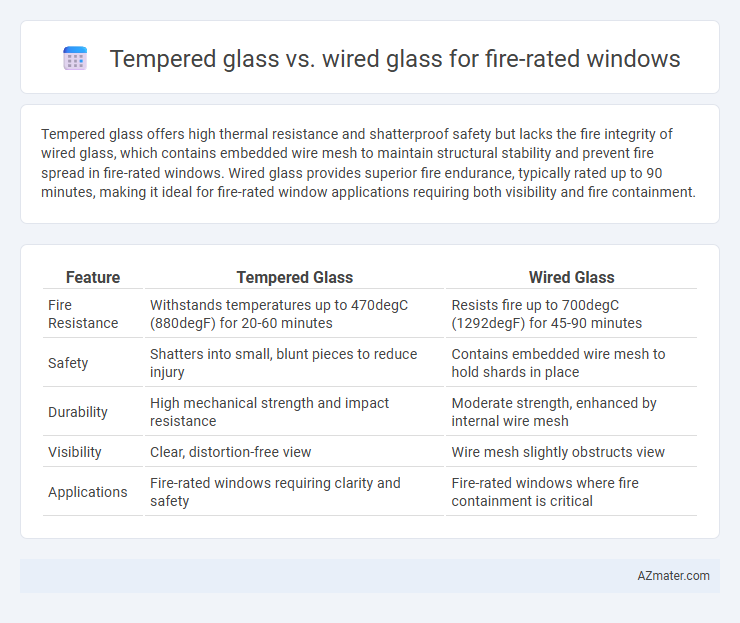
Tempered glass offers high thermal resistance and shatterproof safety but lacks the fire integrity of wired glass, which contains embedded wire mesh to maintain structural stability and prevent fire spread in fire-rated windows. Wired glass provides superior fire endurance, typically rated up to 90 minutes, making it ideal for fire-rated window applications requiring both visibility and fire containment.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tempered Glass | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Withstands temperatures up to 470degC (880degF) for 20-60 minutes | Resists fire up to 700degC (1292degF) for 45-90 minutes |
| Safety | Shatters into small, blunt pieces to reduce injury | Contains embedded wire mesh to hold shards in place |
| Durability | High mechanical strength and impact resistance | Moderate strength, enhanced by internal wire mesh |
| Visibility | Clear, distortion-free view | Wire mesh slightly obstructs view |
| Applications | Fire-rated windows requiring clarity and safety | Fire-rated windows where fire containment is critical |
Introduction to Fire-Rated Windows
Fire-rated windows incorporate specialized glass designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread. Tempered glass offers enhanced strength and shatters into small, less harmful pieces, while wired glass contains embedded metal mesh to hold fragments together during heat exposure. Both types meet fire safety standards, but wired glass is often preferred for its superior fire resistance and structural integrity under extreme conditions.
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to normal glass, making it suitable for fire-rated windows. It is designed to resist high temperatures and, upon breakage, shatters into small, blunt pieces to reduce injury risk. This durability and safety profile make tempered glass a preferred choice over wired glass in many fire-rated window applications.
What is Wired Glass?
Wired glass is a type of fire-rated glass embedded with a metal wire mesh that holds the glass together during exposure to high temperatures, preventing it from shattering and maintaining its integrity. It offers enhanced fire resistance and safety by providing a barrier against flames and smoke while allowing light transmission. Although wired glass offers superior fire protection compared to tempered glass, it is less resistant to impact and can be more prone to breakage under physical stress.
Fire Resistance: Tempered vs Wired Glass
Tempered glass offers moderate fire resistance by withstanding high temperatures up to 470degF before breaking, while wired glass provides superior fire resistance through its embedded wire mesh that holds the glass intact under extreme heat and fire exposure. Wired glass is specifically designed to resist fire penetration and maintain structural integrity, making it a preferred choice for fire-rated windows requiring enhanced safety performance. The wired mesh in wired glass prevents the spread of flames and smoke, whereas tempered glass may shatter more rapidly under prolonged fire conditions despite its strength.
Safety and Impact Performance Comparison
Tempered glass offers superior impact resistance due to its heat-treated fabrication process, making it less likely to shatter dangerously upon impact compared to wired glass. Wired glass contains embedded wire mesh that holds fragments together during a fire but is more prone to catastrophic breakage under impact, posing higher safety risks. Both glass types meet fire-rating standards, yet tempered glass provides enhanced safety and durability for fire-rated windows exposed to physical stress.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Tempered glass offers a sleek, clear appearance that enhances modern fire-rated window aesthetics by providing unobstructed views and greater light transmission. Wired glass, with its embedded mesh, creates a distinctive textured look that may limit design flexibility but adds a traditional or industrial charm. Design options expand with tempered glass due to its ability to be cut, curved, and laminated, whereas wired glass is typically limited to flat panes, impacting overall architectural creativity.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Tempered glass for fire-rated windows offers easier installation due to its uniform strength and compatibility with standard framing systems, reducing labor time and costs. Wired glass requires specialized handling and secure mounting to prevent wire mesh displacement during installation, increasing complexity and potential for errors. Maintenance of tempered glass is simpler, as it resists scratches and impacts without compromising fire integrity, whereas wired glass demands frequent inspections to check for wire corrosion or glass delamination that can impair fire performance.
Code Compliance and Certification
Tempered glass and wired glass for fire-rated windows must meet specific code compliance criteria, including ASTM E84 for flame spread and smoke development. Tempered glass offers enhanced strength and shatters into small, less dangerous pieces but requires certification under NFPA 80 and NFPA 101 for egress and fire protection compliance. Wired glass maintains its integrity under heat due to embedded wire mesh, meeting UL 9 and UL 10B standards for hose stream and fire endurance tests, making it a reliable choice for fire-rated glazing where visibility and fire resistance are critical.
Cost Analysis: Tempered vs Wired Glass
Tempered glass typically costs 20-40% more than wired glass due to advanced manufacturing processes and higher impact resistance. Wired glass offers budget-friendly fire-rated window solutions but sacrifices some durability and safety standards compared to tempered glass. For projects prioritizing cost-efficiency, wired glass is a practical option, whereas tempered glass delivers better long-term value through enhanced strength and compliance with stringent fire safety codes.
Making the Right Choice for Fire-Rated Windows
Tempered glass offers high heat resistance and shatters into small, less dangerous pieces, making it suitable for fire-rated windows requiring safety and durability. Wired glass contains embedded wire mesh that holds glass fragments together during a fire, providing enhanced structural integrity and visibility under extreme heat. Selecting the right fire-rated window depends on balancing safety needs, building codes, and specific fire-resistance ratings, with tempered glass favored for impact resistance and wired glass preferred for fire endurance.
Infographic: Tempered glass vs Wired glass for Fire-rated window
 azmater.com
azmater.com