Transparent wood glass offers enhanced impact resistance and eco-friendly sustainability compared to aluminosilicate glass, which excels in scratch resistance and optical clarity for smartphone screens. Choosing transparent wood glass can reduce environmental footprint while maintaining durability, whereas aluminosilicate glass remains the industry standard for high hardness and transparency.
Table of Comparison
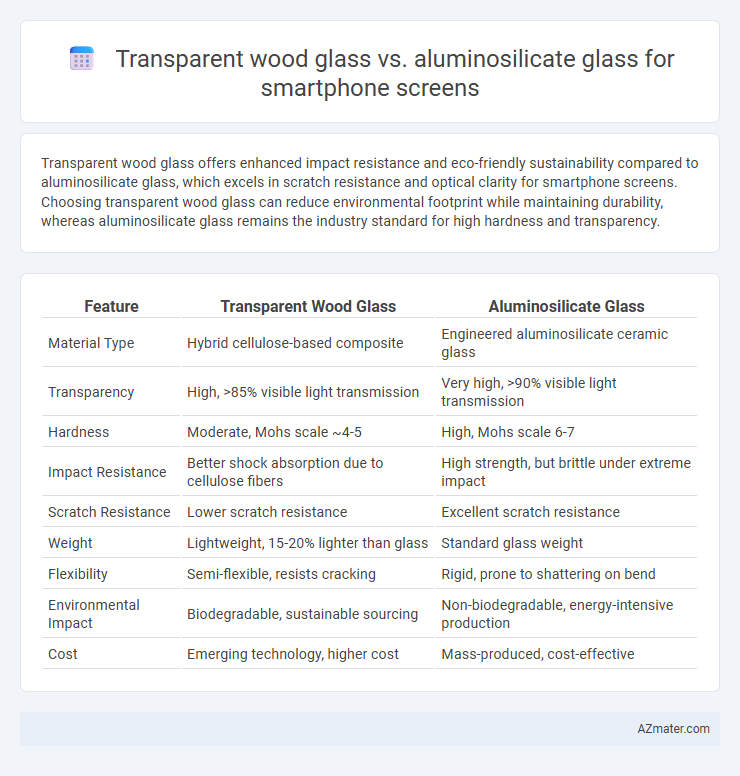
| Feature | Transparent Wood Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Hybrid cellulose-based composite | Engineered aluminosilicate ceramic glass |
| Transparency | High, >85% visible light transmission | Very high, >90% visible light transmission |
| Hardness | Moderate, Mohs scale ~4-5 | High, Mohs scale 6-7 |
| Impact Resistance | Better shock absorption due to cellulose fibers | High strength, but brittle under extreme impact |
| Scratch Resistance | Lower scratch resistance | Excellent scratch resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight, 15-20% lighter than glass | Standard glass weight |
| Flexibility | Semi-flexible, resists cracking | Rigid, prone to shattering on bend |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, sustainable sourcing | Non-biodegradable, energy-intensive production |
| Cost | Emerging technology, higher cost | Mass-produced, cost-effective |
Introduction to Next-Gen Smartphone Screen Materials
Transparent wood glass offers enhanced flexibility, lightweight properties, and natural sustainability, making it a promising alternative to conventional aluminosilicate glass in next-generation smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass, known for its high hardness, scratch resistance, and impact durability, remains a standard in protecting displays from daily wear and accidental drops. Emerging research focuses on integrating transparent wood composites with aluminosilicate coatings to balance ecological benefits with superior mechanical performance in future smartphones.
What is Transparent Wood Glass?
Transparent wood glass is an innovative material combining natural wood fibers with cellulose-based polymers to create a lightweight, durable, and eco-friendly alternative to traditional glass. Unlike aluminosilicate glass, which is prized for its scratch resistance and high strength due to its silicate and aluminum oxide composition, transparent wood glass offers enhanced flexibility and biodegradability while maintaining optical clarity. This emerging technology aims to reduce environmental impact without compromising the protective qualities required for smartphone screens.
