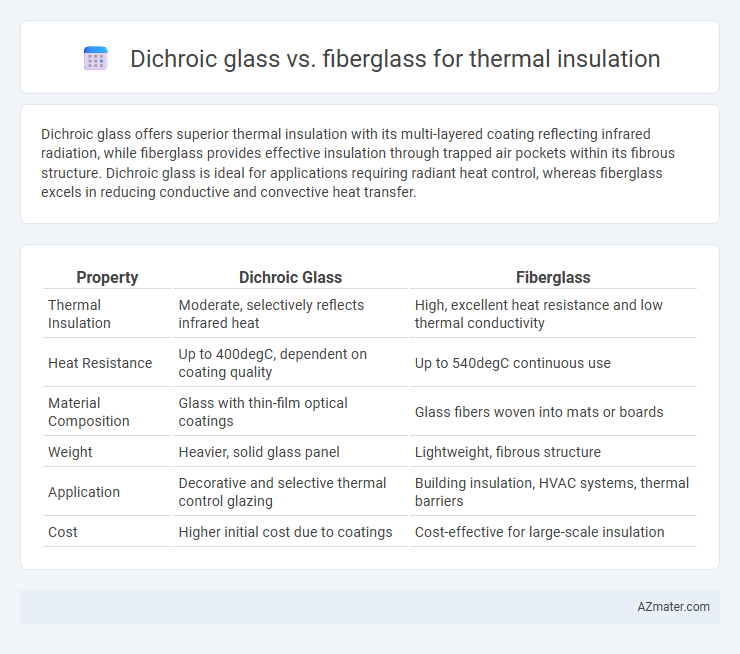
Dichroic glass offers superior thermal insulation with its multi-layered coating reflecting infrared radiation, while fiberglass provides effective insulation through trapped air pockets within its fibrous structure. Dichroic glass is ideal for applications requiring radiant heat control, whereas fiberglass excels in reducing conductive and convective heat transfer.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dichroic Glass | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate, selectively reflects infrared heat | High, excellent heat resistance and low thermal conductivity |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 400degC, dependent on coating quality | Up to 540degC continuous use |
| Material Composition | Glass with thin-film optical coatings | Glass fibers woven into mats or boards |
| Weight | Heavier, solid glass panel | Lightweight, fibrous structure |
| Application | Decorative and selective thermal control glazing | Building insulation, HVAC systems, thermal barriers |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to coatings | Cost-effective for large-scale insulation |
Introduction to Thermal Insulation Materials
Thermal insulation materials such as dichroic glass and fiberglass play crucial roles in energy efficiency and temperature regulation. Dichroic glass provides selective thermal control by reflecting specific wavelengths of heat while allowing visible light transmission, making it ideal for architectural applications requiring both insulation and aesthetic appeal. Fiberglass offers excellent thermal resistance through its fine glass fibers that trap air, widely used in building insulation for its cost-effectiveness and high R-value performance.
Understanding Dichroic Glass: Properties and Composition
Dichroic glass features multiple ultra-thin layers of metal oxides, creating its unique ability to reflect specific wavelengths of light while transmitting others, making it a selective thermal barrier. Unlike fiberglass, which insulates primarily through trapped air within glass fibers, dichroic glass controls heat transfer by modulating infrared radiation, resulting in enhanced energy efficiency. Its composition allows for customizable optical properties without compromising transparency, offering innovative applications in thermal insulation where light control and heat resistance are critical.
Exploring Fiberglass: Structure and Advantages
Fiberglass thermal insulation consists of fine glass fibers woven into a dense mat, providing excellent heat resistance and sound absorption properties. Its structure creates numerous air pockets that reduce heat transfer, making it highly efficient for maintaining consistent indoor temperatures. This material offers superior fire resistance, durability, and flexibility compared to traditional insulation options, enhancing energy efficiency in residential and commercial buildings.
Thermal Conductivity: Dichroic Glass vs Fiberglass
Dichroic glass exhibits significantly higher thermal conductivity compared to fiberglass, making it less effective as an insulator in thermal applications. Fiberglass typically has a low thermal conductivity value around 0.04 W/m*K, which provides excellent resistance to heat transfer. In contrast, dichroic glass, composed primarily of silica and metal oxides, has a thermal conductivity near 1 W/m*K, limiting its use for efficient thermal insulation purposes.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Dichroic glass offers superior energy efficiency by selectively filtering solar radiation, reducing heat gain while allowing natural light, which lowers cooling costs in buildings. Fiberglass insulation primarily acts as a thermal barrier by trapping air, providing high R-values that minimize heat transfer through walls and ceilings but does not influence solar heat gain directly. Combining dichroic glass with fiberglass insulation optimizes energy efficiency by addressing both solar heat control and conductive heat loss.
Durability and Longevity of Each Material
Dichroic glass offers superior durability with resistance to UV radiation, thermal stress, and corrosion, ensuring long-lasting performance in thermal insulation applications. Fiberglass provides excellent thermal resistance but may degrade over time due to moisture absorption and mechanical wear, potentially reducing its lifespan. When prioritizing longevity, dichroic glass outperforms fiberglass by maintaining structural integrity and insulating properties under prolonged exposure to harsh environmental conditions.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Dichroic glass requires precise installation due to its delicate coating that can be damaged by improper handling, demanding skilled professionals and protective measures during fitting. Fiberglass insulation is easier to install, often available in batts or rolls, but requires protective gear to handle safely due to irritant fibers. Maintenance for dichroic glass involves regular cleaning with non-abrasive materials to preserve its thermal properties, whereas fiberglass may degrade or trap moisture over time, necessitating periodic inspection and replacement.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-term Savings
Dichroic glass offers superior aesthetic appeal and selective light transmission but involves a higher initial investment compared to fiberglass, which is significantly more affordable upfront. Fiberglass provides effective thermal insulation with lower maintenance costs, resulting in substantial long-term savings despite its lower upfront price. Evaluating both materials requires balancing dichroic glass's premium cost against fiberglass's proven energy efficiency and durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Dichroic glass offers enhanced thermal insulation while being recyclable and contributing to reduced energy consumption in buildings, making it a sustainable choice with a lower environmental footprint compared to traditional materials. Fiberglass insulation, although widely used for its affordability and thermal performance, involves energy-intensive manufacturing and potential health hazards due to airborne fibers, raising concerns about its environmental impact. The sustainability benefits of dichroic glass align with green building standards, whereas fiberglass requires careful handling and disposal to mitigate its ecological consequences.
Best Applications: Choosing Between Dichroic Glass and Fiberglass
Dichroic glass excels in thermal insulation applications requiring selective wavelength reflection, such as high-performance solar control in architectural glazing and specialized laboratory environments. Fiberglass offers superior versatility and cost-effectiveness for general thermal insulation in industrial machinery, building envelopes, and HVAC systems due to its excellent thermal resistance and ease of installation. Selecting between dichroic glass and fiberglass depends on prioritizing spectral control and aesthetic properties versus broad-spectrum insulation efficiency and budget constraints.
Infographic: Dichroic glass vs Fiberglass for Thermal insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com