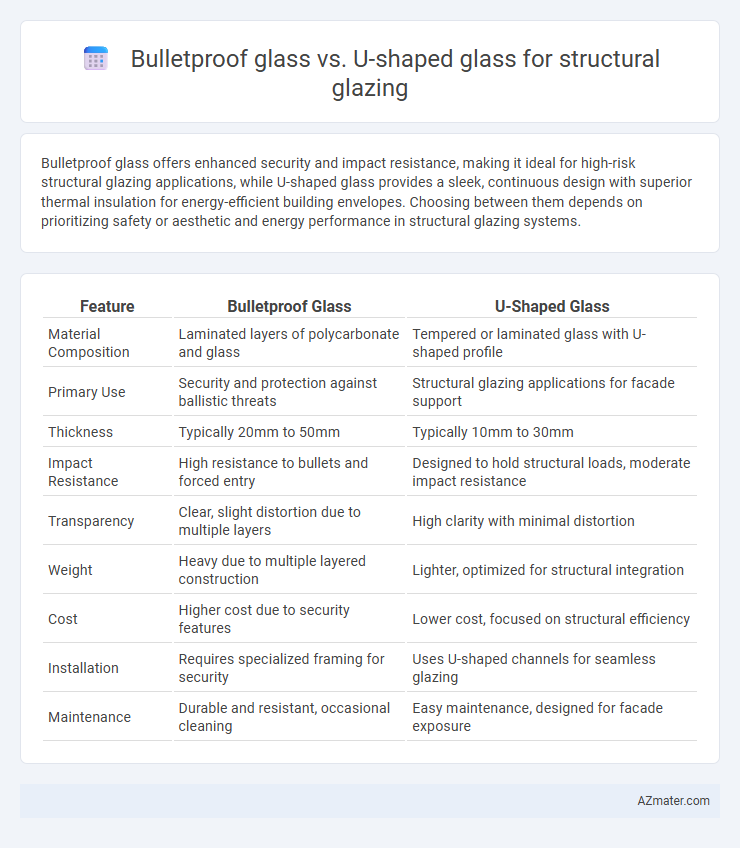
Bulletproof glass offers enhanced security and impact resistance, making it ideal for high-risk structural glazing applications, while U-shaped glass provides a sleek, continuous design with superior thermal insulation for energy-efficient building envelopes. Choosing between them depends on prioritizing safety or aesthetic and energy performance in structural glazing systems.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bulletproof Glass | U-Shaped Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Laminated layers of polycarbonate and glass | Tempered or laminated glass with U-shaped profile |
| Primary Use | Security and protection against ballistic threats | Structural glazing applications for facade support |
| Thickness | Typically 20mm to 50mm | Typically 10mm to 30mm |
| Impact Resistance | High resistance to bullets and forced entry | Designed to hold structural loads, moderate impact resistance |
| Transparency | Clear, slight distortion due to multiple layers | High clarity with minimal distortion |
| Weight | Heavy due to multiple layered construction | Lighter, optimized for structural integration |
| Cost | Higher cost due to security features | Lower cost, focused on structural efficiency |
| Installation | Requires specialized framing for security | Uses U-shaped channels for seamless glazing |
| Maintenance | Durable and resistant, occasional cleaning | Easy maintenance, designed for facade exposure |
Introduction to Structural Glazing Solutions
Structural glazing solutions enhance building safety and aesthetics by integrating specialized glass types like bulletproof glass and U-shaped glass, each offering distinct performance benefits. Bulletproof glass provides high-impact resistance and security, ideal for facades requiring protection against forced entry or ballistic threats. U-shaped glass, designed for seamless corner glazing, ensures structural integrity and sleek visual continuity in modern architectural designs.
What is Bulletproof Glass?
Bulletproof glass, also known as ballistic glass or bullet-resistant glass, is a type of laminated glass designed to withstand high-velocity impacts from bullets or blasts by combining multiple layers of glass and polycarbonate materials. This specialized glass is commonly used in security-sensitive applications, including structural glazing for buildings requiring enhanced protection against forced entry and ballistic threats. Unlike U-shaped glass, which primarily serves as a structural framing component in glazing systems, bulletproof glass provides critical safety and security by preventing penetration and minimizing damage from projectiles.