Understanding Aluminosilicate Glass Technology
Aluminosilicate glass technology involves a chemically strengthened glass composed primarily of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, providing exceptional hardness and resistance to scratches and impacts compared to traditional glass types. This advanced material undergoes an ion-exchange process, replacing smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions to create a compression layer that enhances durability and reduces the risk of screen shattering. While transparent wood glass offers promising biodegradability and lightweight properties, aluminosilicate glass remains the preferred choice for smartphone screens due to its superior transparency, toughness, and resistance to daily wear and tear.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Transparent wood glass offers enhanced impact resistance and flexibility compared to aluminosilicate glass, making it less prone to shattering under stress. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in premium smartphones like Gorilla Glass, provides superior hardness and scratch resistance but can be more brittle. While transparent wood glass excels in durability against bending and drops, aluminosilicate glass maintains higher surface hardness and longevity against daily wear.
Optical Clarity and Display Performance
Transparent wood glass offers enhanced optical clarity with reduced glare and higher light transmittance compared to aluminosilicate glass, improving smartphone display brightness and visibility under various lighting conditions. Aluminosilicate glass excels in scratch resistance and durability but can slightly diminish contrast and color accuracy due to its lower light transmission properties. The choice between the two materials directly affects display performance, balancing optical clarity with mechanical strength for optimal user experience.
Environmental Sustainability and Eco-Impact
Transparent wood glass offers a sustainable alternative to aluminosilicate glass by utilizing renewable wood fibers, which significantly reduce carbon emissions during production. Unlike energy-intensive aluminosilicate manufacturing, transparent wood relies on biodegradable materials and has a lower ecological footprint throughout its lifecycle. This eco-friendly advantage makes transparent wood glass a promising choice for smartphone screens aiming to minimize environmental impact.
Cost and Manufacturing Scalability
Transparent wood glass offers a lower production cost due to the abundance and renewability of wood fibers combined with simpler processing techniques compared to aluminosilicate glass, which requires high-temperature melting and complex chemical treatments. Manufacturing scalability favors aluminosilicate glass, as it benefits from established large-scale industrial processes and global supply chains, enabling consistent mass production and thinner, harder screens. Cost advantages of transparent wood may drive niche eco-friendly markets, but aluminosilicate remains dominant in mainstream smartphone screens for its proven durability and manufacturing maturity.
Touch Sensitivity and User Experience
Transparent wood glass offers improved touch sensitivity due to its natural fibrous structure that enhances haptic feedback, providing a more responsive and tactile user experience compared to traditional aluminosilicate glass. Aluminosilicate glass, while highly durable and scratch-resistant, can sometimes feel less sensitive to touch and less comfortable for prolonged use. Users often report that transparent wood glass screens deliver a warmer, more natural feel, making interactions smoother and more satisfying on smartphones.
Challenges and Future Development
Transparent wood glass offers promising sustainability and flexibility advantages over aluminosilicate glass, yet faces significant challenges in achieving comparable hardness and scratch resistance essential for smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass remains the industry standard due to its exceptional durability and chemical stability but struggles with brittleness and recycling difficulties. Future developments aim to enhance transparent wood glass's mechanical properties through nanostructuring and hybrid composites while improving aluminosilicate glass by optimizing manufacturing techniques for better toughness and eco-friendliness.
Conclusion: Transparent Wood Glass or Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass outperforms transparent wood glass for smartphone screens due to its superior hardness, scratch resistance, and cost-effective mass production capabilities. Transparent wood glass offers enhanced flexibility and eco-friendliness but currently lacks the transparency and durability standards required for everyday smartphone use. Consequently, aluminosilicate glass remains the preferred material in the industry, balancing strength, clarity, and affordability for consumer electronics.
Infographic: Transparent wood glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Smartphone screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com