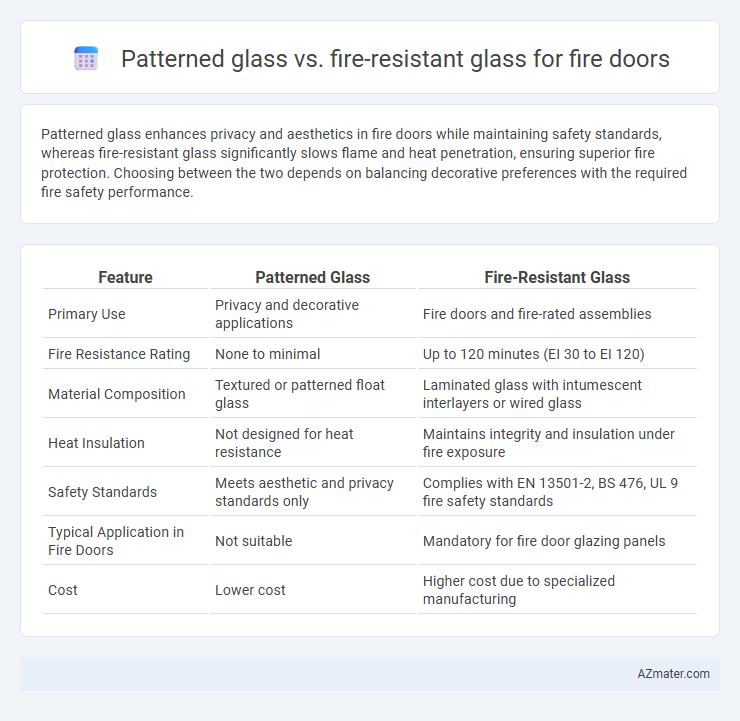
Patterned glass enhances privacy and aesthetics in fire doors while maintaining safety standards, whereas fire-resistant glass significantly slows flame and heat penetration, ensuring superior fire protection. Choosing between the two depends on balancing decorative preferences with the required fire safety performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Patterned Glass | Fire-Resistant Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Privacy and decorative applications | Fire doors and fire-rated assemblies |
| Fire Resistance Rating | None to minimal | Up to 120 minutes (EI 30 to EI 120) |
| Material Composition | Textured or patterned float glass | Laminated glass with intumescent interlayers or wired glass |
| Heat Insulation | Not designed for heat resistance | Maintains integrity and insulation under fire exposure |
| Safety Standards | Meets aesthetic and privacy standards only | Complies with EN 13501-2, BS 476, UL 9 fire safety standards |
| Typical Application in Fire Doors | Not suitable | Mandatory for fire door glazing panels |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to specialized manufacturing |
Introduction to Fire Door Glazing Options
Fire door glazing options primarily include patterned glass and fire-resistant glass, each serving unique functions in safety and design. Patterned glass enhances privacy and aesthetic appeal while allowing light diffusion but does not provide fire resistance. Fire-resistant glass is engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread, making it essential for compliance with fire safety regulations in fire door applications.
What is Patterned Glass?
Patterned glass is a textured glass type featuring embossed designs that provide privacy while allowing light transmission, commonly used in fire doors to obscure visibility without compromising natural illumination. Unlike fire-resistant glass, patterned glass does not offer inherent fire resistance but can be combined with special fire-rated interlayers to meet fire safety standards. The choice between patterned and fire-resistant glass depends on balancing aesthetic privacy needs with critical fire protection requirements in door applications.
What is Fire-Resistant Glass?
Fire-resistant glass is specially engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames and smoke in fire doors, offering critical safety benefits. Unlike patterned glass, which primarily serves decorative and privacy purposes, fire-resistant glass provides thermal insulation and structural integrity during a fire event. Its multi-layered construction often includes intumescent interlayers that expand under heat to maintain the barrier against fire and smoke.
Key Differences Between Patterned and Fire-Resistant Glass
Patterned glass offers decorative textures and obscures visibility, enhancing privacy in fire doors without providing fire protection, whereas fire-resistant glass is engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread. Fire-resistant glass contains specialized layers or intumescent materials that maintain integrity during fire exposure, unlike patterned glass which lacks thermal protection. Key differences include functional performance in fire safety, opacity levels, and compliance with fire door safety standards.
Fire Safety Standards and Building Regulations
Fire-resistant glass for fire doors complies with stringent fire safety standards such as BS 476 and EN 13501-2, ensuring effective protection by withstanding high temperatures and preventing fire spread for specified durations. Patterned glass, primarily designed for aesthetic purposes, typically lacks certification for fire resistance and does not meet the fire safety requirements mandated by building regulations. Building codes prioritize the use of fire-resistant glass in fire doors to maintain compartmentalization and occupant safety during fire incidents.
Aesthetic and Functional Benefits of Patterned Glass
Patterned glass in fire doors enhances aesthetic appeal by obscuring visibility while allowing natural light to diffuse evenly, creating a stylish yet private environment. Its textured surface complements various architectural designs, adding visual interest without compromising safety standards. Functionally, patterned glass maintains fire resistance while reducing glare and fingerprints, contributing to both durability and ease of maintenance in high-traffic areas.
Performance and Protection: Fire-Resistant Glass Advantages
Fire-resistant glass offers superior performance and protection in fire doors by withstanding high temperatures and preventing the spread of flames and smoke, unlike patterned glass which primarily serves aesthetic purposes. Engineered with intumescent layers or special coatings, fire-resistant glass maintains integrity and visibility during fire incidents, ensuring safety and compliance with fire safety regulations. Its ability to provide thermal insulation and delay heat transfer significantly enhances occupant protection in emergency situations.
Cost Comparison: Patterned vs Fire-Resistant Glass
Patterned glass for fire doors generally costs less than fire-resistant glass due to simpler manufacturing processes and lower material specifications. Fire-resistant glass demands advanced technologies such as ceramic interlayers or multi-laminated panels to meet stringent safety standards, significantly increasing its price. Choosing between patterned and fire-resistant glass depends on budget considerations and the required fire protection level in compliance with local building codes.
Choosing the Right Glass for Fire Doors
Choosing the right glass for fire doors requires careful consideration of both safety and functionality, with fire-resistant glass specifically engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent flame spread, complying with stringent fire safety standards. Patterned glass, while offering aesthetic appeal and privacy, typically lacks the fire-resistance properties necessary for fire doors and is not suitable for critical fire-rated applications. Prioritizing fire-resistant glass ensures compliance with building codes and maximizes occupant protection during fire emergencies.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions for Fire Safety
Choosing between patterned glass and fire-resistant glass for fire doors depends primarily on safety requirements and functionality. Fire-resistant glass is engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames and smoke, making it essential for fire safety compliance. Patterned glass offers aesthetic value but lacks the fire resistance needed for critical fire door applications, so fire-resistant glass remains the optimal choice for maximum protection.
Infographic: Patterned glass vs Fire-resistant glass for Fire door
 azmater.com
azmater.com