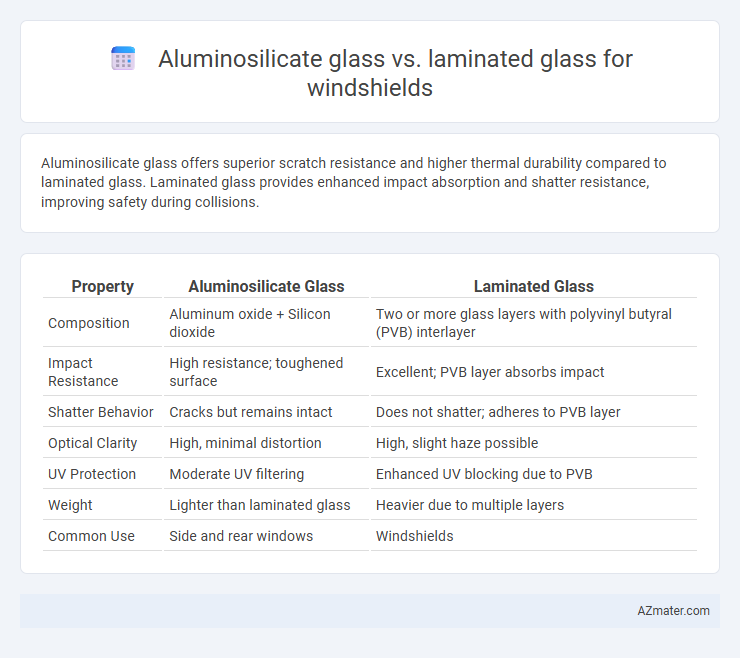
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior scratch resistance and higher thermal durability compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass provides enhanced impact absorption and shatter resistance, improving safety during collisions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminosilicate Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminum oxide + Silicon dioxide | Two or more glass layers with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer |
| Impact Resistance | High resistance; toughened surface | Excellent; PVB layer absorbs impact |
| Shatter Behavior | Cracks but remains intact | Does not shatter; adheres to PVB layer |
| Optical Clarity | High, minimal distortion | High, slight haze possible |
| UV Protection | Moderate UV filtering | Enhanced UV blocking due to PVB |
| Weight | Lighter than laminated glass | Heavier due to multiple layers |
| Common Use | Side and rear windows | Windshields |
Introduction to Windshield Glass Types
Aluminosilicate glass, known for its high strength and thermal resistance, is commonly used in modern windshields due to its durability and ability to withstand impact and temperature fluctuations. Laminated glass, composed of two or more glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, provides enhanced safety by preventing shattering and holding glass fragments together upon impact. Both types offer distinct advantages in windshield applications, with aluminosilicate glass emphasizing structural integrity and laminated glass prioritizing occupant protection during collisions.
What is Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass is a type of durable, heat-resistant glass primarily composed of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, making it highly resistant to thermal shock and mechanical stress. In windshield applications, aluminosilicate glass provides enhanced strength and scratch resistance compared to standard laminated glass, improving safety and longevity. This glass is often used in high-performance vehicles where durability and resistance to harsh environmental conditions are critical factors.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which enhances impact resistance and prevents shattering. This structure provides superior safety for windshields by holding glass fragments in place during collisions, reducing the risk of injury. Comparatively, aluminosilicate glass is chemically strengthened for hardness but lacks the layered safety feature intrinsic to laminated glass.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Aluminosilicate glass used in windshields primarily consists of silicon dioxide (SiO2) with added alumina (Al2O3), enhancing chemical durability and thermal resistance compared to standard laminated glass layers. Laminated glass combines two or more layers of annealed glass with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, resulting in a composite structure with different mechanical and chemical properties, including improved impact resistance and shatter retention. The chemical composition of aluminosilicate glass leads to higher resistance against scratches and thermal shock, while laminated glass relies more on its interlayer for strength and occupant protection.
Strength and Impact Resistance
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior strength and enhanced impact resistance due to its chemically strengthened structure, making it more durable against scratches and minor impacts. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers with an interlayer, provides excellent impact resistance by preventing shattering and maintaining structural integrity upon impact. In automotive windshields, laminated glass is preferred for safety as it holds together during collisions, while aluminosilicate glass excels in resisting everyday wear and tear.
Optical Clarity and Visibility
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior optical clarity due to its higher hardness and chemical durability, which reduces surface distortions and scratches over time, resulting in better visibility for drivers. Laminated glass, while designed to enhance safety by holding shards together upon impact, may suffer from slight optical distortions caused by the interlayer adhesive, potentially affecting clarity under certain lighting conditions. Overall, aluminosilicate glass provides a clearer and more consistent visual experience, whereas laminated glass prioritizes safety with modest compromises in optical performance.
Safety Performance in Accidents
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior impact resistance due to its enhanced chemical durability and thermal stability, reducing the likelihood of shattering during collisions. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers bonded by a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, maintains structural integrity upon impact, preventing shards from dispersing and reducing occupant injury risk. The combination of shock absorption in laminated glass and the toughness of aluminosilicate glass significantly improves windshield safety performance in vehicular accidents.
Durability and Longevity
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior durability due to its enhanced chemical composition, resisting scratches and impacts better than conventional laminated glass. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers including a plastic interlayer, provides excellent shatter resistance but may degrade over time under UV exposure, affecting its longevity. For windshields, aluminosilicate glass ensures longer-lasting strength and clarity, while laminated glass prioritizes safety with impact absorption.
Cost and Availability
Aluminosilicate glass for windshields is typically more expensive due to its enhanced strength and heat resistance, making it less commonly used and harder to source in bulk compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass is widely available and cost-effective, combining layers of glass with plastic interlayer to ensure safety and durability at a lower price point. The affordability and easier procurement of laminated glass make it the industry standard for most automotive windshields.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Windshield
Aluminosilicate glass offers high thermal resistance and exceptional durability, making it ideal for windshields exposed to extreme temperature changes and impacts. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, provides superior safety by preventing shattering and ensuring windshield integrity during collisions. When choosing the right glass for your windshield, prioritize laminated glass for its enhanced safety features and Aluminosilicate glass if thermal stability and scratch resistance are critical.
Infographic: Aluminosilicate glass vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com