Transparent wood glass offers enhanced durability and thermal insulation compared to low iron glass, making it a sustainable alternative for solar panels. Low iron glass provides higher light transmittance and efficiency, essential for maximizing solar energy capture.
Table of Comparison
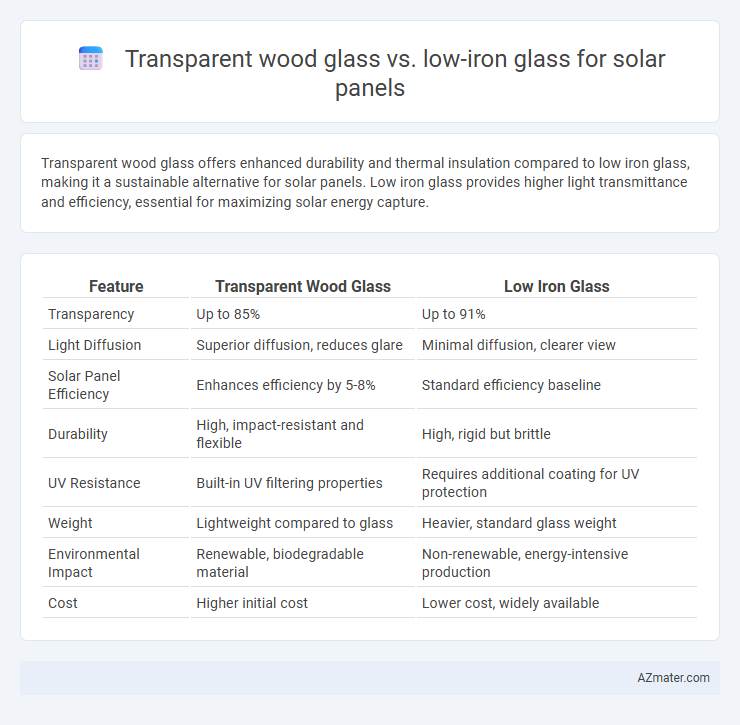
| Feature | Transparent Wood Glass | Low Iron Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Up to 85% | Up to 91% |
| Light Diffusion | Superior diffusion, reduces glare | Minimal diffusion, clearer view |
| Solar Panel Efficiency | Enhances efficiency by 5-8% | Standard efficiency baseline |
| Durability | High, impact-resistant and flexible | High, rigid but brittle |
| UV Resistance | Built-in UV filtering properties | Requires additional coating for UV protection |
| Weight | Lightweight compared to glass | Heavier, standard glass weight |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, biodegradable material | Non-renewable, energy-intensive production |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, widely available |
Understanding Transparent Wood Glass: Composition and Properties
Transparent wood glass is an innovative material composed of delignified wood infiltrated with a transparent polymer, providing high optical transparency combined with exceptional mechanical strength and thermal insulation. Its unique cellular structure enhances light diffusion while reducing heat loss, making it a promising alternative to traditional low iron glass in solar panels. Unlike low iron glass, which offers high clarity and low iron content to minimize light absorption, transparent wood glass offers improved environmental sustainability and potential for enhanced energy efficiency in photovoltaic applications.
What is Low Iron Glass? Definition and Key Features
Low iron glass is a type of glass specially manufactured to have reduced iron content, resulting in higher transparency and less greenish tint compared to regular glass. Key features include enhanced light transmission up to 91%, superior clarity for improved solar panel efficiency, and increased durability with options for tempered or laminated finishes. This glass type is ideal for solar panels as it maximizes sunlight penetration and energy output.
Light Transmission: Transparent Wood Glass vs Low Iron Glass
Transparent wood glass offers light transmission rates typically around 85% to 90%, benefiting from its engineered cellulose structure while maintaining strength and durability. Low iron glass generally provides superior light transmission, often exceeding 91% due to its reduced iron content minimizing green tint and maximizing solar efficiency. For solar panels, low iron glass remains the preferred option when highest optical clarity and energy yield are critical, whereas transparent wood glass presents an eco-friendly alternative with competitive transparency.
Thermal Performance Comparison for Solar Panels
Transparent wood glass exhibits superior thermal insulation compared to low iron glass due to its lower thermal conductivity, which reduces heat loss and improves solar panel efficiency in colder climates. Low iron glass allows higher solar transmittance but can lead to increased heat gain, potentially raising the operating temperature of the panel and decreasing overall performance. Thermal management in solar panels benefits from transparent wood glass as it balances sufficient light transmission with reduced thermal conduction, enhancing energy conversion efficiency.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Transparent wood glass offers superior mechanical strength due to its cellulose fiber matrix, providing enhanced impact resistance compared to low iron glass used in solar panels. Its durability is increased by natural resistance to environmental degradation, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations, which often cause micro-cracks in low iron glass. Low iron glass, while highly transparent and efficient in light transmission, tends to be more brittle and prone to breakage under mechanical stress, limiting its long-term durability in harsh outdoor conditions.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Transparent wood glass offers superior sustainability compared to low iron glass due to its renewable biomass origin and lower energy consumption during production, significantly reducing carbon footprint. It enhances solar panel efficiency by allowing better light transmission and improved insulation, leading to decreased energy loss and extended panel lifespan. Low iron glass, while improving clarity over standard glass, involves high-energy manufacturing processes and limited recyclability, resulting in greater environmental impact over the product lifecycle.
Manufacturing Process: Differences and Innovations
Transparent wood glass is produced through a bioengineering process that removes lignin from wood, replacing it with a transparent polymer, resulting in lightweight, renewable material with improved thermal insulation. Low iron glass undergoes an industrial refining process that reduces iron content, enhancing solar transmittance and decreasing greenish tint, crucial for maximizing photovoltaic efficiency. Innovations in transparent wood focus on scalability and integrating nano-coatings for durability, while low iron glass advancements include ultra-thin, anti-reflective surface treatments to boost energy yield in solar panels.
Cost Analysis: Transparent Wood Glass vs Low Iron Glass
Transparent wood glass typically incurs higher production costs due to advanced manufacturing processes and limited commercial availability, whereas low iron glass benefits from established mass production techniques, resulting in lower prices. Despite the higher upfront cost, transparent wood glass offers better thermal insulation and durability, potentially reducing long-term operational expenses in solar panel applications. The cost analysis should weigh initial investment against efficiency gains and lifespan, with low iron glass favored for budget-sensitive projects and transparent wood gaining appeal in sustainable, high-performance installations.
Application Potential in Solar Panel Technology
Transparent wood glass offers enhanced thermal insulation and mechanical strength, making it a promising substitute for low iron glass in solar panel applications. Low iron glass provides superior light transmittance and durability, essential for maximizing solar energy capture and panel longevity. Combining the eco-friendly benefits of transparent wood with the high clarity of low iron glass could significantly improve solar panel efficiency and sustainability.
Future Prospects and Industry Trends
Transparent wood glass offers enhanced sustainability and mechanical strength, making it a promising material for next-generation solar panels focused on eco-friendly and lightweight designs. Low iron glass remains dominant due to its high transparency and cost-effectiveness, driving continued innovation in solar efficiency and large-scale manufacturing. Industry trends indicate a growing interest in hybrid materials combining transparent wood and low iron glass to optimize durability, light transmittance, and overall solar panel performance.
Infographic: Transparent wood glass vs Low iron glass for Solar panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com