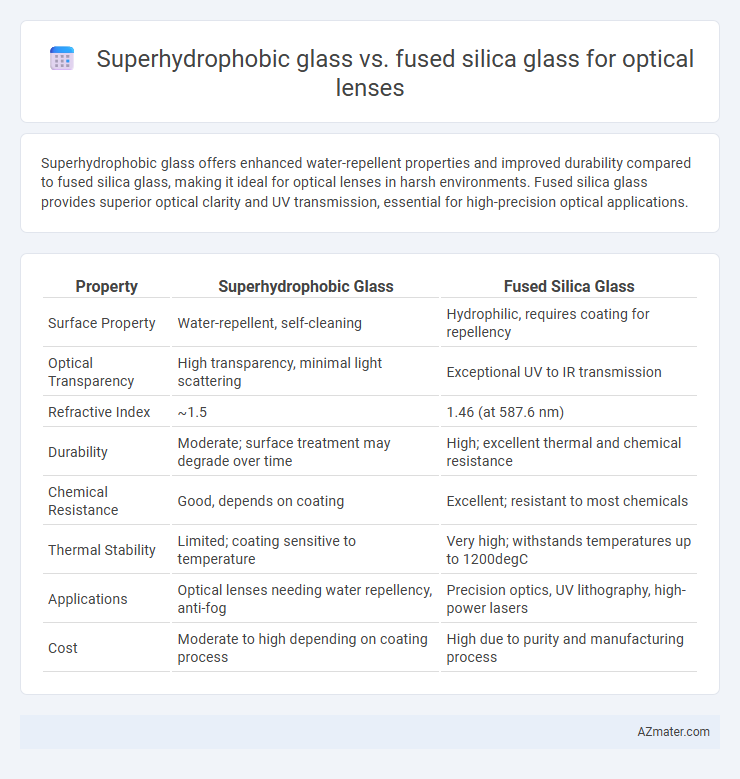
Superhydrophobic glass offers enhanced water-repellent properties and improved durability compared to fused silica glass, making it ideal for optical lenses in harsh environments. Fused silica glass provides superior optical clarity and UV transmission, essential for high-precision optical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Superhydrophobic Glass | Fused Silica Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Property | Water-repellent, self-cleaning | Hydrophilic, requires coating for repellency |
| Optical Transparency | High transparency, minimal light scattering | Exceptional UV to IR transmission |
| Refractive Index | ~1.5 | 1.46 (at 587.6 nm) |
| Durability | Moderate; surface treatment may degrade over time | High; excellent thermal and chemical resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, depends on coating | Excellent; resistant to most chemicals |
| Thermal Stability | Limited; coating sensitive to temperature | Very high; withstands temperatures up to 1200degC |
| Applications | Optical lenses needing water repellency, anti-fog | Precision optics, UV lithography, high-power lasers |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on coating process | High due to purity and manufacturing process |
Introduction to Optical Lens Materials
Superhydrophobic glass features a nano-structured surface coating that repels water and reduces dirt accumulation, enhancing optical clarity and durability in lenses. Fused silica glass, composed of high-purity silicon dioxide, offers exceptional optical transparency, low thermal expansion, and high resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for precision lenses. These materials differ significantly in their surface properties and thermal stability, affecting performance based on application requirements in optical systems.
What is Superhydrophobic Glass?
Superhydrophobic glass features an ultra-water-repellent surface achieved through microscopic nanostructures combined with low-surface-energy coatings, significantly reducing water adhesion and enhancing self-cleaning properties. Fused silica glass is a highly pure, silica-based material known for its exceptional optical clarity, thermal stability, and resistance to UV radiation, making it ideal for precision optical lenses. Compared to fused silica, superhydrophobic glass integrates surface treatments to improve lens durability and performance in wet or contaminated environments without compromising optical transmission.
Key Properties of Fused Silica Glass
Fused silica glass exhibits exceptional optical clarity, low thermal expansion, and high resistance to UV radiation, making it ideal for precision optical lenses. Its superior hardness and chemical stability outperform many coatings like superhydrophobic glass, ensuring long-term durability and minimal surface degradation. These key properties allow fused silica lenses to maintain consistent optical performance in harsh environments and high-power laser applications.
Optical Performance Comparison
Superhydrophobic glass exhibits enhanced water repellency and self-cleaning properties that maintain optical clarity by reducing surface contamination, while fused silica glass offers superior ultraviolet transparency, low thermal expansion, and high laser damage threshold crucial for precision optical lenses. In terms of optical performance, fused silica glass provides exceptional refractive index homogeneity and minimal chromatic aberration, making it ideal for high-precision imaging and laser systems. Superhydrophobic coatings on glass substrates may introduce slight surface irregularities, potentially impacting scattering and transmittance, but advancements in coating uniformity are narrowing the performance gap compared to bare fused silica lenses.
Surface Durability and Maintenance
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water and dirt repellency compared to fused silica glass, significantly reducing surface contamination and cleaning frequency for optical lenses. Fused silica glass provides excellent inherent durability with high resistance to scratching and thermal shock but lacks the self-cleaning properties of superhydrophobic coatings. The enhanced surface durability of superhydrophobic glass results in lower maintenance requirements, prolonging lens performance in challenging environmental conditions.
Light Transmission and Clarity
Superhydrophobic glass enhances light transmission by minimizing surface reflections and repelling water, maintaining clarity under wet conditions, whereas fused silica glass inherently offers excellent optical clarity and high transmission rates due to its low impurity levels and superior homogeneity. The hydrophobic coating on superhydrophobic glass reduces glare and prevents fogging, improving visual performance in challenging environments. Fused silica's stable refractive index and low thermal expansion further contribute to consistent optical quality across various wavelengths.
Resistance to Environmental Conditions
Superhydrophobic glass exhibits superior resistance to environmental conditions compared to fused silica glass, repelling water, dirt, and oils that can compromise lens clarity and performance. The nanostructured surface coating on superhydrophobic glass minimizes corrosion, fogging, and contamination under harsh humidity, rain, or dust exposure, enhancing long-term optical reliability. In contrast, fused silica glass, while chemically inert and thermally stable, lacks intrinsic hydrophobic properties, requiring additional treatments to achieve comparable environmental protection.
Practical Applications in Optics
Superhydrophobic glass offers enhanced anti-fogging and self-cleaning properties, making it ideal for outdoor optical lenses in harsh environments, such as camera lenses and protective eyewear. Fused silica glass provides superior optical clarity, low thermal expansion, and high UV transparency, which are critical for high-precision applications like laser systems, microscopy, and space optics. Combining these materials' benefits improves the durability and performance of optical lenses in demanding practical applications.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Superhydrophobic glass typically involves specialized coatings that increase manufacturing costs compared to fused silica glass, which is widely available and more cost-effective due to its established production processes. The enhanced water-repellent properties of superhydrophobic glass add value for specific applications but require more complex treatment methods, leading to higher prices and limited suppliers. Fused silica glass remains the preferred choice for optical lenses where budget constraints and material availability are critical factors.
Choosing the Right Glass for Optical Lenses
Superhydrophobic glass offers enhanced water and dirt repellency, significantly reducing maintenance and improving clarity in various environmental conditions compared to fused silica glass. Fused silica glass is renowned for its exceptional optical clarity, low thermal expansion, and high resistance to UV radiation, making it ideal for precision optical applications. Selecting the right glass depends on the lens's exposure to harsh conditions and performance requirements, with superhydrophobic coatings providing added durability while fused silica ensures superior optical quality and stability.
Infographic: Superhydrophobic glass vs Fused silica glass for Optical lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com