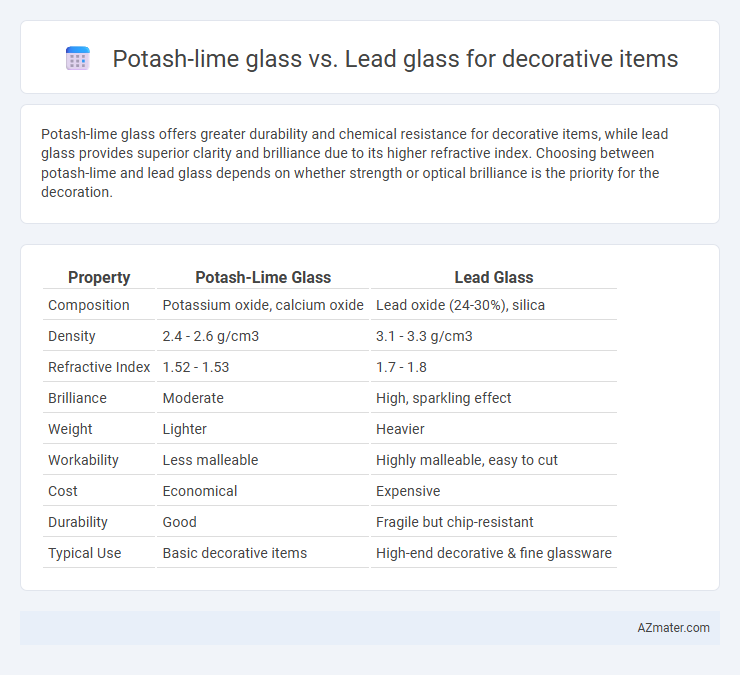
Potash-lime glass offers greater durability and chemical resistance for decorative items, while lead glass provides superior clarity and brilliance due to its higher refractive index. Choosing between potash-lime and lead glass depends on whether strength or optical brilliance is the priority for the decoration.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Potash-Lime Glass | Lead Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Potassium oxide, calcium oxide | Lead oxide (24-30%), silica |
| Density | 2.4 - 2.6 g/cm3 | 3.1 - 3.3 g/cm3 |
| Refractive Index | 1.52 - 1.53 | 1.7 - 1.8 |
| Brilliance | Moderate | High, sparkling effect |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Workability | Less malleable | Highly malleable, easy to cut |
| Cost | Economical | Expensive |
| Durability | Good | Fragile but chip-resistant |
| Typical Use | Basic decorative items | High-end decorative & fine glassware |
Introduction to Glass Types for Decorative Items
Potash-lime glass and lead glass are common materials used in decorative items, each offering distinct optical qualities and durability. Potash-lime glass is prized for its high clarity, chemical resistance, and affordability, making it suitable for everyday decorative pieces. Lead glass, containing higher lead oxide content, provides superior brilliance, weight, and refractive index, often preferred for premium crystal-like decorations and intricate designs.
What is Potash-lime Glass?
Potash-lime glass, a type of soda-lime glass enriched with potassium oxide, offers enhanced durability and chemical resistance compared to standard soda-lime glass, making it suitable for decorative items requiring robustness and clarity. This glass contains potassium oxide derived from potash, contributing to its lower thermal expansion and improved scratch resistance, which benefits ornamental pieces exposed to handling and temperature variations. Compared to lead glass, potash-lime glass has lower density and refractive index, resulting in less brilliance but a more environmentally friendly and cost-effective option for decorative applications.
Understanding Lead Glass Composition
Lead glass, also known as crystal glass, contains a high percentage of lead oxide, typically between 18% and 40%, which significantly enhances its refractive index and brilliance compared to potash-lime glass. Potash-lime glass primarily consists of silica, potash, and lime, offering lower density and less optical clarity but greater chemical durability. The lead content in lead glass increases weight, improves workability during cutting and engraving, and produces a distinct sparkling effect that is highly valued in decorative items.
Visual Differences: Potash-lime vs Lead Glass
Potash-lime glass exhibits a more subdued brilliance with moderate clarity, making it suitable for decorative items requiring durability and a softer visual appeal. Lead glass boasts higher refractive indices, resulting in exceptional sparkle, clarity, and weight that enhance the visual impact of intricate designs in decorative pieces. The contrast between the muted sheen of potash-lime and the radiant shimmer of lead glass defines their distinct aesthetic roles in ornamental applications.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Potash-lime glass, composed primarily of potassium oxide and lime, offers moderate durability with good resistance to thermal shock, making it suitable for everyday decorative items that require longevity without significant fragility. Lead glass, enriched with lead oxide up to 30-35%, provides superior brilliance and clarity but is softer and more prone to scratching and chipping, reducing its long-term durability compared to potash-lime glass. In applications where durability and longevity are critical, potash-lime glass outperforms lead glass due to its enhanced structural strength and resistance to environmental wear.
Decorative Potential: Cutting, Coloring, and Shaping
Potash-lime glass offers moderate hardness and better thermal resistance, allowing precise cutting and intricate shaping suitable for various decorative items, while its composition supports a wide range of vibrant colorants. Lead glass, with higher refractive index and density, excels in brilliance and clarity, enhancing decorative potential through intricate cutting techniques such as faceting and engraving, resulting in sparkling effects ideal for luxury pieces. Both glasses respond well to coloring, but lead glass's softness facilitates finer detail work, making it preferred for ornate, high-end decorative glassware.
Health and Safety Considerations
Potash-lime glass is generally safer for decorative items due to its absence of toxic lead content, reducing health risks associated with lead exposure. Lead glass, while offering superior brilliance and clarity, poses potential hazards such as lead leaching, especially if used for food or drink containers. Choosing potash-lime glass minimizes concerns related to lead poisoning and environmental contamination, making it a safer option for decorative purposes.
Environmental Impact of Both Glass Types
Potash-lime glass exhibits a lower environmental impact due to its simpler composition and more abundant raw materials, resulting in reduced energy consumption during production compared to lead glass. Lead glass contains toxic lead oxide which poses significant environmental hazards during manufacturing, disposal, and potential leaching into ecosystems. Recycling potash-lime glass is more straightforward and eco-friendly, while lead glass requires specialized handling to prevent lead contamination and mitigate long-term environmental risks.
Cost and Market Availability
Potash-lime glass offers a cost-effective alternative to lead glass, making it more accessible for mass production of decorative items. Lead glass, known for its higher refractive index and brilliance, tends to be more expensive due to the use of lead oxide and stricter regulations on lead content. Market availability favors potash-lime glass, as it is widely produced and easier to source globally, whereas lead glass is often limited to specialized manufacturers catering to luxury or artisanal markets.
Choosing the Right Glass for Decorative Purposes
Potash-lime glass offers excellent durability and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for sturdy decorative items with subtle clarity. Lead glass, with its higher refractive index and brilliance, provides superior sparkle and weight, enhancing luxury decorative pieces like chandeliers and fine vases. Selecting between potash-lime and lead glass depends on the desired balance of aesthetic brilliance, durability, and budget constraints for the intended decorative application.
Infographic: Potash-lime glass vs Lead glass for Decorative item
 azmater.com
azmater.com