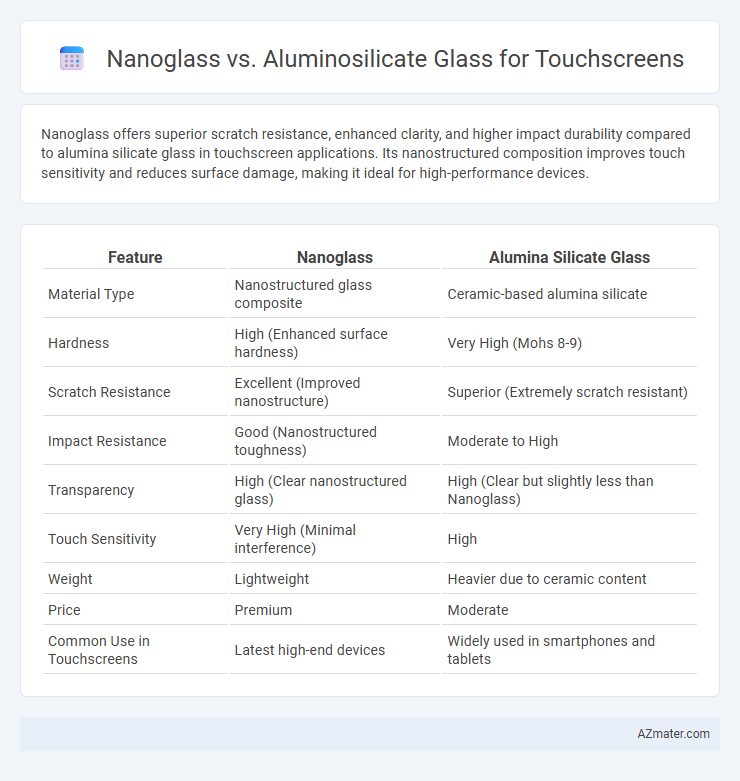
Nanoglass offers superior scratch resistance, enhanced clarity, and higher impact durability compared to alumina silicate glass in touchscreen applications. Its nanostructured composition improves touch sensitivity and reduces surface damage, making it ideal for high-performance devices.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nanoglass | Alumina Silicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Nanostructured glass composite | Ceramic-based alumina silicate |
| Hardness | High (Enhanced surface hardness) | Very High (Mohs 8-9) |
| Scratch Resistance | Excellent (Improved nanostructure) | Superior (Extremely scratch resistant) |
| Impact Resistance | Good (Nanostructured toughness) | Moderate to High |
| Transparency | High (Clear nanostructured glass) | High (Clear but slightly less than Nanoglass) |
| Touch Sensitivity | Very High (Minimal interference) | High |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to ceramic content |
| Price | Premium | Moderate |
| Common Use in Touchscreens | Latest high-end devices | Widely used in smartphones and tablets |
Introduction to Touchscreen Glass Technologies
Nanoglass and alumina silicate glass represent advanced materials used in touchscreen technologies, each offering distinct properties critical for durability and clarity. Nanoglass incorporates nanostructured elements that enhance scratch resistance and optical transparency, making it ideal for high-performance touchscreens in smartphones and tablets. Alumina silicate glass, known for its robust chemical and thermal stability, provides superior impact resistance and long-term durability, commonly utilized in devices where toughness and reliability are paramount.
What is Nanoglass?
Nanoglass is an advanced material composed of nanoscale glass particles fused to create a highly durable and scratch-resistant surface ideal for touchscreens. Compared to traditional alumina silicate glass, nanoglass offers superior hardness and enhanced impact resistance due to its unique nanostructure, resulting in longer-lasting displays. Its reduced thickness and improved optical clarity make it a preferred choice for next-generation touchscreen technology.
Understanding Alumina Silicate Glass
Alumina silicate glass is engineered for touchscreens with a high concentration of aluminum oxide that enhances its hardness and durability, making it resistant to scratches and impacts. This type of glass balances clarity and strength, offering superior thermal resistance and chemical stability compared to standard glass types. Its structural composition provides a reliable and cost-effective solution for touchscreen devices requiring robust performance in everyday use.
Mechanical Strength: Nanoglass vs Alumina Silicate Glass
Nanoglass demonstrates superior mechanical strength compared to alumina silicate glass due to its nanoscale grain boundaries that hinder crack propagation and enhance toughness. Alumina silicate glass, commonly used in touchscreens, offers good durability but lacks the enhanced fracture resistance provided by nanoglass structures. The higher fracture toughness and improved hardness of nanoglass make it more resistant to scratches and impacts, extending touchscreen longevity in demanding applications.
Scratch and Impact Resistance Comparison
Nanoglass exhibits superior scratch resistance compared to alumina silicate glass, thanks to its high-density nanostructure that effectively disperses surface stress and prevents abrasion. In terms of impact resistance, nanoglass also outperforms alumina silicate glass by absorbing and redistributing impact energy more efficiently, reducing the likelihood of cracks or shattering. These enhanced mechanical properties make nanoglass a leading material choice for durable, high-performance touchscreen applications.
Optical Clarity and Display Quality
Nanoglass offers superior optical clarity compared to alumina silicate glass, with higher light transmittance and reduced haze, enhancing touchscreen visibility and color accuracy. Its advanced nano-structured surface minimizes reflection and glare, resulting in sharper images and better contrast under various lighting conditions. Alumina silicate glass provides durability but often compromises slightly on display brilliance due to lower transmission efficiency and increased surface scattering.
Touch Sensitivity and User Experience
Nanoglass offers superior touch sensitivity compared to alumina silicate glass due to its smoother surface texture and enhanced conductivity, allowing for faster and more accurate finger response. Alumina silicate glass, while highly durable and resistant to scratches, can sometimes reduce tactile feedback, slightly diminishing user experience during prolonged use. The advanced nanostructure of Nanoglass significantly improves multi-touch accuracy and reduces latency, resulting in a more responsive and immersive touchscreen interaction.
Durability and Longevity in Daily Use
Nanoglass exhibits superior scratch resistance and impact durability compared to alumina silicate glass, making it ideal for high-usage touchscreens. Its enhanced hardness and flexibility reduce micro-fractures and wear over time, extending the screen's lifespan in daily environments. Alumina silicate glass, while durable, tends to show more surface degradation after prolonged exposure to frequent tapping and drops.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Nanoglass offers superior scratch resistance and durability compared to alumina silicate glass, but its higher production costs and complex manufacturing processes limit its widespread adoption in touchscreens. Alumina silicate glass remains more cost-effective due to established mass production techniques and readily available raw materials, making it the preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications. Manufacturers balance cost-efficiency and performance by selecting alumina silicate glass for most touchscreens, reserving nanoglass for premium or specialized devices where durability justifies expense.
Which Glass is Better for Touchscreens?
Nanoglass offers superior scratch resistance and higher transparency compared to alumina silicate glass, enhancing touchscreen durability and visual clarity. Alumina silicate glass provides excellent chemical stability and impact resistance, making it a cost-effective choice for everyday touchscreen use. For premium devices requiring enhanced toughness and optical performance, nanoglass is generally considered the better option.
Infographic: Nanoglass vs Alumina silicate glass for Touchscreen
 azmater.com
azmater.com