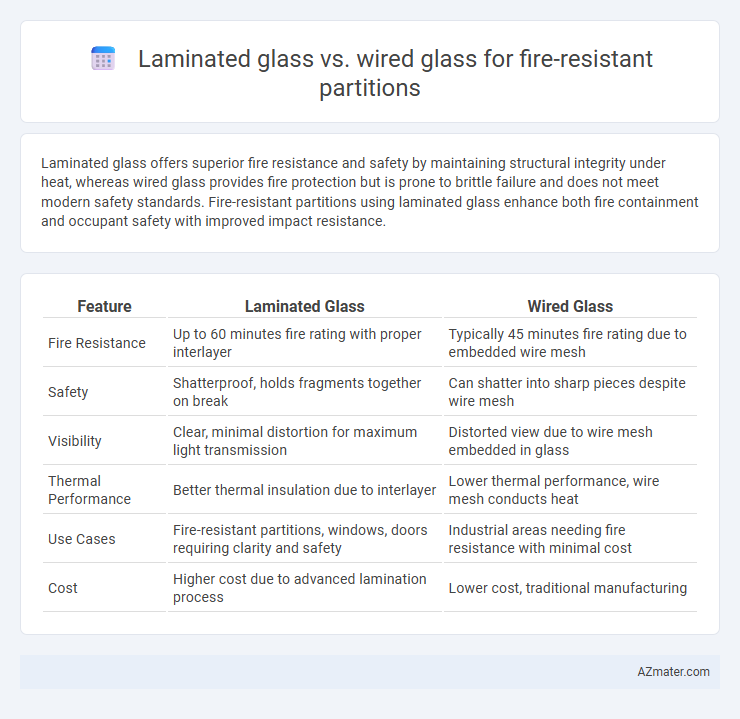
Laminated glass offers superior fire resistance and safety by maintaining structural integrity under heat, whereas wired glass provides fire protection but is prone to brittle failure and does not meet modern safety standards. Fire-resistant partitions using laminated glass enhance both fire containment and occupant safety with improved impact resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Up to 60 minutes fire rating with proper interlayer | Typically 45 minutes fire rating due to embedded wire mesh |
| Safety | Shatterproof, holds fragments together on break | Can shatter into sharp pieces despite wire mesh |
| Visibility | Clear, minimal distortion for maximum light transmission | Distorted view due to wire mesh embedded in glass |
| Thermal Performance | Better thermal insulation due to interlayer | Lower thermal performance, wire mesh conducts heat |
| Use Cases | Fire-resistant partitions, windows, doors requiring clarity and safety | Industrial areas needing fire resistance with minimal cost |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced lamination process | Lower cost, traditional manufacturing |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant Partition Glazing
Fire-resistant partition glazing requires materials that can withstand intense heat and prevent flame spread to enhance building safety. Laminated glass offers superior impact resistance and can hold together when shattered, providing extended fire protection by maintaining barrier integrity. Wired glass, embedded with a metal mesh, enhances fire resistance by preventing glass fragmentation and ensuring structural stability during fire exposure.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass is a type of safety glass made by bonding two or more layers of glass with an interlayer, usually polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which holds the layers together upon impact. This composition enhances fire resistance by preventing shattering and maintaining an effective barrier against heat and flames in fire-resistant partitions. Laminated glass offers superior clarity, strength, and thermal protection compared to wired glass, making it ideal for modern fire-rated applications.
What is Wired Glass?
Wired glass is a type of fire-resistant glass embedded with a metal mesh grid that maintains structural integrity during high temperatures, preventing the glass from shattering. It offers increased fire protection and smoke resistance, commonly used in fire-rated partitions to contain fire and limit its spread. Unlike laminated glass, wired glass provides enhanced heat resistance but may compromise clarity and impact resistance.
Fire Resistance Ratings: Laminated vs Wired Glass
Laminated glass typically offers fire resistance ratings ranging from 20 to 120 minutes, effectively preventing fire spread and providing safety during emergencies. Wired glass, often rated between 45 to 90 minutes, contains embedded metal wires that help maintain structural integrity under heat but may have reduced visibility and impact resistance. The choice between laminated and wired glass for fire-resistant partitions depends on the required fire rating, application needs, and durability considerations.
Safety Performance and Impact Resistance
Laminated glass offers superior safety performance in fire-resistant partitions by maintaining structural integrity under heat and preventing shards from dispersing upon impact, thanks to its interlayer bonding. Wired glass, while fire-resistant and capable of withstanding high temperatures without immediate breakage, tends to lose impact resistance as the embedded wire mesh can cause it to crack and fall out under force. The choice between laminated and wired glass hinges on balancing impact resistance--where laminated glass excels--and fire endurance, where wired glass provides reliable thermal protection but lower safety in violent impacts.
Acoustic and Thermal Benefits Compared
Laminated glass offers superior acoustic insulation due to its interlayer that dampens sound vibrations, making it ideal for fire-resistant partitions requiring noise reduction. Wired glass, while providing basic fire resistance, lacks significant soundproofing properties and tends to transfer heat more readily. Thermal performance of laminated glass also exceeds wired glass by maintaining temperature control and minimizing heat transfer, enhancing energy efficiency in fire-rated partitions.
Visual Clarity and Aesthetic Considerations
Laminated glass offers superior visual clarity and a smooth, transparent appearance, making it ideal for fire-resistant partitions where aesthetics and unobstructed views are crucial. Wired glass contains embedded metal wires that reduce visibility and create a grid-like pattern, often detracting from the overall aesthetic and offering a more industrial look. Choosing laminated glass enhances natural light flow and modern design appeal, while wired glass prioritizes fire safety with a compromised visual experience.
Code Compliance and Certification
Laminated glass and wired glass both serve as fire-resistant partitions, but laminated glass typically meets higher performance standards under modern fire safety codes such as UL 972 and NFPA 80 due to its enhanced integrity and heat resistance. Wired glass, while historically favored for its embedded wire mesh providing fire resistivity, often faces stricter limitations or is being phased out in certain jurisdictions because of shattering risks and lower impact resistance. Certification for fire-rated partitions requires adherence to ASTM E119 or UL 9 standards, where laminated glass frequently offers superior compliance and certification options that align with contemporary building codes.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Laminated glass for fire-resistant partitions offers easier installation due to its lightweight structure and compatibility with standard glazing systems, while wired glass requires specialized framing to accommodate its heavier and more brittle nature. Maintenance of laminated glass is simpler, as its laminated layers prevent shattering and maintain integrity upon impact, reducing the need for frequent replacements compared to wired glass, which is prone to cracking and requires regular inspection to ensure embedded wire mesh remains intact. Both glass types must comply with fire safety regulations, but laminated glass often provides enhanced durability and lower life-cycle costs in fire-resistant applications.
Cost Analysis and Long-Term Value
Laminated glass offers higher upfront costs compared to wired glass but provides superior fire resistance and enhanced safety, making it a cost-effective option over time due to reduced repair and replacement needs. Wired glass is generally less expensive initially but may incur higher long-term expenses due to lower durability and potential safety risks during fire incidents. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals laminated glass as a better long-term investment for fire-resistant partitions, balancing price with performance and regulatory compliance.
Infographic: Laminated glass vs Wired glass for Fire-resistant partition
 azmater.com
azmater.com