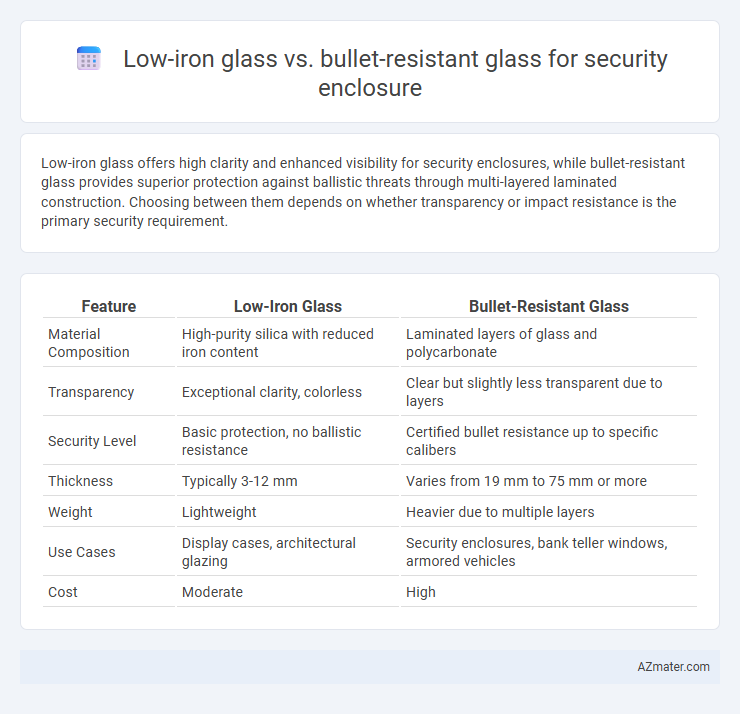
Low-iron glass offers high clarity and enhanced visibility for security enclosures, while bullet-resistant glass provides superior protection against ballistic threats through multi-layered laminated construction. Choosing between them depends on whether transparency or impact resistance is the primary security requirement.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Low-Iron Glass | Bullet-Resistant Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-purity silica with reduced iron content | Laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate |
| Transparency | Exceptional clarity, colorless | Clear but slightly less transparent due to layers |
| Security Level | Basic protection, no ballistic resistance | Certified bullet resistance up to specific calibers |
| Thickness | Typically 3-12 mm | Varies from 19 mm to 75 mm or more |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to multiple layers |
| Use Cases | Display cases, architectural glazing | Security enclosures, bank teller windows, armored vehicles |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
Introduction to Security Enclosure Glass Types
Low-iron glass offers enhanced clarity and minimal color distortion, making it ideal for security enclosures where visual transparency and aesthetic appeal are critical. Bullet-resistant glass, constructed from multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, provides robust protection against ballistic threats while maintaining acceptable visibility. Choosing between these glass types depends on the specific security level required and the balance between transparency and impact resistance.
What is Low-Iron Glass?
Low-iron glass is a type of glass known for its high clarity and reduced greenish tint compared to standard glass, making it ideal for security enclosures where visual transparency is critical. This glass is manufactured using raw materials with minimal iron content, enhancing light transmission and providing a crisp, clear view essential for monitoring and aesthetic purposes. In contrast to bullet-resistant glass, which is designed primarily for impact resistance and protection, low-iron glass focuses on optical quality while still offering structural strength suitable for various security applications.
What is Bullet-Resistant Glass?
Bullet-resistant glass is a specialized safety material composed of multiple layers of glass and polycarbonate designed to absorb and disperse the energy from gunfire, thereby preventing penetration. Unlike low-iron glass, which offers enhanced clarity and purity by reducing the green tint, bullet-resistant glass prioritizes protection against ballistic threats over visual aesthetics. This makes bullet-resistant glass an essential component in security enclosures requiring certified impact resistance and occupant safety.
Visual Clarity: Low-Iron vs Bullet-Resistant Glass
Low-iron glass offers superior visual clarity compared to bullet-resistant glass due to its reduced green tint and higher light transmittance, making it ideal for security enclosures where clear visibility is critical. Bullet-resistant glass, while providing enhanced protection against ballistic threats, often compromises clarity because of its multiple laminated layers and thickness, resulting in potential optical distortions or reduced light transmission. Selecting low-iron glass prioritizes aesthetic transparency, whereas bullet-resistant glass emphasizes security, requiring a balance based on enclosure exposure and functional needs.
Strength and Impact Resistance Comparison
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and aesthetic appeal but lacks the strength and impact resistance needed for security enclosures compared to bullet-resistant glass, which is engineered with multiple laminated layers to absorb and dissipate ballistic energy. Bullet-resistant glass provides enhanced protection against high-velocity impacts, featuring a thickness that can range from 0.5 to over 3 inches, designed to meet various threat levels specified by standards such as UL 752 or NIJ. While low-iron glass improves visibility and light transmission, bullet-resistant glass significantly outperforms it in terms of structural integrity and ability to withstand repeated impacts, making it essential for high-security environments.
Security Performance: Which Offers Better Protection?
Bullet-resistant glass provides superior security performance compared to low-iron glass, as it is specifically engineered to withstand ballistic impacts and forced entry attempts. Low-iron glass offers enhanced clarity and aesthetic appeal but lacks the multi-layered construction and impact resistance necessary for effective protection in security enclosures. For applications demanding high-level security, bullet-resistant glass is the preferred choice due to its certified ability to absorb and dissipate the energy from projectiles and physical attacks.
Cost Analysis: Low-Iron Glass vs Bullet-Resistant Glass
Low-iron glass typically costs between $25 and $50 per square foot, offering high clarity for security enclosures at a more affordable price point compared to bullet-resistant glass, which ranges from $50 to $150 per square foot depending on protection level. Bullet-resistant glass incorporates multiple layers of laminated polycarbonate and glass, significantly driving up material and installation costs due to its complex manufacturing and certification requirements. Choosing low-iron glass lowers upfront expenses but compromises ballistic protection, whereas bullet-resistant glass justifies its higher cost through enhanced security and durability in threat-prone environments.
Application Suitability in Security Enclosures
Low-iron glass offers enhanced clarity and is ideal for security enclosures where maximum visibility and aesthetic appeal are priorities, such as in retail showcases or museum displays. Bullet-resistant glass provides superior protection against ballistic threats, making it suitable for high-security environments like banks, government buildings, and secure entry points. Choosing between these materials depends on whether the primary concern is visual clarity or security level in the enclosure's application.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Low-iron glass offers higher clarity and aesthetic appeal but requires more frequent cleaning to maintain its pristine look due to its exposure to environmental elements. Bullet-resistant glass, constructed from multiple laminated layers, demands specialized inspection and maintenance to ensure its structural integrity and protective capabilities over time. Both materials require tailored maintenance regimens; low-iron glass focuses on surface care, while bullet-resistant glass emphasizes monitoring for delamination or impact damage to maximize longevity in security enclosures.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Security Needs
Low-iron glass offers high transparency and minimal color distortion, ideal for security enclosures requiring clear visibility and aesthetic appeal. Bullet-resistant glass, composed of multiple laminated layers including polycarbonate, provides enhanced protection against ballistic threats but often sacrifices clarity and increases weight. Selecting the appropriate glass depends on balancing security level requirements with optical performance and budget constraints for effective enclosure design.
Infographic: Low-iron glass vs Bullet-resistant glass for Security enclosure
 azmater.com
azmater.com