Anti-reflective glass reduces glare and enhances natural light transmission, improving visibility and energy efficiency in windows. Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety by resisting impact and shattering into small, blunt pieces, making it ideal for durability and security.
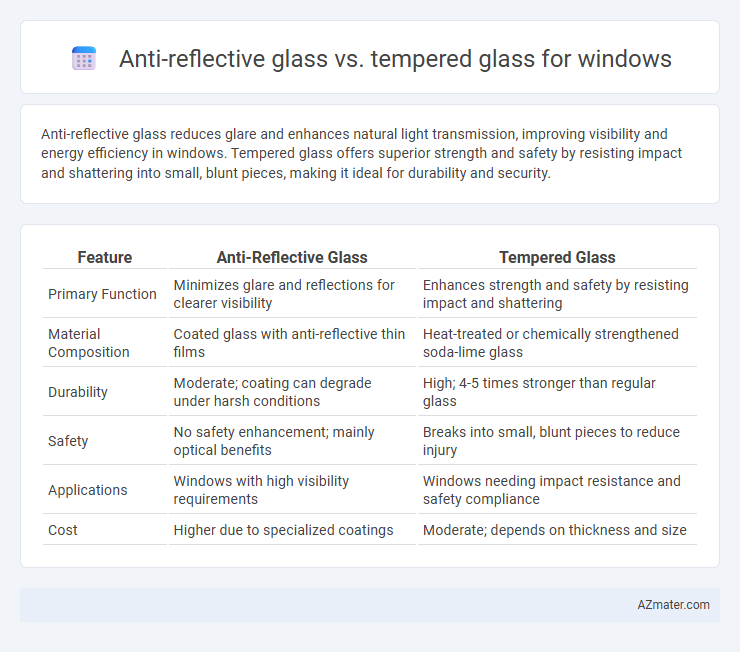
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-Reflective Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Minimizes glare and reflections for clearer visibility | Enhances strength and safety by resisting impact and shattering |
| Material Composition | Coated glass with anti-reflective thin films | Heat-treated or chemically strengthened soda-lime glass |
| Durability | Moderate; coating can degrade under harsh conditions | High; 4-5 times stronger than regular glass |
| Safety | No safety enhancement; mainly optical benefits | Breaks into small, blunt pieces to reduce injury |
| Applications | Windows with high visibility requirements | Windows needing impact resistance and safety compliance |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized coatings | Moderate; depends on thickness and size |
Introduction to Anti-Reflective and Tempered Glass
Anti-reflective glass features a specialized coating that reduces glare and enhances visibility by minimizing surface reflections, making it ideal for windows in high-light environments. Tempered glass is heat-treated to increase its strength and safety, shattering into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards when broken. Both types serve distinct purposes: anti-reflective glass improves clarity and comfort, while tempered glass ensures durability and impact resistance for window applications.
What is Anti-Reflective Glass?
Anti-reflective glass is engineered with a special coating that reduces glare and reflections, enhancing clarity and visibility through windows in various lighting conditions. This type of glass improves natural light transmission by minimizing surface reflections, making it ideal for applications requiring clear views, such as office buildings, residential windows, and display cases. Compared to tempered glass, which prioritizes strength and safety through heat treatment, anti-reflective glass focuses on optical performance without compromising structural integrity.
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed through controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to normal glass. It is designed to shatter into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, reducing injury risk during breakage. Tempered glass is widely used in windows, doors, and automotive glass for its durability and safety features.
Key Differences Between Anti-Reflective and Tempered Glass
Anti-reflective glass reduces glare and enhances visibility by minimizing reflections, making it ideal for windows requiring clarity in bright environments, while tempered glass is engineered for safety, offering high strength and shatter resistance through heat treatment. Unlike tempered glass, which breaks into small, blunt pieces to prevent injury, anti-reflective glass maintains its structural integrity but lacks impact resistance. The key differences lie in their primary functions: anti-reflective glass optimizes visual performance, whereas tempered glass prioritizes durability and safety in window applications.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission Comparison
Anti-reflective glass offers superior optical clarity by minimizing surface reflections and maximizing light transmission, typically allowing over 98% of natural light to pass through. Tempered glass provides enhanced strength and safety but often reduces light transmission slightly to around 90-92% due to its heat treatment and thickness. For applications prioritizing clear, unobstructed views with high daylight penetration, anti-reflective glass is the optimal choice over tempered glass.
Durability and Safety: Which Glass Performs Better?
Tempered glass offers superior durability and safety for windows due to its heat-treated strength and shatter-resistant properties, making it ideal for impact-prone environments. Anti-reflective glass enhances visual clarity by reducing glare but lacks the reinforced durability of tempered glass, rendering it less reliable in safety-critical applications. For applications prioritizing durability and safety, tempered glass outperforms anti-reflective glass significantly.
Energy Efficiency and UV Protection
Anti-reflective glass enhances energy efficiency by reducing glare and improving natural light transmission, which lowers reliance on artificial lighting and decreases energy consumption in buildings. Tempered glass provides strong UV protection by blocking harmful ultraviolet rays, safeguarding interior furnishings from fading and reducing heat buildup. Combining both materials in window applications offers optimized solar control, better thermal insulation, and enhanced occupant comfort.
Cost Differences and Installation Factors
Anti-reflective glass typically costs 20-40% more than tempered glass due to its specialized coating that reduces glare and enhances visibility. Tempered glass is generally more affordable and widely used for window safety and durability, offering higher resistance to impact and thermal stress. Installation of anti-reflective glass requires careful handling to preserve its coating, often leading to higher labor costs, whereas tempered glass installation is more straightforward and less labor-intensive.
Best Use Cases for Anti-Reflective vs Tempered Glass in Windows
Anti-reflective glass is ideal for windows in offices, museums, and retail spaces where maximizing natural light and reducing glare enhances visibility and aesthetic appeal. Tempered glass is best suited for safety-critical applications like residential windows, storefronts, and high-traffic areas, offering superior strength and shatter resistance. Choosing between anti-reflective and tempered glass depends on balancing visual clarity with structural durability requirements.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Glass for Your Windows
Anti-reflective glass enhances visibility by minimizing glare and reflections, making it ideal for windows in bright environments or spaces requiring clear views. Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety, shattering into small, less harmful pieces upon impact, which suits windows in high-traffic or vulnerable areas. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing the need for clarity and glare reduction with safety and durability requirements specific to your window's location and use.
Infographic: Anti-reflective glass vs Tempered glass for Window
 azmater.com
azmater.com