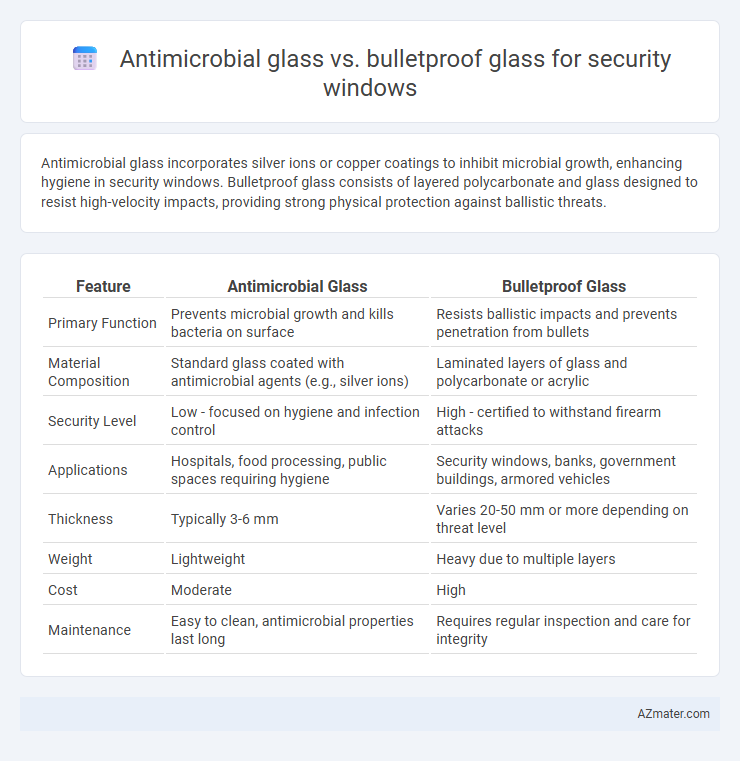
Antimicrobial glass incorporates silver ions or copper coatings to inhibit microbial growth, enhancing hygiene in security windows. Bulletproof glass consists of layered polycarbonate and glass designed to resist high-velocity impacts, providing strong physical protection against ballistic threats.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Antimicrobial Glass | Bulletproof Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Prevents microbial growth and kills bacteria on surface | Resists ballistic impacts and prevents penetration from bullets |
| Material Composition | Standard glass coated with antimicrobial agents (e.g., silver ions) | Laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate or acrylic |
| Security Level | Low - focused on hygiene and infection control | High - certified to withstand firearm attacks |
| Applications | Hospitals, food processing, public spaces requiring hygiene | Security windows, banks, government buildings, armored vehicles |
| Thickness | Typically 3-6 mm | Varies 20-50 mm or more depending on threat level |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy due to multiple layers |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, antimicrobial properties last long | Requires regular inspection and care for integrity |
Introduction to Security Window Technologies
Security window technologies combine materials engineered to enhance safety and protection; antimicrobial glass incorporates surface treatments or coatings that inhibit microbial growth, promoting hygiene in high-contact environments. Bulletproof glass, typically made from laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate, provides robust resistance against ballistic impacts to prevent penetration and injury. Selecting the appropriate security window material depends on the specific security needs, balancing microbial control with physical protection requirements.
Defining Antimicrobial Glass and Its Core Features
Antimicrobial glass incorporates a special coating embedded with ions such as silver or copper, which inhibit the growth of bacteria and viruses on the surface, enhancing hygiene in high-contact security windows. Unlike bulletproof glass designed primarily for impact resistance through layered polycarbonate and laminated glass, antimicrobial glass prioritizes microbial control without compromising clarity or structural integrity. Its core features include long-lasting antimicrobial efficacy, easy maintenance, and compatibility with other security glass technologies for integrated protection.
