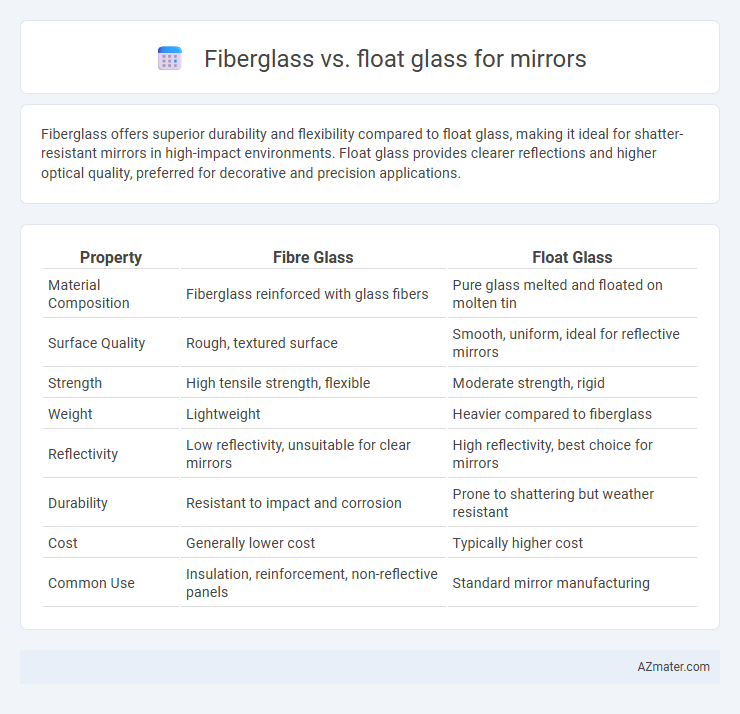
Fiberglass offers superior durability and flexibility compared to float glass, making it ideal for shatter-resistant mirrors in high-impact environments. Float glass provides clearer reflections and higher optical quality, preferred for decorative and precision applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fibre Glass | Float Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Fiberglass reinforced with glass fibers | Pure glass melted and floated on molten tin |
| Surface Quality | Rough, textured surface | Smooth, uniform, ideal for reflective mirrors |
| Strength | High tensile strength, flexible | Moderate strength, rigid |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier compared to fiberglass |
| Reflectivity | Low reflectivity, unsuitable for clear mirrors | High reflectivity, best choice for mirrors |
| Durability | Resistant to impact and corrosion | Prone to shattering but weather resistant |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost |
| Common Use | Insulation, reinforcement, non-reflective panels | Standard mirror manufacturing |
Introduction to Mirror Glass Types
Mirror glass types primarily include fibre glass and float glass, each offering distinct properties for reflective surfaces. Fibre glass mirrors provide lightweight durability and resistance to shattering, ideal for safety applications and environments prone to impact. Float glass mirrors deliver superior clarity and smoothness due to their manufacturing process, making them the preferred choice for high-quality reflective finishes in decorative and architectural uses.
What Is Fibre Glass?
Fibre glass is a composite material made from fine glass fibers woven into a fabric and bonded with resin, providing lightweight strength and flexibility for mirror backings. Unlike float glass, which is a solid sheet formed by floating molten glass on molten metal to create a smooth surface, fibre glass offers superior impact resistance and moisture resistance, ideal for durable mirror applications. Its ability to absorb vibrations and resist shattering makes fibre glass a preferred choice in environments requiring safety and longevity.
What Is Float Glass?
Float glass is a type of flat glass made by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal, typically tin, resulting in a uniform thickness and extremely smooth surface ideal for mirrors. Unlike fibreglass, which is a composite material composed of glass fibers embedded in resin, float glass provides superior clarity, reflectivity, and durability essential for high-quality mirror production. Its consistent flatness and transparency make float glass the standard choice for optical applications and architectural mirrors.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Fiberglass mirrors involve a complex manufacturing process where glass fibers are woven into a mat and coated with resin, followed by curing to create a strong, lightweight backing resistant to corrosion and impact. Float glass mirrors are produced by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal, typically tin, resulting in a smooth, uniform thickness ideal for high-quality reflective surfaces with excellent clarity. The float glass method offers superior optical properties but lacks the flexibility and enhanced durability provided by fiberglass-backed mirrors in harsh environments.
Optical Clarity and Reflection Quality
Float glass offers superior optical clarity and reflection quality compared to fiberglass, making it the preferred choice for high-quality mirrors. Its uniform surface and minimal distortion ensure sharp, true reflections with excellent light transmission. Fiberglass mirrors often exhibit slight waviness and lower reflectivity, resulting in less precise imagery and reduced overall visual performance.
Strength and Durability Differences
Fibre glass mirrors offer superior impact resistance and flexibility compared to float glass mirrors, which are more prone to cracking under stress. Float glass provides a smooth, high-quality reflective surface but lacks the tensile strength and shatter resistance characteristic of fibre glass. The durability of fibre glass mirrors makes them ideal for environments requiring enhanced toughness and longevity, while float glass mirrors suit applications prioritizing clarity and optical precision.
Weight and Handling Considerations
Fiberglass mirrors weigh significantly less than float glass mirrors, enhancing portability and ease of installation in various applications. The lightweight nature of fiberglass reduces strain during handling and lowers the risk of accidents or breakage compared to the heavier, more brittle float glass. Maintenance and transportation costs are also minimized with fiberglass mirrors due to their durability and resilience under impact.
Cost Comparison of Fibre and Float Glass
Fibre glass mirrors typically cost more than float glass mirrors due to higher raw material expenses and manufacturing complexity. Float glass offers a more economical solution for mirror production with consistent quality at a lower price point. When budgeting for mirror applications, float glass provides a cost-effective alternative without compromising clarity and durability.
Suitability for Mirror Applications
Fibre glass offers excellent flexibility and impact resistance, making it suitable for decorative or lightweight mirror applications where durability is essential. Float glass provides a smooth, uniform surface with superior optical clarity and scratch resistance, ideal for high-quality mirrors requiring precise reflection. For mirror applications prioritizing flawless reflection and durability, float glass remains the preferred material, while fibre glass suits specialized or safety-conscious environments.
Choosing the Right Glass for Mirrors
When choosing the right glass for mirrors, float glass is preferred for its smooth surface, clarity, and consistent thickness, delivering high-quality reflections. Fiberglass mirrors, though lighter and more shatter-resistant, often have a textured finish that can distort reflections and reduce image sharpness. Prioritizing float glass ensures optimal visual accuracy and durability, making it the superior option for most mirror applications.
Infographic: Fibre glass vs Float glass for Mirror
 azmater.com
azmater.com