Overview of U-Shaped Glass
U-shaped glass, designed with a channel-like profile, provides enhanced structural support and facilitates seamless integration into framing systems for structural glazing applications. This glass variant offers superior resistance to wind loads and thermal expansion compared to standard flat glass, making it ideal for high-rise facades and curtain walls. Its geometric configuration enables efficient load distribution and improved anchorage, optimizing both safety and aesthetic appeal in modern architectural designs.
Key Material Properties Compared
Bulletproof glass exhibits high-impact resistance and multi-layered laminated construction, ensuring superior ballistic protection and durability for structural glazing applications. U-shaped glass is engineered with precise channel edges for seamless integration and enhanced structural support, optimizing load distribution in curtain wall systems. Both materials feature excellent optical clarity and weather resistance, but bulletproof glass prioritizes security, while U-shaped glass emphasizes structural stability and ease of installation.
Impact Resistance and Safety Standards
Bulletproof glass offers superior impact resistance by utilizing multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate to absorb and disperse kinetic energy, meeting stringent safety standards such as UL 752 for ballistic protection. U-shaped glass, designed primarily for structural glazing, provides robust support and load distribution but generally lacks the multi-layer impact resistance found in bulletproof variants, making it less effective against high-velocity impacts. Safety standards for U-shaped glass often focus on structural integrity and thermal performance rather than ballistic resistance, highlighting the importance of selecting bulletproof glass for environments requiring enhanced security against forced entry or projectiles.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Considerations
Bulletproof glass offers enhanced security for structural glazing while maintaining thickness that can limit design flexibility compared to U-shaped glass, which allows for seamless, minimalist profiles and greater curvature options in facade designs. U-shaped glass provides superior aesthetic appeal through its ability to create smooth, continuous glass surfaces with fewer visible joints, ideal for modern architectural expressions. Selection depends on balancing security requirements against desired visual impact and structural adaptability within the building envelope.
Applications in Modern Architecture
Bulletproof glass enhances security and impact resistance in high-risk environments such as government buildings, banks, and airports, providing safety without compromising visibility in structural glazing. U-shaped glass offers sleek aesthetics and seamless connections ideal for modern facades, commercial complexes, and curtain wall systems, emphasizing transparency and minimalistic design. Both materials cater to distinct architectural needs, combining safety and style in contemporary building envelopes.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Bulletproof glass requires specialized handling and professional installation due to its multi-layered composition and weight, often involving reinforced framing systems to ensure structural integrity. U-shaped glass used in structural glazing offers simpler installation with its continuous channel design that facilitates easier alignment and sealing, reducing labor time and complexity. Maintenance for bulletproof glass often entails careful inspection for delamination and damage repair, while U-shaped glass systems benefit from straightforward sealant replacement and easier glass panel removal when needed.
Cost Analysis: Bulletproof vs U-Shaped Glass
Bulletproof glass typically incurs higher initial costs due to its multi-layered laminate construction designed for impact resistance, making it up to 30-50% more expensive per square foot than standard U-shaped glass. U-shaped glass, favored for its sleek aesthetics and ease of installation in structural glazing, offers cost benefits through reduced framing and material usage, lowering overall project expenditure by approximately 20%. When analyzing lifecycle costs, bulletproof glass may require less frequent replacement and maintenance under high-security demands, but U-shaped glass provides a cost-effective solution for moderate safety applications and enhanced architectural design flexibility.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Bulletproof glass offers enhanced security and impact resistance, making it ideal for high-risk structural glazing projects requiring safety and protection against forced entry or explosions. U-shaped glass provides seamless, frameless aesthetic appeal with strong structural integrity, perfect for modern architectural designs emphasizing transparency and minimalism. Selecting the right glass depends on project-specific needs such as security level, design preferences, budget constraints, and regulatory compliance for building codes.
Infographic: Bulletproof glass vs U-shaped glass for Structural glazing
 azmater.com
azmater.com