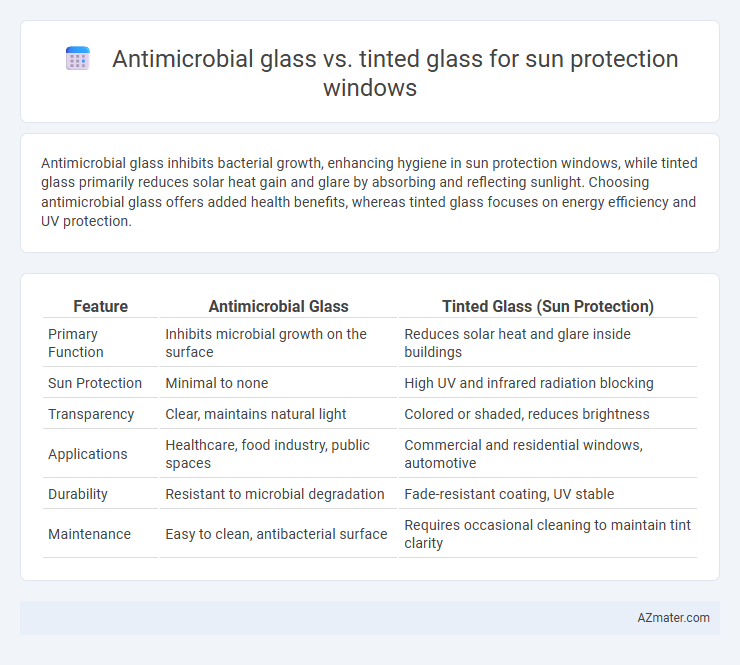
Antimicrobial glass inhibits bacterial growth, enhancing hygiene in sun protection windows, while tinted glass primarily reduces solar heat gain and glare by absorbing and reflecting sunlight. Choosing antimicrobial glass offers added health benefits, whereas tinted glass focuses on energy efficiency and UV protection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Antimicrobial Glass | Tinted Glass (Sun Protection) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Inhibits microbial growth on the surface | Reduces solar heat and glare inside buildings |
| Sun Protection | Minimal to none | High UV and infrared radiation blocking |
| Transparency | Clear, maintains natural light | Colored or shaded, reduces brightness |
| Applications | Healthcare, food industry, public spaces | Commercial and residential windows, automotive |
| Durability | Resistant to microbial degradation | Fade-resistant coating, UV stable |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, antibacterial surface | Requires occasional cleaning to maintain tint clarity |
Introduction to Sun Protection Window Technologies
Sun protection window technologies include antimicrobial glass and tinted glass, each offering unique benefits for energy efficiency and health safety. Antimicrobial glass incorporates ionized metals like silver or copper to inhibit microbial growth while maintaining high visibility and UV protection. Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain by filtering out infrared and UV rays, enhancing indoor comfort and lowering cooling costs without affecting antimicrobial properties.
Understanding Antimicrobial Glass: Definition and Properties
Antimicrobial glass incorporates agents such as silver ions or copper nanoparticles to inhibit bacterial growth on its surface, enhancing hygiene and durability. This glass type offers protection against microbial contamination, making it ideal for high-contact areas while maintaining transparency and mechanical strength. Unlike tinted glass, which primarily reduces solar heat and glare through pigment absorption, antimicrobial glass focuses on surface sanitation without significantly altering light transmission.
Tinted Glass: Features and Sun Protection Mechanism
Tinted glass enhances sun protection by incorporating color pigments that absorb and reflect solar radiation, effectively reducing glare and heat transmission into buildings. Its features include UV blocking capabilities, reduced solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC), and improved energy efficiency by minimizing the reliance on air conditioning systems. The sun protection mechanism of tinted glass relies on selective absorption of visible and infrared light wavelengths, which decreases interior fading and enhances occupant comfort.
Comparative UV and Infrared Blocking Efficiency
Antimicrobial glass incorporates special coatings that not only inhibit microbial growth but also offer moderate UV blocking capabilities, typically blocking up to 70-80% of UV rays, while tinted glass excels at solar heat reduction by absorbing and reflecting up to 90% of infrared radiation. Tinted glass provides superior infrared blocking efficiency, significantly reducing solar heat gain and enhancing indoor temperature control, whereas antimicrobial glass prioritizes hygiene with modest solar protection performance. For comprehensive sun protection, combining antimicrobial coatings with high-performance tinted glass can optimize both UV and infrared blocking efficiencies.
Impact on Indoor Air Quality and Hygiene
Antimicrobial glass incorporates surface treatments that inhibit the growth of bacteria and mold, directly enhancing indoor air quality by reducing airborne microbial contaminants. Tinted glass primarily reduces solar heat gain and glare, improving thermal comfort but offering limited influence on indoor hygiene and microbial control. For environments prioritizing health and hygiene, antimicrobial glass provides superior benefits by actively minimizing pathogens on window surfaces, thereby supporting cleaner and safer indoor air.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Antimicrobial glass features a specialized coating that resists microbial growth, enhancing durability by preventing surface degradation and reducing the need for frequent cleaning, which is particularly beneficial in high-contact environments. In contrast, tinted glass primarily blocks solar heat and UV rays but may degrade over time due to prolonged sun exposure, requiring periodic inspection and maintenance to address fading or discoloration. Both types offer distinct advantages; antimicrobial glass ensures longer-lasting surface integrity with minimal upkeep, while tinted glass demands regular maintenance to preserve its sun protection effectiveness.
Aesthetic Differences: Appearance and Design Flexibility
Antimicrobial glass maintains a clear, transparent appearance that preserves natural light and offers versatile design options for modern interiors, making it ideal for spaces requiring hygiene without compromising aesthetics. Tinted glass provides varying shades and colors that reduce glare and enhance privacy while adding a stylistic element to windows, allowing designers to create mood and ambiance through color selection. The choice between antimicrobial and tinted glass depends on the desired balance between functional cleanliness and customizable visual impact in sun protection windows.
Energy Efficiency and Thermal Insulation Performance
Antimicrobial glass primarily enhances hygiene by inhibiting bacterial growth but typically offers limited impact on energy efficiency and thermal insulation. Tinted glass, designed with solar control properties, significantly reduces solar heat gain and improves thermal insulation, lowering cooling costs and enhancing indoor comfort. For energy-efficient sun protection windows, tinted glass provides superior performance by effectively blocking UV rays and maintaining stable indoor temperatures.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-Term Savings
Antimicrobial glass typically involves higher initial investment due to specialized coatings that inhibit bacterial growth, whereas tinted glass offers a more cost-effective upfront price focused on solar heat reduction. Over time, antimicrobial glass can deliver long-term savings by reducing maintenance and cleaning costs in environments requiring high hygiene standards, while tinted glass primarily saves on energy bills by decreasing cooling loads. Cost analysis should factor in specific application needs, balancing antimicrobial benefits against the simpler, lower initial cost and energy efficiency of tinted glass for sun protection windows.
Choosing the Right Glass for Sun Protection: Key Takeaways
Antimicrobial glass offers health benefits by inhibiting microbial growth on surfaces, which is ideal for environments requiring hygiene, while tinted glass provides superior sun protection by reducing glare and blocking UV rays effectively. When choosing the right glass for sun protection, consider tinted glass for energy efficiency and comfort due to its ability to lower solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC). Prioritize antimicrobial glass in settings where reducing bacterial transmission is critical, but for maximum sun protection and cooling savings, tinted glass remains the optimal choice.
Infographic: Antimicrobial glass vs Tinted glass for Sun protection window
 azmater.com
azmater.com