Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability compared to flint glass, making it ideal for precision optical prisms in demanding environments. Flint glass provides higher refractive indices and dispersion, enabling enhanced light splitting capabilities in optical prism applications.
Table of Comparison
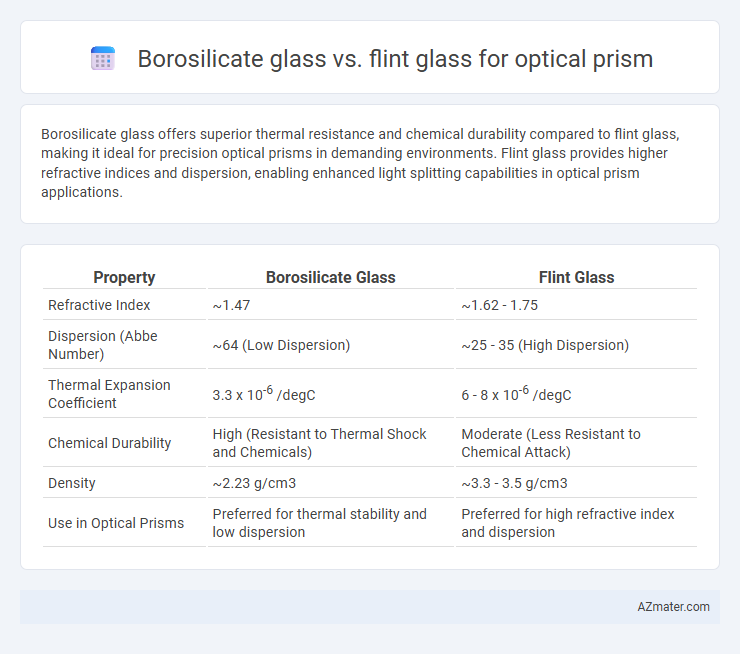
| Property | Borosilicate Glass | Flint Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Refractive Index | ~1.47 | ~1.62 - 1.75 |
| Dispersion (Abbe Number) | ~64 (Low Dispersion) | ~25 - 35 (High Dispersion) |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 3.3 x 10-6 /degC | 6 - 8 x 10-6 /degC |
| Chemical Durability | High (Resistant to Thermal Shock and Chemicals) | Moderate (Less Resistant to Chemical Attack) |
| Density | ~2.23 g/cm3 | ~3.3 - 3.5 g/cm3 |
| Use in Optical Prisms | Preferred for thermal stability and low dispersion | Preferred for high refractive index and dispersion |
Introduction to Optical Glass Types
Borosilicate glass and flint glass are two primary types of optical glass used in prisms, each offering distinct refractive indices and dispersion properties crucial for light manipulation. Borosilicate glass features low thermal expansion and high chemical durability, making it ideal for applications requiring dimensional stability and resistance to thermal shock. Flint glass, characterized by a higher refractive index and greater dispersion due to its lead oxide content, provides enhanced chromatic aberration correction in precision optical systems.
Overview of Borosilicate Glass in Optics
Borosilicate glass is widely favored in optical prisms due to its low thermal expansion and high chemical durability, ensuring stable performance in varying environmental conditions. Its excellent optical clarity and resistance to thermal shock make it suitable for precision instruments and high-accuracy light deflection applications. Compared to flint glass, borosilicate offers superior mechanical strength and reduced chromatic aberration, enhancing the overall quality of optical systems.
Characteristics of Flint Glass for Prisms
Flint glass for optical prisms exhibits a high refractive index and significant dispersion, enabling superior chromatic aberration correction in complex lens systems. Its density is greater than borosilicate glass, resulting in enhanced light bending capabilities essential for precise optical applications. The increased lead content in flint glass improves its optical clarity and color fidelity, making it ideal for high-quality prisms used in spectroscopy and imaging.
Comparative Refractive Index: Borosilicate vs Flint
Borosilicate glass typically has a refractive index around 1.47, offering moderate light bending capabilities suitable for precision optical prisms. Flint glass exhibits a higher refractive index ranging from approximately 1.56 to 1.75, enabling stronger light refraction and superior dispersion control in high-performance prisms. The difference in refractive index between borosilicate and flint glass directly impacts optical design choices, affecting lens efficiency and chromatic aberration correction.
Dispersion Properties and Chromatic Performance
Borosilicate glass exhibits lower dispersion and superior chromatic performance compared to flint glass, making it ideal for optical prisms requiring minimal color fringing and high image clarity. Flint glass typically has higher refractive indices and greater dispersion, which can lead to more pronounced chromatic aberrations and color distortion. Optical prisms made from borosilicate glass benefit applications demanding high precision and accurate color representation due to their enhanced control of light refraction and reduced chromatic dispersion.
Thermal and Chemical Stability Comparison
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior thermal stability with a low coefficient of thermal expansion (~3.3 x 10-6 /degC), minimizing distortion under temperature fluctuations, compared to flint glass which typically has a higher expansion coefficient (~7-10 x 10-6 /degC). Chemically, borosilicate glass resists corrosion and alkali attack due to its boron oxide content, ensuring long-term durability in harsh environments, whereas flint glass, rich in lead oxide, is more susceptible to chemical degradation. These properties make borosilicate glass the preferred choice for optical prisms requiring high thermal resistance and chemical robustness.
Impact on Prism Light Transmission
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal and chemical stability with a lower refractive index, resulting in less chromatic aberration and more precise light transmission in optical prisms. Flint glass, characterized by its high refractive index and dispersion, enhances image brightness but can cause increased chromatic aberration and light scattering in prisms. Selecting borosilicate glass benefits applications demanding clarity and minimal light distortion, while flint glass suits designs prioritizing color correction and light intensity.
Cost and Availability in Optical Applications
Borosilicate glass offers cost-effective pricing and widespread availability, making it a preferred choice for optical prisms in budget-sensitive applications. Flint glass, although more expensive and less commonly available, provides higher refractive indices essential for precise light dispersion in advanced optical instruments. The choice between borosilicate and flint glass hinges on balancing cost constraints with performance requirements in optical system design.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Borosilicate glass offers superior durability for optical prisms due to its high resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making it ideal for laboratory and industrial applications. Flint glass, while providing higher refractive indices and better dispersion for advanced optics, is more susceptible to scratching and chemical degradation, requiring careful maintenance. Regular cleaning with non-abrasive agents is essential for both, but borosilicate prisms typically demand less frequent upkeep, enhancing long-term performance.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Prism Needs
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for high-precision optical prisms used in demanding environments. Flint glass provides higher refractive indices and better dispersion properties, enhancing color separation and image clarity in applications requiring precise light manipulation. Choosing the right glass depends on balancing durability and optical performance, with borosilicate favored for durability and flint glass preferred for superior optical dispersion.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs Flint glass for Optical prism
 azmater.com
azmater.com