Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for rugged camera lenses in extreme environments. Optical glass, specifically engineered for high refractive index and low dispersion, delivers exceptional image clarity and color accuracy in professional photography lenses.
Table of Comparison
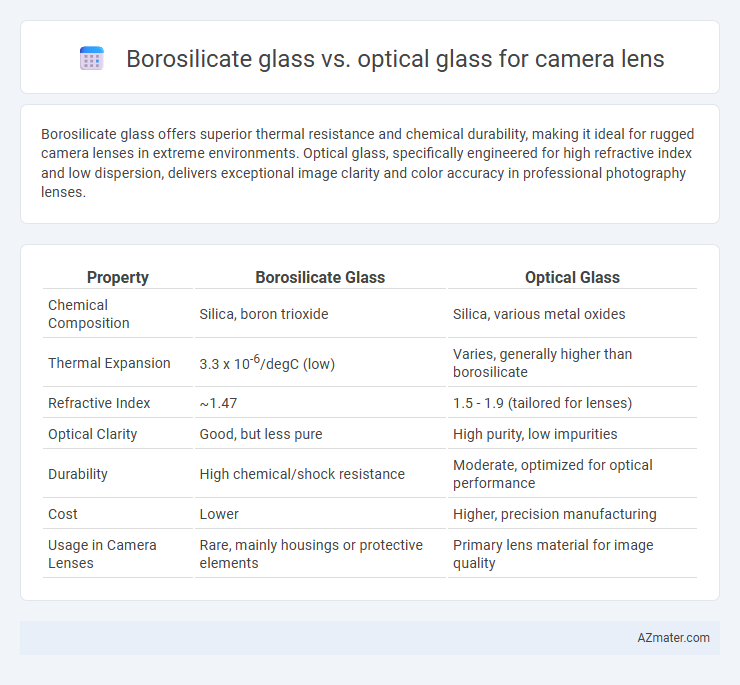
| Property | Borosilicate Glass | Optical Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Silica, boron trioxide | Silica, various metal oxides |
| Thermal Expansion | 3.3 x 10-6/degC (low) | Varies, generally higher than borosilicate |
| Refractive Index | ~1.47 | 1.5 - 1.9 (tailored for lenses) |
| Optical Clarity | Good, but less pure | High purity, low impurities |
| Durability | High chemical/shock resistance | Moderate, optimized for optical performance |
| Cost | Lower | Higher, precision manufacturing |
| Usage in Camera Lenses | Rare, mainly housings or protective elements | Primary lens material for image quality |
Introduction to Camera Lens Materials
Borosilicate glass and optical glass are essential materials used in camera lens manufacturing, each offering distinct optical properties. Borosilicate glass provides excellent thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it suitable for lenses requiring high thermal stability and reduced chromatic aberration. Optical glass, engineered with precise refractive indices and dispersion characteristics, is preferred for high-performance lenses demanding superior clarity, light transmission, and image sharpness.
What Is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass known for its low thermal expansion, high durability, and resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for harsh environments and precision optics. This glass contains boron trioxide, which enhances its thermal and mechanical properties compared to standard soda-lime glass commonly used in optical applications. In camera lenses, borosilicate glass offers improved temperature stability and scratch resistance, but optical glass generally provides superior light transmission and refractive index control essential for high-quality image capture.
Understanding Optical Glass
Optical glass used in camera lenses is specially formulated to minimize distortions and enhance light transmission, providing superior clarity and color accuracy compared to borosilicate glass. Borosilicate glass is valued for its thermal resistance and durability but lacks the precise refractive properties essential for high-quality imaging. Understanding the specific optical properties such as refractive index, dispersion, and light transmission of optical glass is crucial for optimizing lens performance in photography.
Key Differences Between Borosilicate and Optical Glass
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability due to its low coefficient of thermal expansion, making it ideal for lenses exposed to fluctuating temperatures. Optical glass, specifically engineered for high refractive index and low dispersion, provides enhanced image clarity and reduced chromatic aberration essential for camera lenses. The key differences lie in borosilicate's mechanical strength and thermal stability versus optical glass's optimized light transmission and image quality performance.
Optical Performance Comparison
Borosilicate glass offers high thermal resistance and durability but has lower refractive index and dispersion compared to optical glass, which is engineered for superior light transmission and minimal chromatic aberration in camera lenses. Optical glass features precise control over optical properties, resulting in sharper images, better contrast, and enhanced color fidelity crucial for professional photography. The higher Abbe number and tailored coatings of optical glass significantly reduce distortions, making it the preferred choice for high-performance camera lenses.
Durability and Chemical Resistance
Borosilicate glass offers superior durability and chemical resistance compared to optical glass, making it highly resistant to thermal shock, scratches, and corrosive substances commonly encountered in harsh environments. Optical glass, while optimized for clarity and light transmission, tends to be more susceptible to scratching and chemical degradation under exposure to acids or alkalis. The enhanced mechanical strength and low coefficient of thermal expansion in borosilicate glass provide longer-lasting lens protection and maintain optical performance even in demanding industrial or outdoor photography applications.
Cost Implications: Borosilicate vs Optical Glass
Borosilicate glass offers a cost-effective solution for camera lenses due to its lower manufacturing expenses and high thermal resistance, making it suitable for budget-friendly or mass-produced optics. In contrast, optical glass, featuring superior clarity and precise refractive indices, commands higher prices but delivers enhanced image quality and durability for professional-grade lenses. Choosing between borosilicate and optical glass directly impacts production costs and final product pricing, with borosilicate benefiting lower-cost applications while optical glass is preferred for premium imaging performance.
Common Uses in Photography Lenses
Borosilicate glass offers high thermal and chemical resistance, making it suitable for durable camera lenses used in outdoor and industrial photography. Optical glass, known for its superior clarity and low dispersion, is preferred in high-end camera lenses to minimize chromatic aberration and enhance image quality. Photographers select borosilicate glass for rugged conditions, while optical glass is favored for professional and precision applications.
Pros and Cons of Borosilicate Glass for Lenses
Borosilicate glass offers excellent thermal and chemical stability, making camera lenses durable under extreme conditions and resistant to scratches and corrosion. However, borosilicate glass has lower refractive index and optical clarity compared to specialized optical glass, potentially resulting in reduced image sharpness and increased chromatic aberration. Its affordable cost and robustness suit applications requiring ruggedness, but high-end lenses typically prefer optical glass for superior light transmission and precise optical performance.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Camera Lens
Borosilicate glass offers exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for lenses exposed to extreme temperature changes and harsh environments. Optical glass, specifically formulated for superior light transmission and minimal aberrations, provides higher clarity and precision essential for professional photography. Choosing between borosilicate and optical glass depends on the camera user's priorities: durability and resilience versus image quality and optical performance.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs Optical glass for Camera lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com