Bulletproof Glass: Composition and Protective Capabilities
Bulletproof glass, primarily composed of layered polycarbonate and laminated glass, provides exceptional resistance against high-velocity projectiles and impact forces, making it ideal for security windows. Its multi-layered structure distributes the energy from bullets or debris, preventing penetration and minimizing shattering. Unlike antimicrobial glass, which focuses on hygiene by inhibiting microbial growth, bulletproof glass prioritizes physical protection, ensuring safety in high-risk environments such as banks, vehicles, and secure facilities.
Comparing Mechanisms of Action: Antimicrobial vs Bulletproof
Antimicrobial glass incorporates coatings such as silver ions or copper compounds that disrupt microbial cell membranes, preventing bacterial and viral proliferation on surfaces. Bulletproof glass relies on multiple layers of laminated polycarbonate and glass, distributing and absorbing kinetic energy to resist penetration from projectiles. The antimicrobial mechanism targets biological contaminants at a microscopic level, while bulletproof glass provides physical protection against ballistic impacts through structural reinforcement.
Security Benefits: Threat Protection and Risk Reduction
Antimicrobial glass enhances security windows by inhibiting microbial growth, reducing health risks in high-traffic or healthcare environments, but it does not provide physical threat protection. Bulletproof glass offers superior threat protection and risk reduction by resisting ballistic impacts, preventing forced entry, and safeguarding occupants from gunfire or explosions. Combining antimicrobial properties with bulletproof capabilities is possible but typically involves layered glass solutions to balance health safety and physical security needs.
Hygiene and Health Considerations in Window Security
Antimicrobial glass incorporates specialized coatings that inhibit bacterial growth, reducing surface contamination and promoting higher hygiene standards in security windows, particularly in healthcare or public settings. Bulletproof glass, while designed primarily for impact resistance and protection against ballistic threats, lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, making it less effective for minimizing pathogen transmission. Prioritizing antimicrobial glass in security windows enhances health considerations by combining physical security with microbial safety, critical in environments demanding stringent hygiene control.
Durability and Maintenance of Antimicrobial vs Bulletproof Glass
Bulletproof glass offers superior durability with multi-layered composites designed to resist high-impact forces and provide long-lasting protection against ballistic threats. Antimicrobial glass focuses on reducing surface bacteria and pathogens through embedded coatings but typically maintains standard glass strength, requiring more careful handling to avoid scratches or chips that can compromise its cleanliness. Maintenance of antimicrobial glass involves regular cleaning to preserve its germ-resistant properties, while bulletproof glass demands inspections for structural integrity, especially after impacts, to ensure continuous security performance.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-Term Value
Antimicrobial glass typically incurs a lower initial investment compared to bulletproof glass, making it a cost-effective choice for environments prioritizing hygiene alongside basic security. Bulletproof glass demands a significantly higher upfront cost due to its multi-layered design and specialized materials but offers superior long-term value by providing enhanced protection against forced entry and ballistic threats. When evaluating overall value, antimicrobial glass reduces maintenance expenses through its pathogen-resistant properties, whereas bulletproof glass minimizes replacement and repair costs by withstanding physical impact.
Applications: Ideal Environments for Each Glass Type
Antimicrobial glass is ideal for healthcare facilities, laboratories, and food processing plants where controlling microbial growth on surfaces is crucial for hygiene and safety. Bulletproof glass is best suited for high-security environments such as banks, government buildings, and armored vehicles, offering protection against ballistic threats and forced entry. Both types enhance safety but serve distinct purposes depending on the primary security needs of the environment.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Glass for Enhanced Security
Antimicrobial glass offers exceptional hygiene by inhibiting bacterial growth, making it ideal for environments requiring cleanliness, whereas bulletproof glass provides superior physical protection against ballistic threats. For enhanced security in high-risk areas, bulletproof glass is the preferred choice due to its impact resistance and ability to prevent forced entry. Selecting the best glass depends on prioritizing either sanitary safety or robust defense against attacks.
Infographic: Antimicrobial glass vs Bulletproof glass for Security window
 azmater.com
azmater.com