UV lamp manufacturing due to their distinct optical properties and durability under ultraviolet exposure. Ion-exchange glass offers improved strength and resistance to thermal shock through surface ion substitution, making it suitable for moderate UV applications. Fused silica glass provides superior UV transmittance and thermal stability, enabling efficient light output and longevity in high-intensity UV lamp environments.
Overview of Ion-Exchange Glass
Ion-exchange glass enhances UV lamp performance by improving surface durability and chemical resistance through a controlled ion substitution process, typically replacing smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions in the glass matrix. This modification results in increased mechanical strength and reduced susceptibility to surface damage under UV exposure compared to fused silica glass. Ion-exchange glass maintains high UV transparency while offering cost-effective durability advantages, making it suitable for demanding UV lamp applications where extended lifespan and resistance to harsh environments are critical.
Overview of Fused Silica Glass
Fused silica glass is highly prized for UV lamp applications due to its exceptional purity, excellent transmission of ultraviolet light down to 180 nm, and superior thermal stability compared to ion-exchange glass. This material exhibits low thermal expansion and high resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for high-intensity UV environments. Its chemical inertness and durability ensure minimal degradation under prolonged UV exposure, enhancing lamp lifespan and performance.
UV Transmission Properties Compared
Ion-exchange glass exhibits lower UV transmission efficiency compared to fused silica glass, particularly below 300 nm wavelength, due to its higher impurity levels and structural imperfections. Fused silica glass offers superior UV transmission properties, often exceeding 90% transmittance down to 190 nm, making it ideal for high-performance UV lamps. The enhanced purity and molecular structure of fused silica minimize absorption and scattering, thereby maximizing UV output in critical applications.
Chemical and Thermal Durability
Ion-exchange glass exhibits superior chemical durability compared to fused silica glass, resisting corrosion and chemical degradation in harsh UV lamp environments. Fused silica glass offers exceptional thermal stability and can withstand rapid temperature fluctuations without cracking, making it ideal for high-temperature UV lamp applications. The combination of ion-exchange treatment and fused silica properties enhances overall UV lamp performance by balancing chemical resistance with thermal shock resistance.
Mechanical Strength and Toughness
Ion-exchange glass exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength and toughness compared to fused silica glass, making it more resistant to cracking and mechanical impact. The ion-exchange process enhances surface compressive stress, improving durability under thermal and mechanical stress commonly experienced in UV lamp applications. Although fused silica glass offers excellent UV transmission, its lower mechanical toughness limits its lifespan in high-stress environments.
Manufacturing Processes and Cost
Ion-exchange glass undergoes a chemical strengthening process where smaller sodium ions are replaced by larger potassium ions to enhance durability and UV resistance, typically resulting in higher manufacturing complexity and cost. Fused silica glass is produced by melting high-purity silica at extremely high temperatures, offering superior UV transmission and thermal stability but involving more energy-intensive and costly production methods. While ion-exchange glass offers improved mechanical strength at a comparatively moderate cost, fused silica glass's superior optical properties for UV lamps justify its premium price in high-performance applications.
Application Suitability in UV Lamps
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced durability and improved chemical resistance, making it suitable for UV lamps requiring robust performance in harsh environments. Fused silica glass provides superior UV transmittance and thermal stability, which is critical for high-intensity UV lamp applications demanding maximum light output and minimal signal loss. The choice between ion-exchange glass and fused silica depends on the specific UV wavelength range and operational conditions of the lamp.
Lifespan and Maintenance Considerations
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced durability and a longer lifespan for UV lamps due to its increased strength and resistance to thermal shock compared to fused silica glass. Maintenance requirements are reduced with ion-exchange glass since its improved hardness minimizes scratching and surface degradation, preserving UV transmission efficiency over time. Fused silica glass, while highly transparent to UV light, is more susceptible to mechanical damage and thermal stress, potentially resulting in more frequent replacements and higher maintenance costs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Glass for UV Lamps
Ion-exchange glass offers improved strength and durability compared to fused silica glass, making it suitable for UV lamps demanding high mechanical resistance. Fused silica glass provides superior UV transparency and thermal stability, essential for applications requiring minimal light absorption and consistent performance under intense UV radiation. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing the need for mechanical robustness with optimal UV transmission based on specific lamp operating conditions.
Infographic: Ion-exchange glass vs Fused silica glass for UV lamp
 azmater.com
azmater.com