Colored glass for automotive windows offers vibrant, uniform hues that enhance aesthetics and provide UV protection, while tinted glass primarily reduces glare and heat by absorbing solar energy with a darker, more subtle shade. Choosing between colored and tinted glass depends on balancing design preferences with functional benefits like heat rejection and visibility.
Table of Comparison
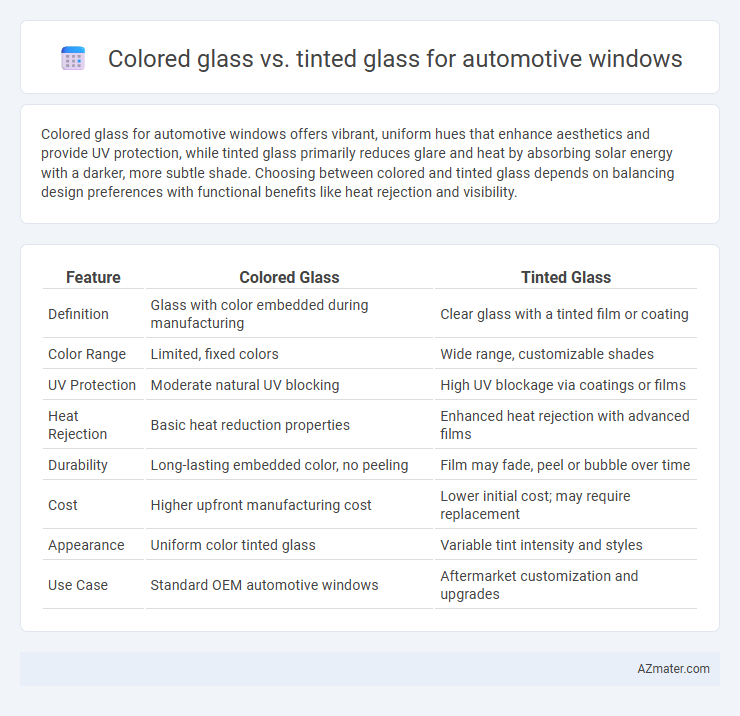
| Feature | Colored Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Glass with color embedded during manufacturing | Clear glass with a tinted film or coating |
| Color Range | Limited, fixed colors | Wide range, customizable shades |
| UV Protection | Moderate natural UV blocking | High UV blockage via coatings or films |
| Heat Rejection | Basic heat reduction properties | Enhanced heat rejection with advanced films |
| Durability | Long-lasting embedded color, no peeling | Film may fade, peel or bubble over time |
| Cost | Higher upfront manufacturing cost | Lower initial cost; may require replacement |
| Appearance | Uniform color tinted glass | Variable tint intensity and styles |
| Use Case | Standard OEM automotive windows | Aftermarket customization and upgrades |
Introduction to Automotive Glass Types
Colored glass and tinted glass serve distinct purposes in automotive windows, with colored glass incorporating pigment during manufacturing, offering uniform coloration and UV protection. Tinted glass involves applying a film or coating post-production, enhancing heat reduction, glare control, and privacy without altering the glass composition. Both types improve driving comfort and safety, with tinted glass providing customizable shades and colored glass offering durable, fade-resistant color.
What is Colored Glass?
Colored glass in automotive windows is glass infused with metal oxides or chemical additives during production to achieve uniform coloration throughout the material. This type of glass offers consistent tint and enhanced UV protection without the need for film coatings. Colored glass improves vehicle aesthetics while reducing glare and heat transmission more effectively than simple tinted films applied on clear glass.
What is Tinted Glass?
Tinted glass for automotive windows is manufactured by adding a metallic or dye coating during the glass production process, reducing glare and blocking UV rays to enhance driver comfort. This type of glass typically offers consistent color and light reduction across the entire surface, improving privacy and heat rejection without compromising visibility. Unlike colored glass, which is uniformly infused with color throughout, tinted glass achieves its shading through surface treatments, making it more effective for controlling solar heat gain in vehicles.
Key Differences Between Colored and Tinted Glass
Colored glass for automotive windows is created by adding metal oxides or other pigments during the glass manufacturing process, resulting in a uniform hue that is embedded throughout the glass, offering consistent color without affecting visibility significantly. Tinted glass is typically clear glass coated with a transparent film or layer that absorbs or reflects solar heat and UV rays, enhancing heat rejection and glare reduction while maintaining a high level of visibility. Key differences include the permanent coloration of colored glass versus the surface-applied nature of window tint films, heat and UV protection levels, and the impact on light transmission and driver visibility.
UV Protection: Colored vs Tinted Glass
Colored glass in automotive windows offers moderate UV protection by incorporating metal oxides during manufacturing, effectively blocking a portion of harmful rays while maintaining natural light transmission. Tinted glass, often achieved through film application or chemical treatments, provides enhanced UV protection by absorbing and reflecting a higher percentage of ultraviolet radiation, reducing interior heat and preventing fading of upholstery. Choosing between colored and tinted glass impacts UV filtration efficiency, heat reduction, and passenger comfort, making tinted glass preferable for superior UV defense in vehicle windows.
Heat Rejection Performance
Colored glass for automotive windows typically absorbs solar radiation, converting it into heat and causing the glass to warm up, which can reduce heat rejection efficiency. Tinted glass incorporates additives or films that selectively block infrared and ultraviolet rays, enhancing heat rejection and keeping the vehicle interior cooler. Studies show tinted glass can reduce solar heat gain by up to 50%, outperforming standard colored glass in thermal control.
Aesthetic Appeal and Customization
Colored glass for automotive windows offers vibrant, uniform hues created during the manufacturing process, providing a sleek, permanent aesthetic that enhances vehicle style with consistent color saturation. Tinted glass, produced by applying films or coatings, allows greater customization options through adjustable tint levels and patterns, enabling personalized light filtration and privacy preferences. Both options improve vehicle appearance, but colored glass emphasizes factory-quality color integration, while tinted glass prioritizes tailored visual effects and functionality.
Durability and Maintenance
Colored glass for automotive windows offers enhanced UV protection and resists fading better over time, contributing to long-term durability. Tinted glass, while effective at reducing glare and heat, may require more frequent maintenance to prevent scratches and discoloration, especially if aftermarket films are applied. Overall, colored glass tends to maintain its appearance and structural integrity longer, reducing upkeep needs compared to tinted options.
Legal Considerations and Regulations
Colored glass and tinted glass for automotive windows are subject to varying legal considerations and regulations depending on jurisdiction, with specific limits on visible light transmission (VLT) percentages to ensure driver visibility and safety. States and countries often require front side windows to allow at least 70% VLT, while rear windows may have more lenient standards or no restrictions. Compliance with regulations such as DOT and ECE certification ensures the glass meets safety standards and avoids penalties or vehicle inspection failures.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Vehicle
Colored glass for automotive windows offers enhanced aesthetic appeal and better UV protection by integrating pigments into the glass, while tinted glass primarily reduces glare and heat through a film or coating applied on the surface. When choosing the best option, consider factors like desired privacy, heat rejection efficiency, and local regulations on allowable tint levels. Evaluating the balance between style, comfort, and legal compliance ensures optimal performance and satisfaction for your vehicle's windows.
Infographic: Colored glass vs Tinted glass for Automotive window
 azmater.com
azmater.com