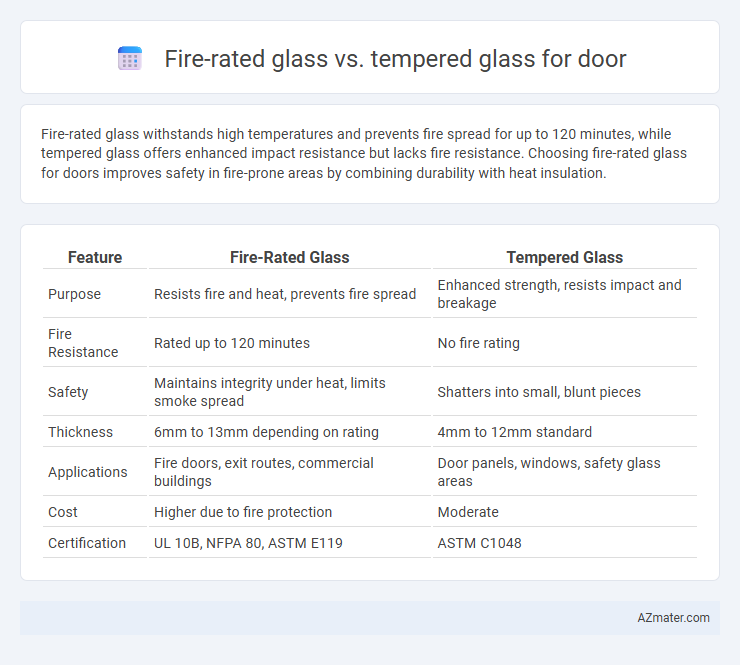
Fire-rated glass withstands high temperatures and prevents fire spread for up to 120 minutes, while tempered glass offers enhanced impact resistance but lacks fire resistance. Choosing fire-rated glass for doors improves safety in fire-prone areas by combining durability with heat insulation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Rated Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Resists fire and heat, prevents fire spread | Enhanced strength, resists impact and breakage |
| Fire Resistance | Rated up to 120 minutes | No fire rating |
| Safety | Maintains integrity under heat, limits smoke spread | Shatters into small, blunt pieces |
| Thickness | 6mm to 13mm depending on rating | 4mm to 12mm standard |
| Applications | Fire doors, exit routes, commercial buildings | Door panels, windows, safety glass areas |
| Cost | Higher due to fire protection | Moderate |
| Certification | UL 10B, NFPA 80, ASTM E119 | ASTM C1048 |
Understanding Fire-Rated Glass
Fire-rated glass is specifically designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke for a designated period, often ranging from 20 to 120 minutes, ensuring safety and containment in emergency situations. Unlike tempered glass, which is strengthened through a heat treatment process to increase impact resistance but lacks fire containment capabilities, fire-rated glass typically consists of multiple layers, including intumescent materials that expand when exposed to heat. Installing fire-rated glass in doors is essential in buildings requiring compliance with fire codes and enhances occupant protection by maintaining fire barriers without compromising visibility.
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to normal glass. It is designed to shatter into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, reducing the risk of injury in case of breakage. While tempered glass offers enhanced durability and safety for doors, it does not provide the fire resistance properties found in fire-rated glass.
Key Differences Between Fire-Rated and Tempered Glass
Fire-rated glass is specifically designed to withstand extreme heat and prevent the spread of fire for a specified time, typically ranging from 20 to 120 minutes, while tempered glass is manufactured to enhance strength and shatter into small, blunt pieces for safety but offers no fire resistance. Fire-rated glass incorporates materials such as intumescent interlayers or ceramic elements that expand under high temperatures, maintaining structural integrity during fire exposure. Tempered glass prioritizes impact resistance and compliance with building safety codes but lacks the specialized heat-resistant properties essential for fire containment in door applications.
Performance in Fire Conditions
Fire-rated glass provides superior performance in fire conditions by withstanding high temperatures and preventing the spread of flames and smoke for a specified period, typically ranging from 20 to 120 minutes. Tempered glass, although stronger and more impact-resistant than standard glass, lacks the necessary fire resistance and quickly fails under intense heat, shattering rapidly. Fire-rated glass often contains multiple layers or intumescent materials that expand when exposed to heat, maintaining integrity and visibility during fire emergencies.
Safety Features Compared
Fire-rated glass offers superior fire resistance by withstanding temperatures up to 2400degF and preventing the spread of flames and smoke for a specified duration, making it ideal for fire safety in doors. Tempered glass provides enhanced strength and shatter resistance, breaking into small, blunt pieces to reduce injury risk but lacks significant fire protection. For door safety, fire-rated glass ensures both structural integrity during a fire and containment, while tempered glass primarily focuses on impact resistance without fire containment properties.
Applications in Door Installations
Fire-rated glass is essential for door installations requiring compliance with fire safety codes, capable of withstanding high temperatures and preventing fire and smoke spread in commercial and institutional buildings. Tempered glass, while offering superior strength and safety through impact resistance, is primarily used in residential and office doors where fire protection is not a critical concern. Choosing between fire-rated and tempered glass hinges on application-specific requirements, with fire-rated glass mandated in stairwells, exit routes, and fire barriers to enhance occupant safety during emergencies.
Code Compliance and Certifications
Fire-rated glass for doors complies with strict building codes such as NFPA 80 and UL 10B, offering certification for fire resistance and preventing smoke and flame spread during fires. Tempered glass meets safety standards like ANSI Z97.1 and CPSC 16 CFR 1201 but lacks fire-resistance certification, making it unsuitable for fire-rated applications. Choosing fire-rated glass ensures compliance with local fire safety regulations and insurance requirements, while tempered glass is primarily used for impact resistance and general safety.
Cost Analysis: Fire-Rated vs Tempered Glass
Fire-rated glass generally costs 20-40% more than tempered glass due to its specialized fire resistance and safety certifications. Installation expenses for fire-rated glass are often higher because it requires compliance with strict building codes and professional fitting to ensure effectiveness during fire emergencies. While tempered glass is more economical upfront, investing in fire-rated glass can significantly reduce potential fire damage costs and insurance premiums, making it cost-effective in the long term.
Aesthetic Options and Design Flexibility
Fire-rated glass offers a range of aesthetic options including clear, wired, and tinted varieties that maintain a sleek appearance while meeting stringent safety standards. Tempered glass provides greater design flexibility with various textures, patterns, and color treatments, enhancing modern and customized door designs. Both materials support diverse architectural styles, but fire-rated glass balances aesthetic appeal with critical fire protection performance.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Door
Selecting the right glass for your door depends on safety requirements and building codes, with fire-rated glass offering critical heat resistance to prevent fire spread, while tempered glass provides enhanced strength and shatter resistance for impact safety. Fire-rated glass is essential in commercial or high-risk areas needing certified fire protection, meeting standards such as UL 9 or BS 476, whereas tempered glass suits residential or low-risk environments due to its durability and breakage pattern. Evaluating factors like fire protection ratings, safety standards, insulation, and application purpose ensures optimal performance and compliance when choosing between fire-rated and tempered glass for doors.
Infographic: Fire-rated glass vs Tempered glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com